Application of 5G in the public sector of future smart cities

Application of 5G in the public sector of future smart cities

- The integration of 5G technology is expected to significantly impact multiple industries and verticals, including urban development operations.
- The advantages of low latency and high data transfer speeds will transform the efficiency, resilience and sustainability of smart cities.
While the Internet of Things has already revolutionized industrial operations, including manufacturing and healthcare, local governments around the world are looking to new technologies to create future-proof smart cities.
However, infrastructure development in urban areas requires more than just the use of smart IoT devices. A high-performance, end-to-end and scalable connectivity framework is the key to success. According to new research from Aberdeen Strategy and Research, 48% of organizations see 5G as a key driver behind connectivity and modernization plans.
According to the GSM Association, a third of the world's population is expected to have access to 5G networks by 2025. The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) recently began repurposing at least 1,500 MHz of available spectrum for 5G satellite ite, mobile and broadband connectivity in the country.
In addition, Vodafone reported on the progress of open RAN infrastructure trials in North America and Europe, with the quotation process expected to begin in 2024. The European Commission has allocated €200 million in funding for smart cities, healthcare, manufacturing and agriculture in January 2023.
When looking to implement 5G public sector solutions, organizations should look for services with high reliability and scalability, leveraging government assistance and funding for specific use cases, while leaving more room for smart city innovation. Working with organizations experienced in urban implementation has also proven beneficial.
Application of 5G Technology in Urban Environment
One of the main advantages of 5G technology is its high-speed data transmission capabilities. 5G can support many devices and sensors simultaneously, collecting and analyzing data on various aspects of city operations, including traffic flow, air quality and energy consumption. People can use this information to optimize infrastructure and make cities more efficient and sustainable.
For example, 5G-enabled sensors monitor traffic in real time, allowing traffic signals to be optimized to reduce congestion and improve air quality. Likewise, smart grids powered by 5G can help cities manage energy usage efficiently, reduce carbon emissions and facilitate sustainable development initiatives.
Public service entities including local governments, fire departments, and police departments can take advantage of better communications and monitor them through smart devices, thereby enhancing the user-friendliness of traffic, public safety, transportation infrastructure, and public buildings. Additionally, leading companies investing in IoT and connectivity technologies are 20% more likely to implement 5G solutions, according to Aberdeen Strategy and Research.
In addition, 5G can help develop new products and services that benefit city dwellers. For example, it can support the development of smart homes and buildings that control and optimize energy consumption. 5G could also enable the development of cutting-edge transportation services such as drones, self-driving cars and drones that are expected to revolutionize urban mobility in the near future.
In addition to the benefits for city dwellers, 5G could help cities be more resilient in the face of natural disasters and other emergencies, significantly improving the effectiveness of first responders. Likewise, according to Aberdeen Strategy and Research, 60 percent of public sector entities have witnessed better security outcomes through faster network connectivity technologies.
For example, 5G-enabled sensors can monitor infrastructure and detect faults and other abnormal operations, enabling early detection and repair through superior situational awareness. 5G could also support real-time communication and coordination systems, allowing city officials to respond to emergencies more quickly and effectively.
While public sector entities cannot easily develop and implement such cutting-edge technologies on their own, smart city solutions can be deployed more quickly by partnering with dedicated service providers working on 5G technology.
Challenges of Implementing 5G
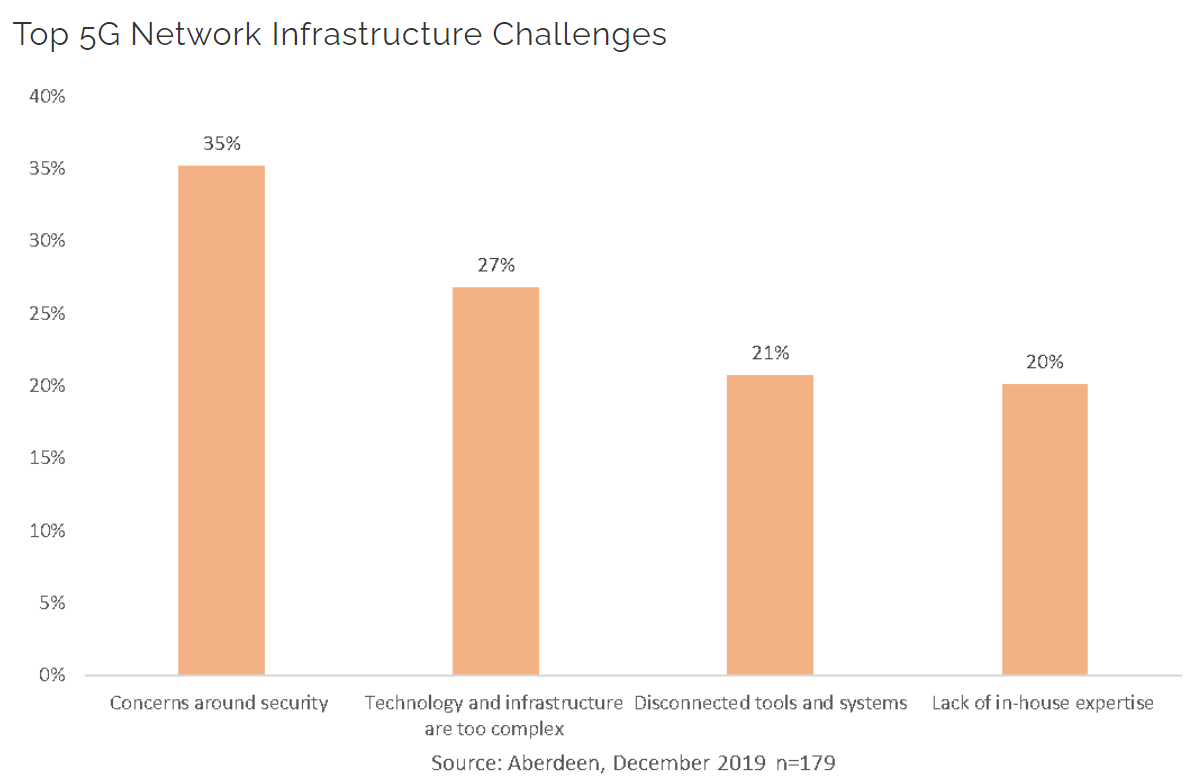
5G Network Infrastructure Challenges Source: Aberdeen Strategy & Research
Despite its potential advantages, deploying 5G technology in urban areas faces significant challenges. One of the most critical challenges is the need for substantial infrastructure investment, including the installation of new base stations and fiber optic cables.
Currently, areas with 5G coverage are still rare. 5G-enabled devices are also rare. Overall, the rollout has been relatively slow. A large part of the 5G network has very complex infrastructure and technical requirements. City managers need a lot of help hiring enough qualified technical expertise to handle this type of infrastructure, which makes the existence of disconnected systems and tools a notable problem.
It is important that city managers address data privacy and security issues to ensure that data collected and transmitted by 5G-enabled devices has adequate safeguards. Malicious actors may take advantage of the transition to 5G when protections are not yet in place.
The Internet of Things, augmented reality, virtual reality and cloud service providers will rise faster with sufficient protection.
In conclusion, 5G will play a key role in urban development operations. Leveraging advanced technological capabilities, public sector leaders can extract and analyze data on different aspects of infrastructure and urban lifestyles, and build new services and products accordingly. However, security and privacy issues need to be addressed as well as substantial infrastructure investment to provide full benefit to the community.