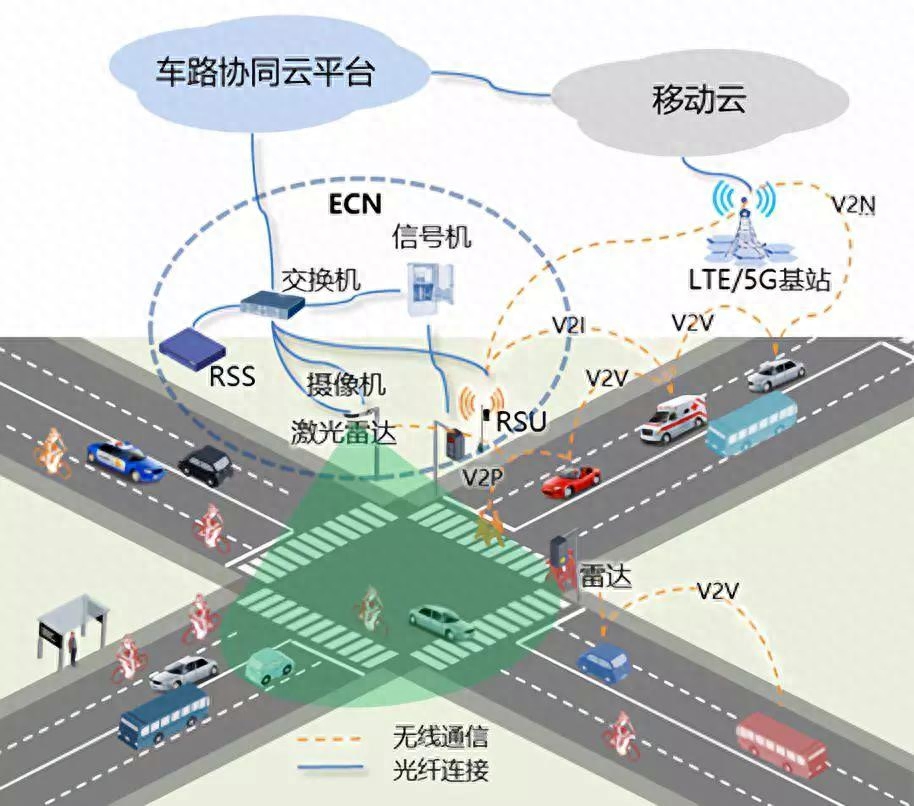
Edge Computing and 5G: Enabling Low-Latency, High-Speed Connections

Edge Computing and 5G: Enabling Low-Latency, High-Speed Connections
With the continuous evolution of the digital age, people's requirements for network connections have become more stringent, especially in scenarios that require high-speed data transmission and low latency, such as the Internet of Things, virtual reality, and smart factories. To meet these needs, the combination of edge computing and 5G technology has become a cutting-edge solution. This powerful combination will not only change the way we live, but will also propel industries towards new and efficient operating models.
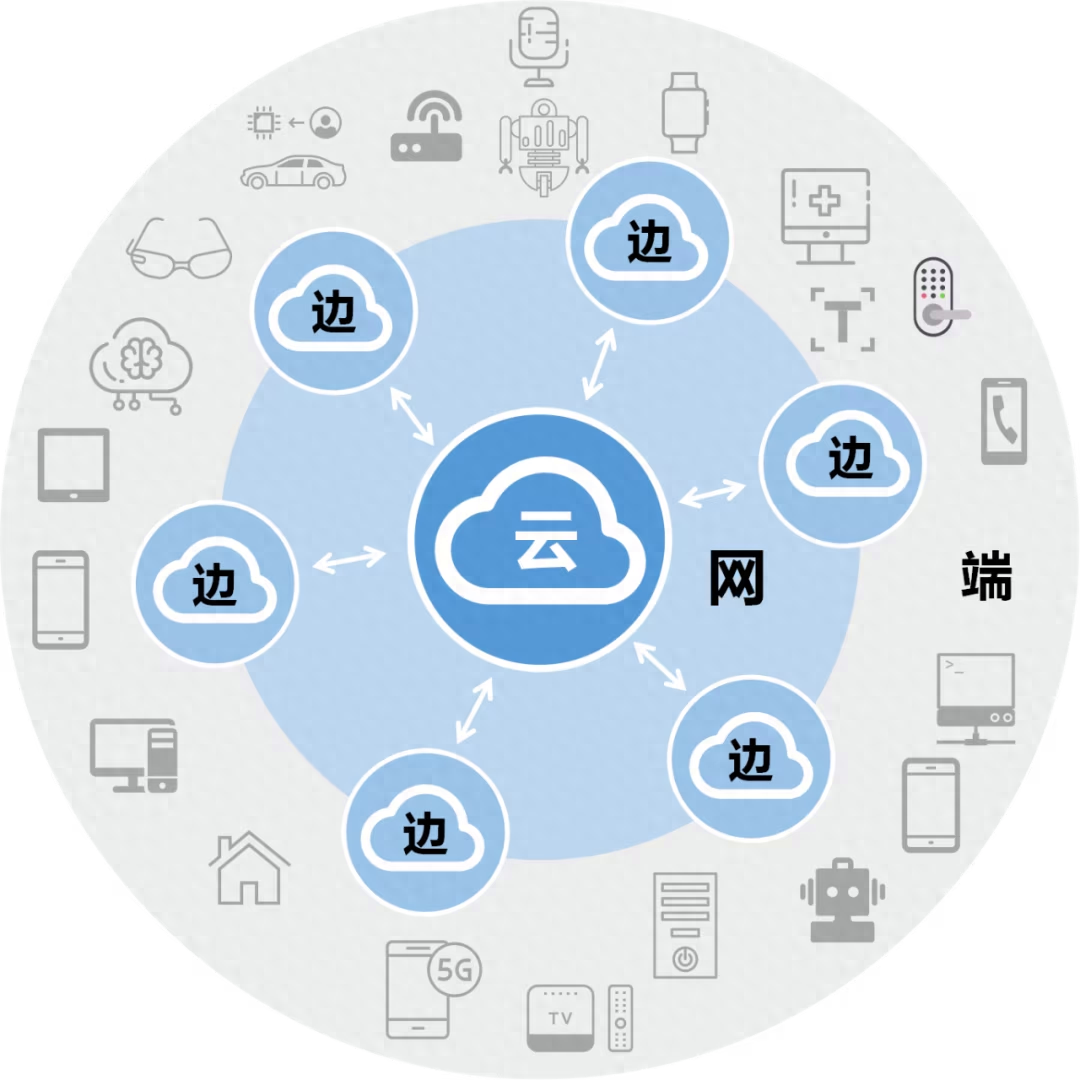
What is edge computing and 5G?
Edge Computing is a new type of computing architecture that pushes computing and data processing closer to the edge of user equipment to reduce data transmission delays and improve application performance. 5G is the fifth generation of mobile communication technology. It has the characteristics of high bandwidth, low latency, and large number of connections. It is the key foundation for realizing high-speed and stable connections.
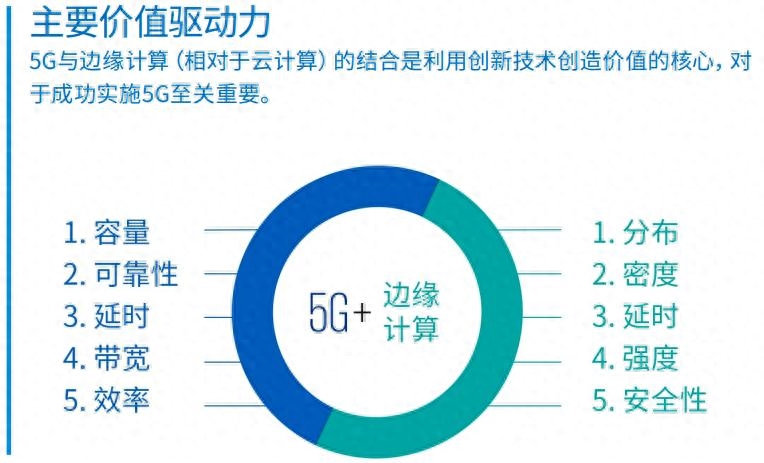
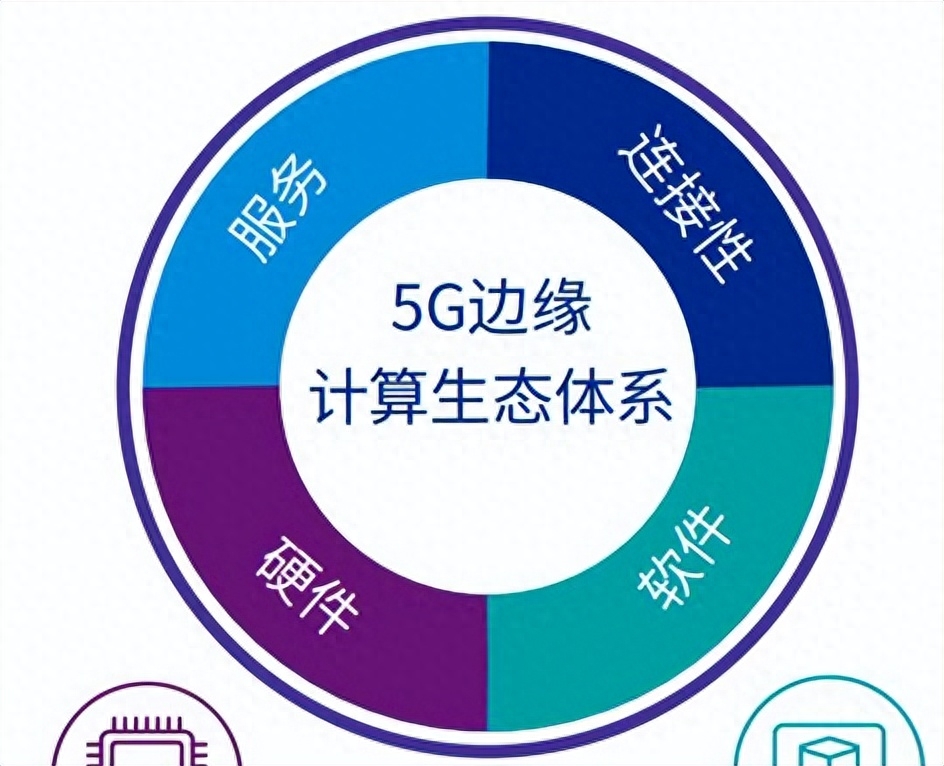
Key Elements of Edge Computing and 5G
- Low latency: The low latency of 5G provides stronger support for edge computing. Edge computing can deploy applications and services on edge servers close to users, and push data processing and decision-making closer to users, thereby significantly reducing transmission delays.
- High-speed connection: 5G provides a high-bandwidth network connection that can meet the needs of large-scale data transmission. Edge computing can use the high-speed connection of 5G to transmit massive data to the cloud in real time for analysis and processing, so as to achieve efficient data utilization.
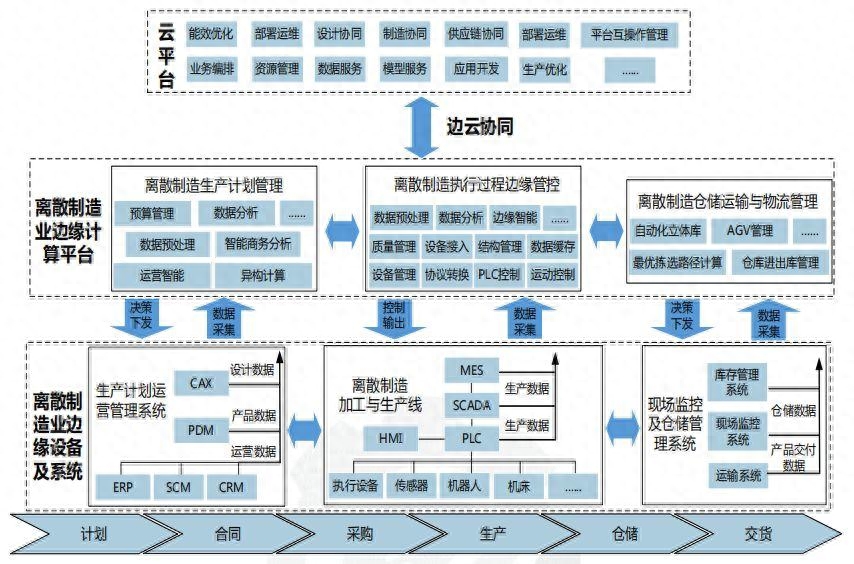
- Large-scale connections: 5G supports large-scale connections, and edge computing can handle a large number of terminal device connections, such as sensors and smart devices in the Internet of Things, and can achieve a wider range of applications.
- Distributed computing: With the help of distributed architecture, edge computing can distribute computing tasks to multiple edge nodes and perform collaborative processing, which improves the utilization and processing efficiency of computing resources.
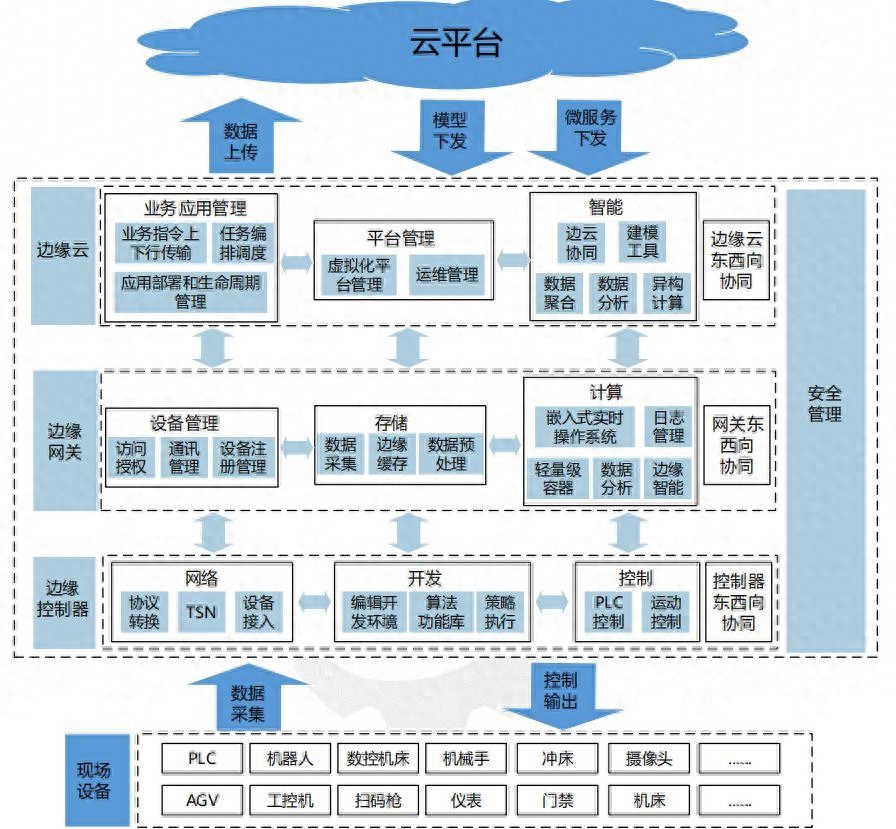
Application Scenario
Edge computing and 5G play an important role in many application scenarios, the following are some typical applications:
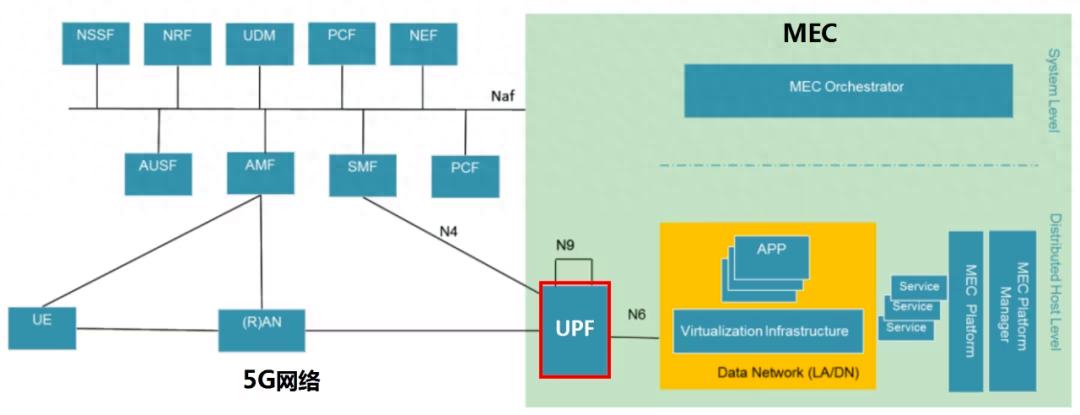
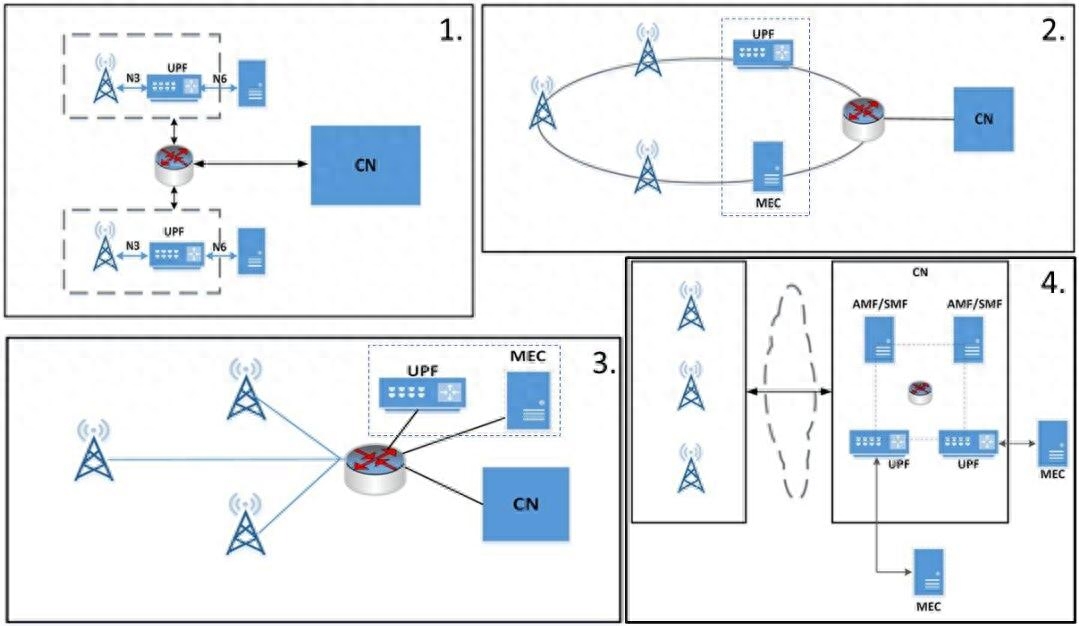
- Smart factory: In the field of smart manufacturing, edge computing and 5G can realize low-latency control and monitoring of factory equipment, improving production efficiency and quality.
- Internet of Things: In Internet of Things applications, edge computing and 5G can realize real-time data transmission and analysis of IoT devices, and support applications such as smart cities, smart homes, and smart transportation.
- Virtual reality and augmented reality: In the field of virtual reality and augmented reality, low latency is the key, and edge computing and 5G can provide a smoother and more realistic user experience.
- Telemedicine: 5G's high-speed connection and low latency make telemedicine possible, and edge computing can realize real-time transmission of medical equipment data and efficient analysis of medical images.
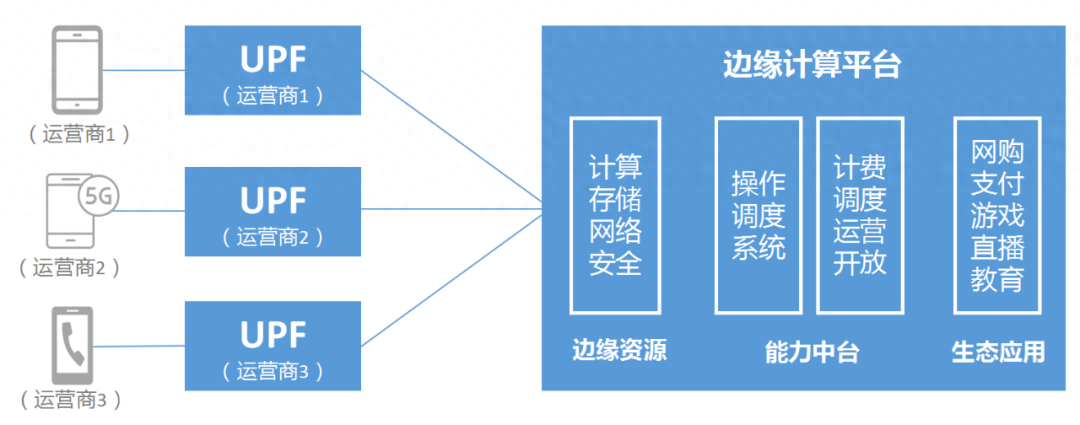
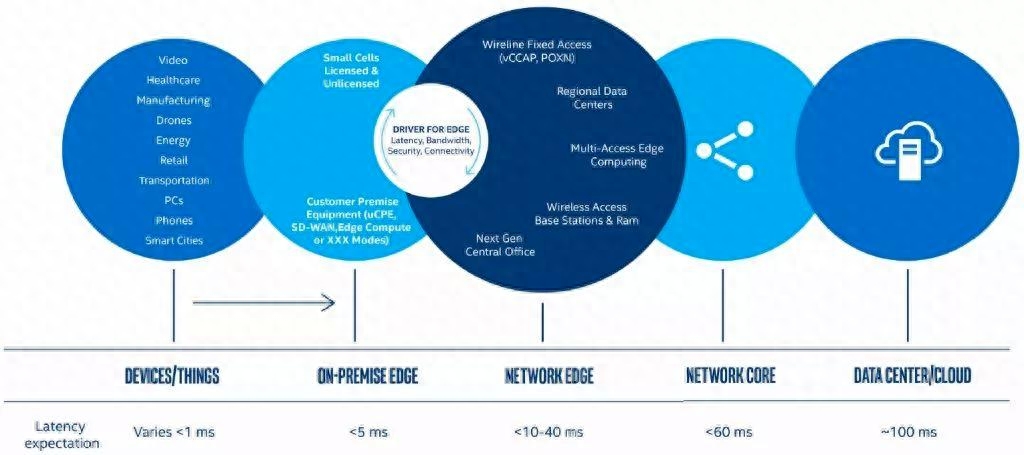
Challenges and Prospects
Although edge computing and 5G have great potential, they also face some challenges in practical applications. These include:
- Network infrastructure: Edge computing and 5G applications require strong network infrastructure support, including the construction of high-density edge servers and 5G base stations to cover a wider area and users.
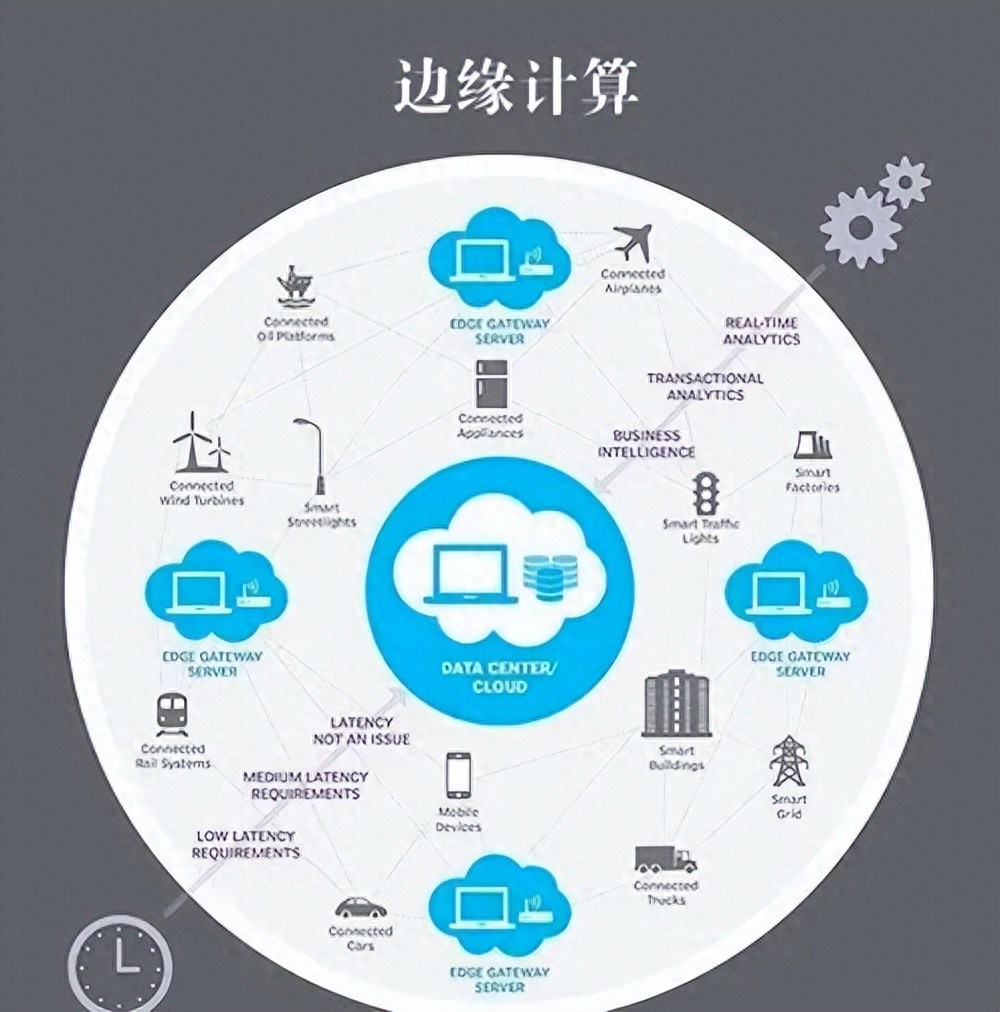
- Data security and privacy: The combination of edge computing and 5G also brings challenges to data security and privacy protection. In the process of data transmission and processing, measures such as data encryption and identity verification need to be strengthened to protect the security of user data.
- Energy consumption and the environment: Edge computing and 5G high-density devices require a large amount of energy supply. At the same time, it is necessary to pay attention to its impact on the environment and propose sustainable solutions.
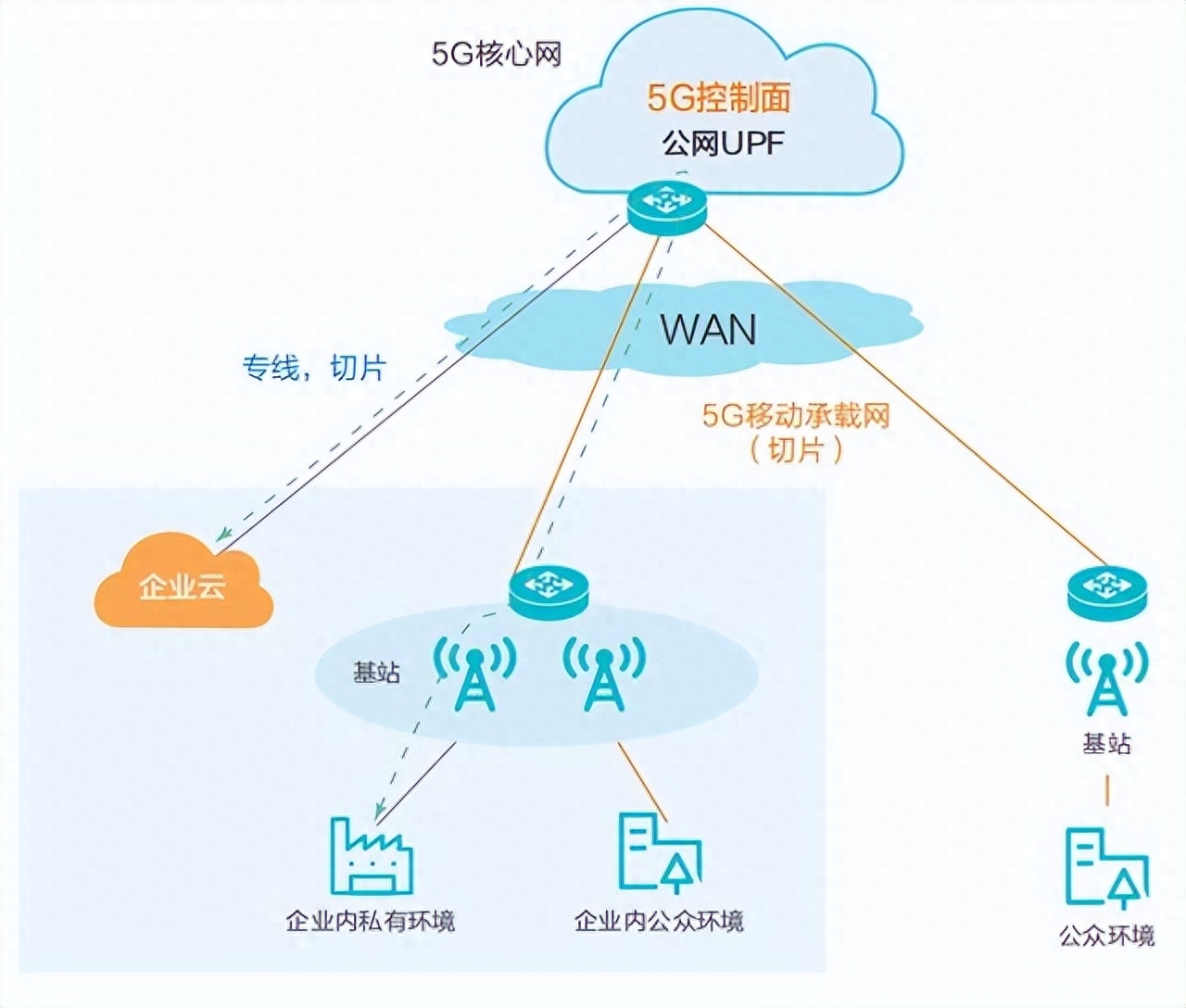
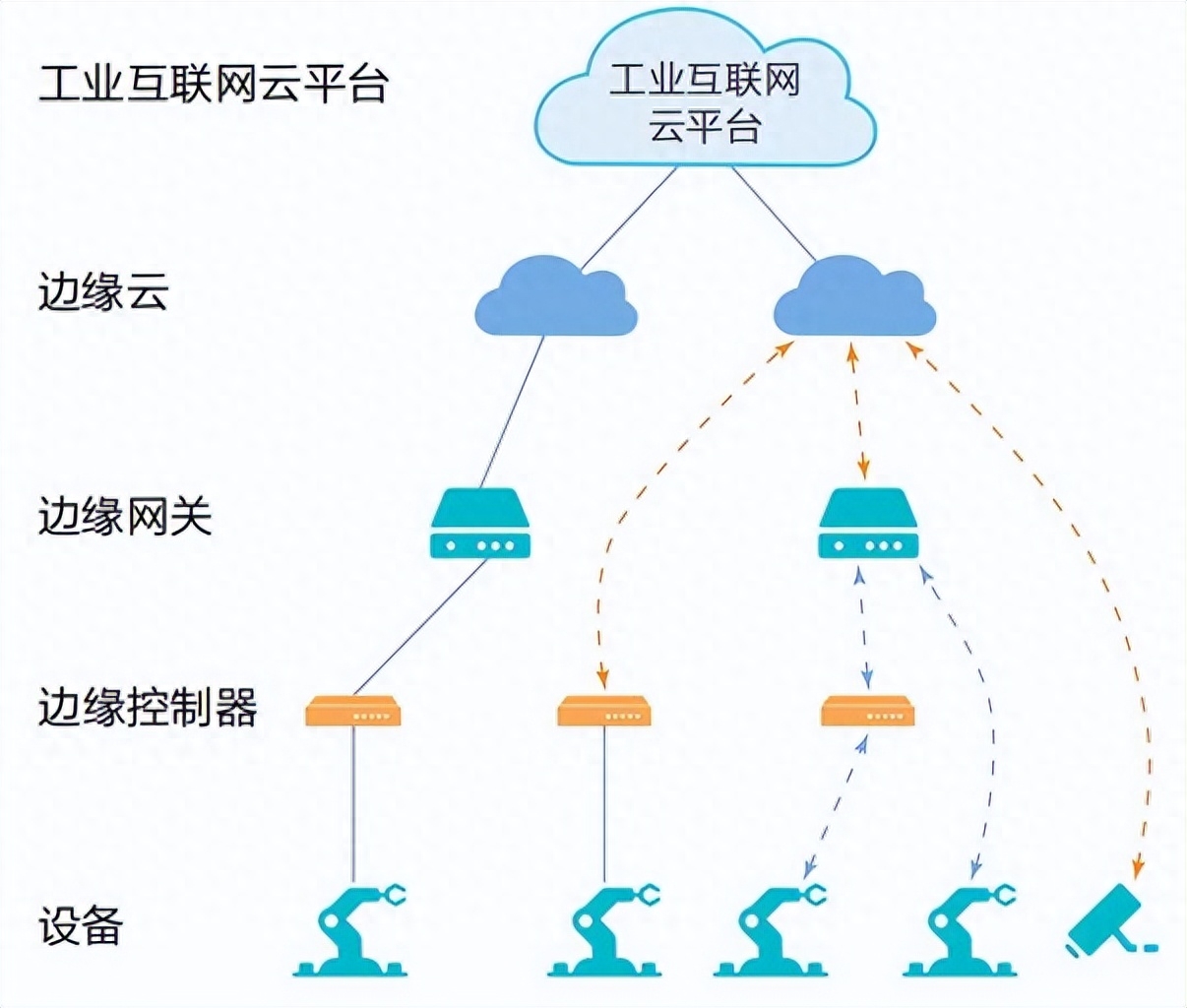
However, with the continuous development and innovation of technology, these challenges will gradually be solved. In the future, we can expect that the combination of edge computing and 5G will create more value in various fields. Especially in the fields of smart manufacturing, Internet of Things, virtual reality, and telemedicine, the combination of edge computing and 5G will greatly improve the efficiency and convenience of applications. This will also bring greater convenience to our digital life and promote the intelligentization of society.
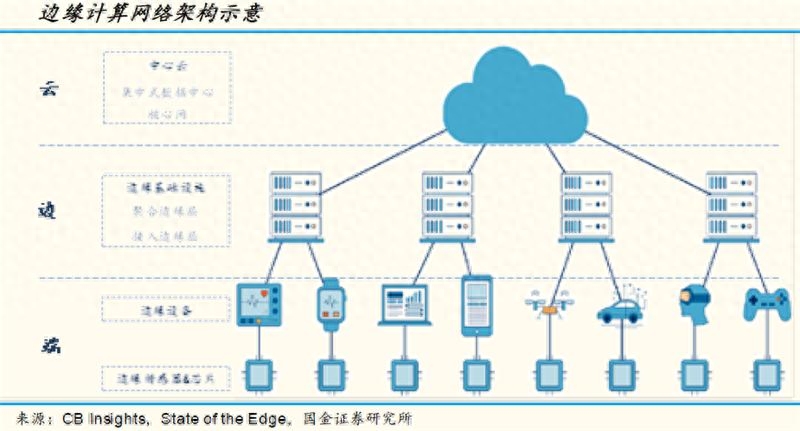
In the future, we can expect more innovative application scenarios to emerge. With the popularization of 5G and the maturity of edge computing, we may see more changes in smart cities, smart transportation, smart medical care and other fields. This powerful combination will bring our society faster, more efficient, and smarter connections, which will not only make our lives more convenient, but will also push the entire society to new heights. The future of edge computing and 5G is full of hope, waiting for our continuous exploration and innovation, let us meet the challenges and opportunities of this digital age together.