High resolution and high refresh rate, do you really need it?

High resolution and high refresh rate, do you really need it?
Do you still have a mobile phone or computer from ten years ago at home? If you can still turn it on, you might as well take it out and compare it with the current device to see if there is any difference between the two. Do you think it was used well ten years ago? My mobile phone suddenly became very backward, but I didn't realize that such a big change had happened.
With the advancement of image technology, the pictures presented by electronic devices are becoming clearer, more stable and smooth, and many terms have gradually appeared, such as resolution, pixels, refresh rate, etc., are they making you dizzy? Don't worry, let Document Master help you sort it out!
resolution
Resolution, also known as resolution and resolution, can be subdivided into display resolution, image resolution, printing resolution and scanning resolution.
Here are the definitions of these resolutions:
- Display resolution is the resolution of the monitor when displaying images. Resolution is measured in points. The "points" on the monitor refer to pixels.
- Image resolution refers to the amount of information stored in the image, which is the number of pixels per inch of the image.
- Printer resolution, also known as output resolution, refers to the maximum number of dots that can be printed per inch in both the horizontal and vertical directions when printing output, usually expressed in "dots/inch" or dpi (dot per inch).
- Scanning resolution refers to the number of points per inch of the scanned object that can be represented by the scanning element when the all-in-one machine implements the scanning function.
This article mainly introduces display resolution.
The numerical value of display resolution refers to the number of horizontal and vertical pixels in the entire viewing area of the display. For example, a resolution of 800×600 means that 800 pixels are displayed horizontally and 600 pixels are displayed vertically on the entire screen.

The total number of horizontal pixels and vertical pixels of the display resolution is always in a certain ratio, usually 4:3, 16:9 or 16:10.
4:3 is the most common screen ratio in the TV era and is an ancient standard passed down from the TV era. Before the rise of widescreen in modern times, most screen resolutions were based on this ratio. See the table below for specifications.
VGA | SVGA | XGA | UXGA | QXGA |
640×480 | 800×600 | 1024×768 | 1600×1200 | 2048×1536 |
16:9 is mainly a commonly used widescreen ratio for movie videos. The commonly heard 720p and 1080p are both this ratio. It is suitable for video viewing and office operations (accommodating two documents to be processed side by side), but it has relatively poor support for games (gradually Get more game support) screen formats. See the table below for specifications.
QHD | HD | FULL HD | Quad HD | UHD |
960×540 (540P) | 1280×720 (720P, quasi-HD) | 1920×1080 (1080P, HD) | 2560×1440 (2K resolution, ultra-high definition) | 3840×2160 (4K resolution, Ultra HD) |
16:10 is the common widescreen ratio for computer screens. See the table below for specifications.
WVGA | WSVGA | WXGA | WXGA+ | WSXGA + | WUXGA | WQXGA |
800×480 | 960×600 | 1280×800 | 1440×900 | 1680×1050 | 1920×1200 | 2560×1600 |
Each monitor has its own maximum resolution and is compatible with other lower display resolutions, so a monitor can display multiple different resolutions. Although the higher the display resolution, the better, but there is another factor to consider, which is whether the human eye can recognize it.
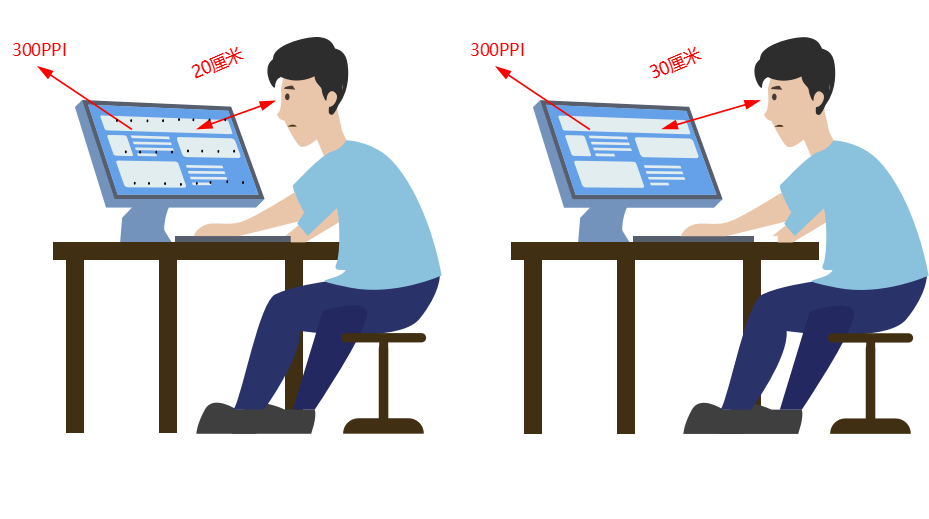
Here we need to mention the concept of PPI (Pixels Per Inch), which is the density unit of pixels, indicating the number of pixels per inch. Therefore, the higher the PPI value, the better the display effect of the screen.
Mr. Qiao proposed a concept: retina screen. Its definition is "when the human eye looks at a screen with a PPI greater than 300 from a distance of 10 inches (25.4 cm), the existence of pixels will not be noticed." Therefore, in addition to the screen quality itself, the viewing distance also has a great impact on detecting the presence or absence of pixels.
Take LED billboards as an example. When viewed from a distance, the pixels are basically invisible, but when viewed up close, they are densely packed with pixels.
From this, the minimum standard of the retina screen obtained by the document is calculated (here, the human eye is 70 cm away from the computer screen as an example):
- At 1080P resolution, monitors below 21.5 inches best meet the requirements of retina screens.
- At 2K resolution, monitors below 27 inches meet the requirements of Retina screens.
- At 4K resolution, screen sizes below 41 inches meet the requirements of retina screens, and the smaller the size, the more delicate the imaging.
At this point, the size standards that meet the retina level at each resolution have been released, but it should be noted that these are only theoretical data. The same display may appear between people due to many factors such as usage environment, sitting posture, myopia, etc. But the usage experience is different.
We often see that when opening a picture or video on a mobile phone, the image does not completely fill the screen, and black edges appear on both sides of the screen. This is due to the mismatch between the image resolution and the mobile phone screen resolution.
For example, there is a computer with a screen resolution of 1920×1080 and several pictures with different resolutions, with resolutions of 2048×1536, 1920×1080, and 1280×800.
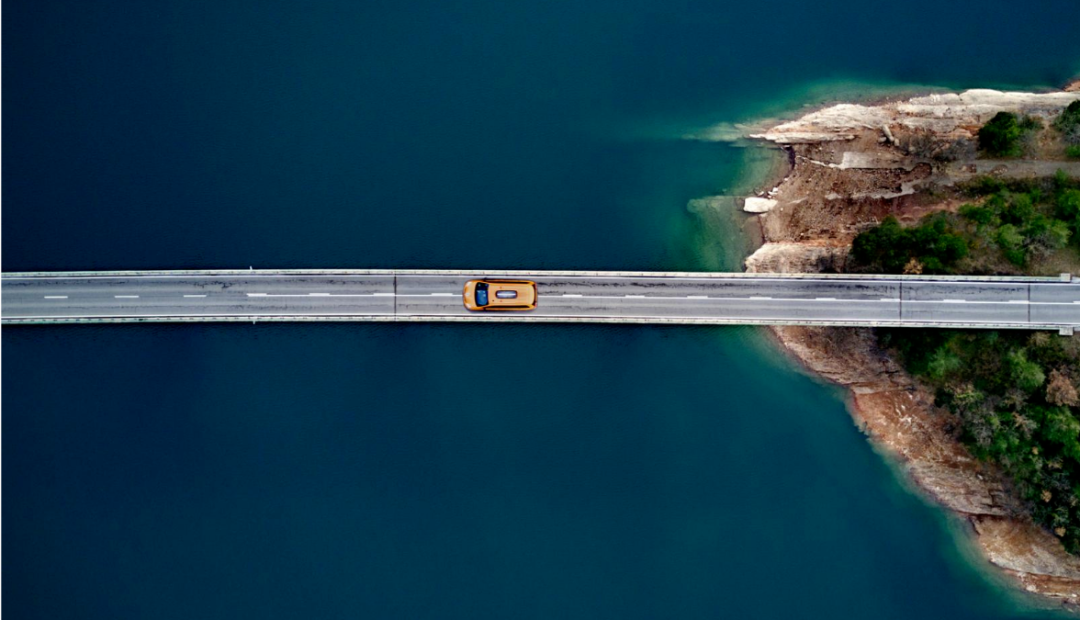 Original picture
Original picture
Let’s take a look at the difference between theoretical display and actual display effects.
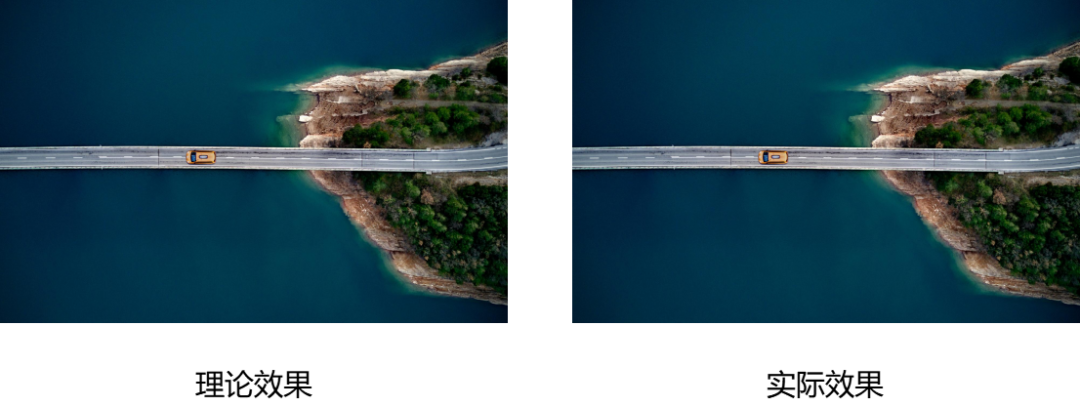
The first is the theoretical and practical display of the resolution specification of 2048×1536.
 Demonstration of theoretical and practical effects with a resolution of 1920×1080
Demonstration of theoretical and practical effects with a resolution of 1920×1080
 Demonstration of theoretical and practical effects with a resolution of 1920×1080
Demonstration of theoretical and practical effects with a resolution of 1920×1080
 picture
picture
You may not be surprised by the display effect of the above-mentioned picture with the specification of 1920 × 1080. It is easy to understand that the same resolution can be displayed on the full screen. But why do the theoretical effects and actual effects of the other two resolution pictures show different results?
The reason is that when the TV displays a picture, it will have a set of display algorithms to process the picture. This set of algorithms will increase the pixels of the image or delete the pixels of the image based on the logical resolution of the image and the physical resolution of the screen, so that the image can have an optimal display effect on the screen after processing.
For a 2048*1536 resolution image, since the number of logical pixels exceeds the number of physical pixels on the screen, the display algorithm will reduce the number of logical pixels in the image until it can be fully displayed on the screen. Until there is an optimal display effect, the deleted pixels are generally invisible to the naked eye.
For a 1280*800 resolution image, since the number of logical pixels is less than the number of physical pixels on the screen, the display algorithm will increase the number of logical pixels of the image until there is an optimal display effect on the screen. For the increased Pixels are generally invisible to the naked eye.
refresh rate
Screen refresh rate is an important parameter of a display device. It represents the number of times the device can update screen content per second. Typically, refresh rate is measured in Hertz (Hz). For example, a 60Hz refresh rate means the device can update screen content 60 times per second.
The higher the screen refresh rate, the more stable and smooth the screen display will be. This is particularly important for applications that require fast dynamic response, such as electronic games and video playback.
If the screen refresh rate is too low, blurry and smeared images may appear on the screen, which may affect the user experience.
In addition to providing a smoother picture, a high refresh rate can also improve the device's response time. The response time of the device refers to the time it takes for the device to receive user input and display related operations.
A high refresh rate reduces response time, allowing the device to respond to user input faster.
In addition, different types of monitors have different refresh rate ranges. For example, ordinary LCD monitors are usually around 60 Hz, while high-end gaming monitors can reach over 240 Hz.
Currently, the monitor refresh rates on the market are mainly divided into 60Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz, 240Hz, etc. Among them, 60Hz is the most common refresh rate and the lowest refresh rate.
High refresh rates such as 120Hz, 144Hz, and 240Hz are monitors that have become increasingly popular in recent years because they can bring smoother picture effects and are especially suitable for scenarios such as playing games and watching high-definition videos.
Below are two refresh rates of 24FPS and 60FPS.


Compared with videos with a refresh rate of 60FPS, the video with a refresh rate of 24FPS can feel a sense of pause in the picture. The boat and waves on the water in the video have obvious lags. This shows how important a high refresh rate is. .
Screen refresh rate is affected by many factors, such as hardware performance, monitor type, and connection method. High refresh rate monitors usually require higher performance hardware support, such as graphics cards, CPUs, etc.
- The hardware level of the monitor: The hardware level of the monitor is one of the most important factors that affects the refresh rate. Generally speaking, high-end monitors will have higher refresh rates.
- Graphics card performance: Graphics card performance is another important factor that affects the monitor refresh rate. If the graphics card performance is insufficient, even if the monitor itself supports a high refresh rate, it will not be able to take full advantage of it.
- Transmission interface standard: The transmission interface standard will also affect the refresh rate of the display. For example, a monitor that uses HDMI 1.4 or DP 1.2 as a data interface can only support a higher refresh rate of 60Hz, while a monitor that uses DP 1.4 or HDMI 2.0 as a data interface can support higher refresh rates.
Summarize
Generally speaking, the higher the resolution and refresh rate of the screen, the better, but in actual use, the editor recommends that it is best to buy according to your actual needs.
First, high resolution and high refresh rate will inevitably lead to high memory consumption, and ordinary people cannot recognize such high-precision images.
Second, the wallets of workers are limited after all. High resolution and high refresh rate mean high consumption. There is no way, the wallets of workers cannot bear it!