Talking about the application of Bluetooth mesh technology and smart home field

Talking about the application of Bluetooth mesh technology and smart home field

Part 01
Bluetooth mesh technical features
-Support many-to-many topology
The Bluetooth mesh network uses a method called "network flooding (flooding)" to publish and relay messages, which can realize the connection and message intercommunication of multiple nodes and multiple nodes in the mesh network.
- Extended physical area coverage
The Bluetooth mesh network can get rid of the shackles that the nodes can only be connected to the gateway or the main router. It can also be used as a relay node and a friend node to support the relay and forwarding of terminal device messages, realize "relay transmission", and overcome the disadvantages of WiFi technology. Difficulties in long-distance device message intercommunication and coverage.
- Remove the central node dependency
The Bluetooth mesh network transmits messages, and does not route messages through a specific route, specific device, or a fixed process. Therefore, it can get rid of the dependence on central nodes (such as gateways, main routing devices, etc.).
-Supports self-healing
In the Bluetooth mesh network, if a single node is faulty or abnormal and unable to communicate, it will perform automatic self-configuration, and transmit or relay messages through other normal working nodes, so as to realize single-point fault self-healing.
Part 02
Bluetooth mesh technology principle
The principle and design of Bluetooth mesh technology are mainly reflected in three aspects: network architecture, topology, node, and address division. The following will take these three aspects as the starting point to analyze the principle of Bluetooth technology.
1️⃣Bluetooth mesh technology network architecture
In the network architecture, Bluetooth mesh works on top of the BLE protocol stack, using the same physical layer and link layer.
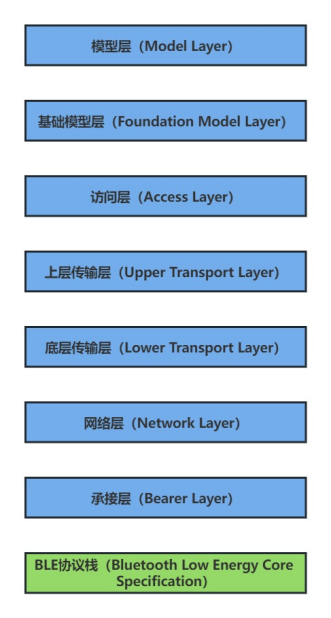
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the Bluetooth mesh protocol stack
From top to bottom, the Bluetooth mesh protocol stack is: Model Layer, Foundation Model Layer, Access Layer, Upper Transport Layer, Lower Transport Layer Layer), Network Layer, and Bearer Layer. Among them, the functions of each layer of the Bluetooth mesh protocol stack are as follows: the model layer defines user scenarios/applications, the basic model layer configures and manages the mesh, the access layer defines how applications use context data, the upper transport layer encrypts and decrypts application data, and the lower transport layer encrypts and decrypts data Segmentation and reassembly, the network layer performs network management, and the receiving layer performs broadcast/GATT bearer.
2️⃣ Bluetooth mesh topology and nodes
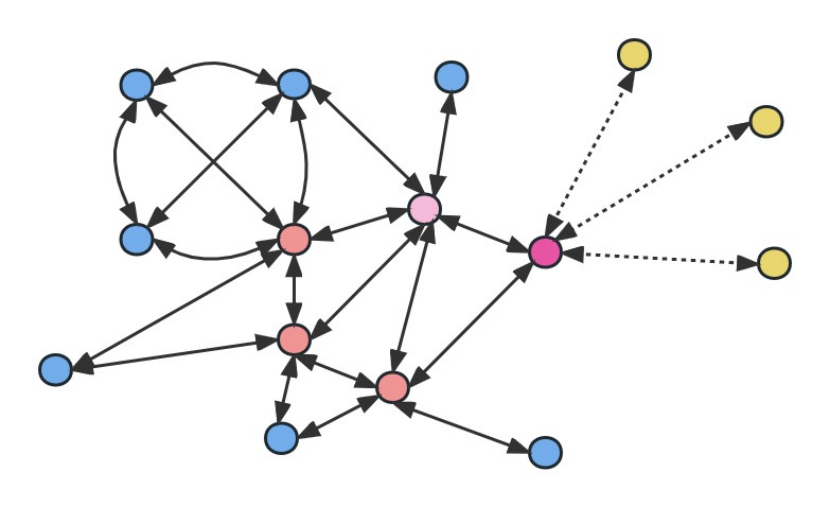
Figure 2 Bluetooth mesh network topology
Bluetooth mesh supports many-to-many communication. Therefore, in a scenario with many devices, Bluetooth mesh generally has a mesh structure. As shown in the figure above, in the Bluetooth mesh network topology, there are generally four types of node types:
(1) Blue nodes represent ordinary terminal nodes, which cannot relay and forward messages in the Bluetooth mesh network, and receive and send messages directly from the Bluetooth mesh network;
(2) The red node is a relay node, which is used to relay messages and realize long-distance transmission of network messages;
(3) Purple nodes represent friend nodes, which are used to transmit messages between low-power nodes and the network;
(4) Yellow nodes represent low-power nodes, which receive or forward messages through friend nodes. These nodes are generally low-power sensors and are powered by batteries, so there will be a sleep mechanism.
Bluetooth mesh technology is based on the information transmission mechanism of network flooding. Once all information is released by a node, it will be broadcast to the network instead of being transmitted to one or more nodes through routing. The WiFi network is around a central node (such as gateways, routers, etc.) for uplink and downlink messages. All network traffic will pass through here. If the central node fails, the entire network will be shut down. Bluetooth mesh technology can effectively remove centralization and get rid of the dependence on central nodes.
3️⃣ Bluetooth mesh address division
The Bluetooth mesh network layer defines four basic types of addresses: unassigned address, unicast address, virtual address, and multicast address, where the address length is 16 bits. The detailed classification of addresses is shown in the table below:
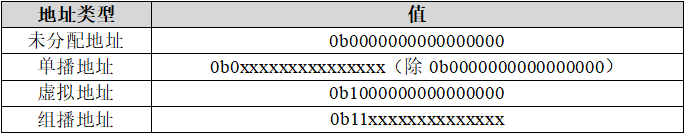
(1) Unassigned address
An unassigned address is an address of a node element that has not been configured or an unassigned address. The value of an unassigned address is 0x0000. For example: A model's message publishing can be disabled by setting the model's publish address to an unassigned address, which must not be used in the source or destination address fields of messages.
(2) Unicast address
The unicast address is a unique address assigned to each element. The value of the unicast address cannot be 0x0000, and the possible value range is 0x0001 to 0x7FFF. In the network distribution phase, the configurator will assign a unicast address to each element of the node during the life cycle of the network node. This address can be unassigned by the configurator, allowing reuse.
(3) Virtual address
A virtual address represents a group of target addresses, each virtual address logically represents a label UUID, and one or more elements can be configured to publish or subscribe to the same label UUID. The tag UUID will not be transmitted and should be used as an additional data field for the message integrity check value in the upper transport layer. The value range of the virtual address is 0x8000 to 0xBFFF.
(4) Multicast address
If the addresses of 0 or more elements are configured as the same address, the address is a multicast address. Multicast addresses from 0xFF00 to 0xFFFF are reserved for fixed purposes, and 0XC000 to 0xFEFF are used for other purposes. The multicast address can only be used in the destination address field of the message, and the message sent to the multicast address will be received by all model entities subscribed to this multicast address.
Part 03
Application of Bluetooth mesh in the field of smart home
In the smart home market, the application of Bluetooth mesh mainly focuses on the two scenarios of network distribution and control of smart home devices.
The so-called Bluetooth mesh distribution network is to add devices to the network through configuration, making it a part of the Bluetooth mesh network. The Bluetooth mesh provisioning network mainly involves three roles: Unprovisioned Device, Provisioner, and Mesh Node. As shown in the figure below, after undistributed network devices go through five stages: beacon stage, invitation stage, public key exchange stage, identity authentication stage, and distribution network data distribution stage, they can be connected to the Bluetooth mesh network to realize the interconnection and intercommunication of messages.
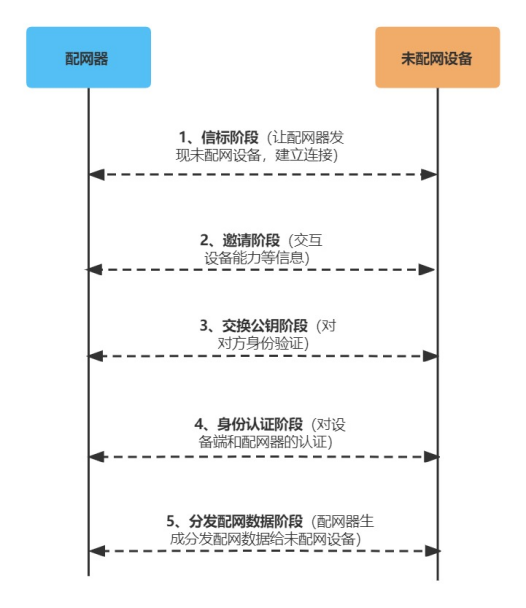
Figure 3 Bluetooth mesh distribution network flow chart
For the management and control of smart home devices, it can realize the simultaneous management and control of multiple smart home devices through inter-node message exchange, broadcasting, etc., and can support remote control and local control. Compared with the simultaneous management and control of multiple devices under the WiFi network, The Bluetooth mesh control method responds faster and has less load on the network.
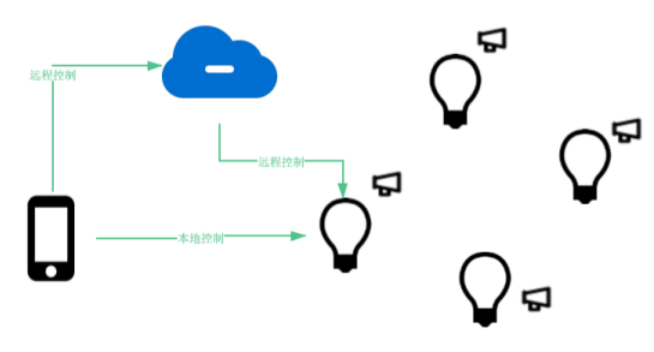
Figure 4 Multiple device management and control in the Bluetooth mesh network
Based on Part 1~Part 3, Bluetooth mesh technology has the characteristics of supporting multi-point to multi-point connection, wide physical coverage area, and removing the dependence on central nodes. Since it meets the growing interconnection needs of smart home devices, it also overcomes the existing The difficulties that WiFi technology cannot solve provide a new solution for the Internet of Things to adapt to different scenarios.