What is a UTP cable?

What is a UTP cable?
The Internet plays a key role in our everyday lives, from work to play, from shopping to paying utility bills. Ever wonder how the world is truly connected to the internet in a mental and physical sense. The physical connection is via UTP cable (unshielded twisted pair). This twisted-pair wiring provides a stable network for data transmission and telephony.
Standard UTP cables consist of 100 ohm copper cables made of 2–1800 unshielded twisted pairs shielded by an outer jacket. Since they have no metal shield, the cable diameter is reduced, but electrical interference cannot be avoided. The twisting of these cables increases immunity to electromagnetic interference and electrical noise. In the jacket of an unshielded twisted pair cable, there are 8 individual wires twisted into 4 pairs. Connectors are placed at the ends of these cables, often referred to as RJ45 plugs.

How UTP Cables Work
The shielded twisted-pair cable consists of 4 pairs of copper wires wrapped in a plastic protective sheath. The greater the number of pairs, the greater the corresponding bandwidth. Twist the two individual copper cables of a single pair around each other, and then twist the other pairs together. This is done to minimize crosstalk and EMI, which can degrade network performance in the long run.
Each twisted pair in a UTP cable is color coded for easy identification. In North America, each wire in a twisted pair is identified by one of 5 colors: blue, orange, green, brown, or slate (gray). This copper wire is then paired with another set of different wires consisting of white, red, black, yellow, or purple. Typically, one copper wire in a twisted pair is a solid color and the second copper wire is striped of its paired color. Example: A solid blue copper cable is paired with a white and blue striped copper cable. This will make identifying and matching them easy. Alexander Graham Bell invented the twisted pair in 1881.
Functions of UTP cables
The main functions of UTP cables are as follows:
- Shielded twisted pair cables are used for network LAN connections, connecting computers to target devices such as printers, modems, etc. It is not recommended to use them in places with high electrical interference as they do not have any metal shielding.
- UTP cables are mainly used for audio signal transmission of NVR (Network Video Recorder), DVR (Digital Video Recorder) and HVR (Hybrid Video Recorder) components in surveillance security systems.
- Unshielded twisted pair cables are widely used in horizontal and backbone cabling subsystems.
- UTP cables are used as Ethernet cables and telephone lines for transmitting data and audio signals over short and medium distances.
- Unshielded twisted-pair cables are also great for low-speed data transmission and don't require grounding.
- They are used for signal transmission in automation and control systems.
- They are used to interface with dumb terminals of mainframe computers.
- They are cheap so they can be used as jumper wires.
- UTP cables are used in gigabit media converters, fiber optic media converters, and fiber optic switches.
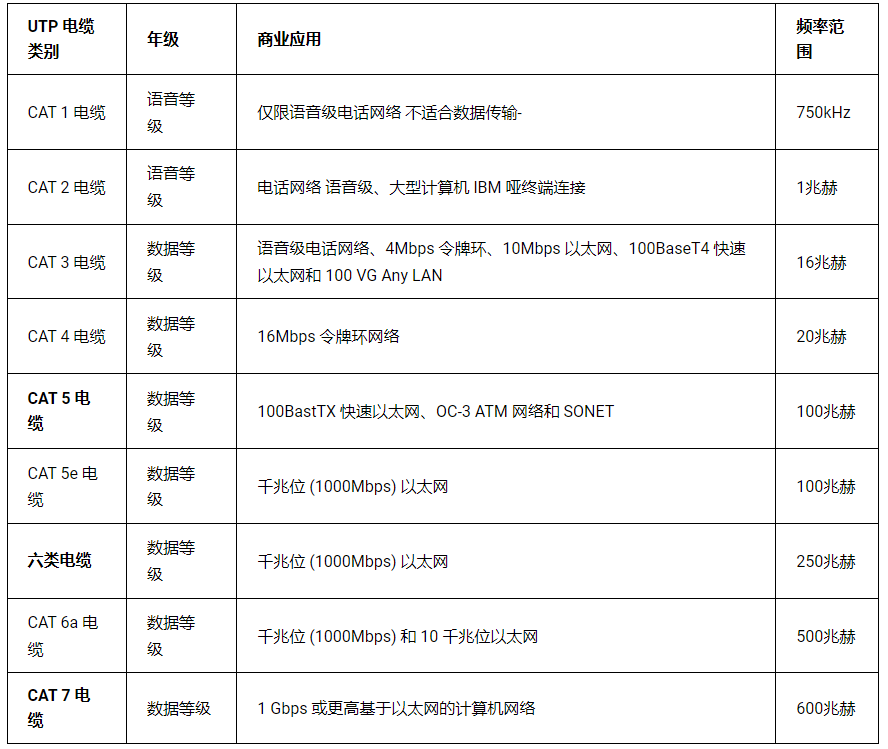
Different categories of UTP cables
- CAT1 cables are commonly used on telephone lines, which transmit data up to 1MBPS.
- CAT2 cables are sub-lower UTP cables used to support digital voice and data communications, and it transmits data up to 4mbps.
- CAT3 cable is a class 3 unshielded twisted pair cable used in Token Ring and 10BASE-T Ethernet applications, which transmits data at speeds up to 10MBPS.
- CAT4 cables have four pairs of UTP copper cables and are used in Token Ring networks, which transfer data at speeds up to 16MBPS.
- CAT5 cables are used in structured cabling for Ethernet, Token Ring and Fast Ethernet connections, and it transmits data up to 100MBPS.
- CAT5e cables are very popular and are used for Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and Fast Ethernet connections, and it transmits data up to 1GBPS.
- CAT6 cable is an advanced UTP cable for Gigabit Ethernet and 10G Ethernet (55m) connections, which transmits data up to 10GBPS.
- CAT6a cables are also used for Gigabit Ethernet and 10G Ethernet (55m), which transmit data up to 10GBPS.
- CAT7 cable is the highest grade UTP cable for Gigabit Ethernet and 10G Ethernet (100m), which transmits data at nearly 10GBPS.
UTP Cable Specifications and Performance
As the name implies, solid conductor unshielded twisted pair cables use a single solid conductive copper cable as the conductor. Due to the larger diameter, it has lower sensitivity to high frequency influences and DC resistance. These characteristics enable these UTP cables to support longer distance transmissions and higher data rates than unshielded twisted pair cables.
Unshielded twisted pair cables are often preferred for use as jumpers in work areas and telecommunications rooms. Also, they commonly use twisted pair cabling for most network connections. When looking at the cross section of an unshielded twisted pair cable, each individual copper conductor is made up of a bunch of smaller sized strands. They are arranged in such a way that multiple wires (usually in the range of 6-18) surround a single wire in the center of the harness. The outer wires are arranged around the individual wires through a stranding process. Together they form a single copper conductor with a diameter similar to a solid conductor UTP cable.
Application of UTP cable
Different applications of UTP cables are:
- For LAN and telephone connections
- Ethernet connection for low to high speed data transfer
- For connecting printers and modems to computers
- For Token Ring and Twisted Pair Ethernet applications
- For OC-3ATM network and SONET applications
- IBM dumb terminal for connection to mainframe computers
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why are UTP cables unshielded?
Since there is no shielding, the diameter of UTP cables becomes smaller, so they are easier to install and take up less space than STP cables, UTP cables become cheaper because they do not require metal covers similar to STP cables, these twisted pairs do not Requires any grounding to work effectively.
The design is designed to resist crosstalk, radio frequency interference, and electromagnetic interference. Almost all network architectures use UTP cables. They are very suitable as jumper cables. For home and office use, UTP is better than STP because they have less electrical interference.
2. How to connect the UTP cable?
- Strip or remove about 2 inches of the Ethernet cable jacket.
- Unwind the UTP cable pair, but do not extend beyond the exposed area when unwinding.
- Align the wires.
- Insert the copper wires into the RJ45 plug, making sure each wire is fully inserted into the front of the RJ45 plug in the correct order.
- Verify that the copper wires are in the correct order and make sure the cable extends to the front of the RJ45 plug and makes good contact with the metal connection in the RJ45 plug.
- Repeat for the second RJ45 plug.
3. What is the difference between UTP and STP cables?
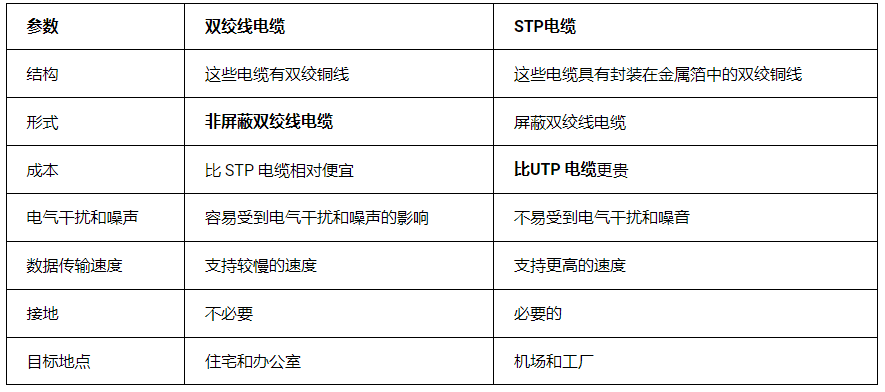
4. Which UTP cable is most commonly used?
Twisted UTP cable is the most commonly used unshielded twisted pair cable for most network connections. The advantages it offers are:
- Much better flexibility than UTP solid conductor cables
- They have a longer shelf life than solid types and have good wear and vibration resistance
- they can be used as jumpers
- Scratches and nicks cause less damage to stranded UTP cables.
- For more flexibility, we can add more copper wires, which is not possible in the solid type.
5. What are UTP cables usually used for?
UTP cables are commonly used as telephone lines and Ethernet cables in telephone connections and LANs (Local Area Networks). It is used to transmit audio signals and electronic data. These are also used for horizontal and backbone cabling subsystems.
6. Why is UTP popular in LAN technology?
The main reasons for the popularity of UTP cables in LAN technology are:
- It is cheaper compared to STP cable
- Quick and easy installation
- Significant space savings due to smaller twisted pair cabling
- Not affected by grounding problems
- It is resistant to RFI, crosstalk and EMI
- It works well even with lower data speeds
7. How does the UTP network cable transmit data?
Data sent over an unshielded twisted pair cable is converted to a binary code consisting of 0s and 1s. Devices transmitting data will send current along the cable at two different voltages (0 volts and 5 volts). On the other hand, the device receiving the data interprets these voltages as binary codes and converts them back to their original format.
8. The difference between shielded twisted pair cable and unshielded twisted pair cable:
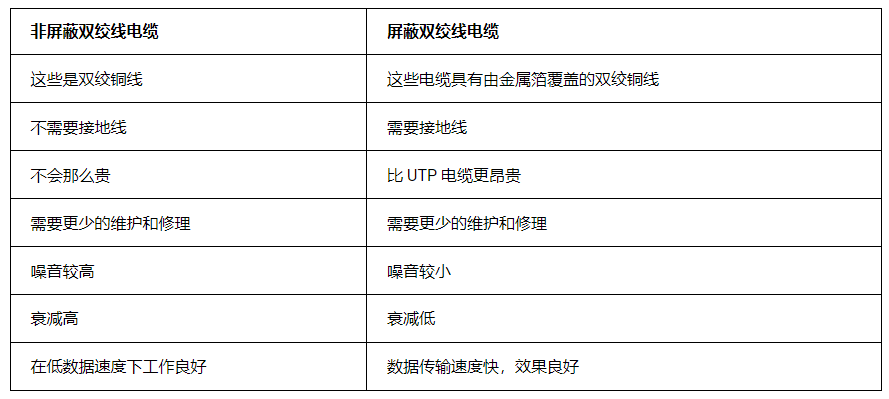
9. What connectors are used for twisted pair cables?
The standard connector configuration for unshielded twisted pair cables is the RJ-45 connector. RJ is short for Registered Jack, which means the connector follows a standard set by the phone company.