Interviewer: What process will be executed after entering the URL?

Interviewer: What process will be executed after entering the URL?
Positioning in the network relies on IP for identity positioning, so the first step in URL access is to obtain the IP address of the server. To obtain the IP address of the server, DNS (Domain Name System, Domain Name System) domain name resolution is required. DNS domain name resolution is to find the corresponding IP address through the URL.After entering the URL in the browser, it will perform the following processes:
Perform DNS domain name resolution;
Encapsulate HTTP request packets;
Encapsulate the TCP request packet;
Establish a TCP connection (3-way handshake);
Parameters are passed from client to server;
After the server gets the client parameters, it performs corresponding business processing, and then encapsulates the result into an HTTP packet and returns it to the client;
服务器端和客户端的交互完成,断开 TCP 连接(4 次挥手);
浏览器通过自身执行引擎,渲染并展示最终结果给用户。
After entering the URL in the browser, it will perform the following processes:
Perform DNS domain name resolution;
Encapsulate HTTP request packets;
Encapsulate the TCP request packet;
Establish a TCP connection (3-way handshake);
Parameters are passed from client to server;
After the server gets the client parameters, it performs corresponding business processing, and then encapsulates the result into an HTTP packet and returns it to the client;
服务器端和客户端的交互完成,断开 TCP 连接(4 次挥手);
浏览器通过自身执行引擎,渲染并展示最终结果给用户。
1.DNS 域名解析
在网络中定位是依靠 IP 进行身份定位的,所以 URL 访问的第一步便是先要得到服务器端的 IP 地址。而得到服务器的 IP 地址需要使用 DNS(Domain Name System,域名系统)域名解析,DNS 域名解析就是通过 URL 找到与之相对应的 IP 地址。
PS:为什么不直接访问 IP 地址来请求服务器?因为 IP 地址很长,不方便记忆,而 URL 地址好记很多,所以会使用 URL 来替代 IP 地址,而 URL 就像 IP 地址的别名一样,用它可以定位到相应的 IP 地址。
DNS 域名解析的大致流程如下:
- 先检查浏览器中的 DNS 缓存,如果浏览器中有对应的记录会直接使用,并完成解析;
- 如果浏览器没有缓存,那就去查询操作系统的缓存,如果查询到记录就可以直接返回 IP 地址,完成解析;
- 如果操作系统没有 DNS 缓存,就会去查看本地 host 文件,Windows 操作系统下,host 文件一般位于 "C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts",如果 host 文件有记录则直接使用;
- 如果本地 host 文件没有相应的记录,会请求本地 DNS 服务器,本地 DNS 服务器一般是由本地网络服务商如移动、电信提供。通常情况下可通过 DHCP 自动分配,当然你也可以自己手动配置。目前用的比较多的是谷歌提供的公用 DNS 是 8.8.8.8 和国内的公用 DNS 是 114.114.114.114。
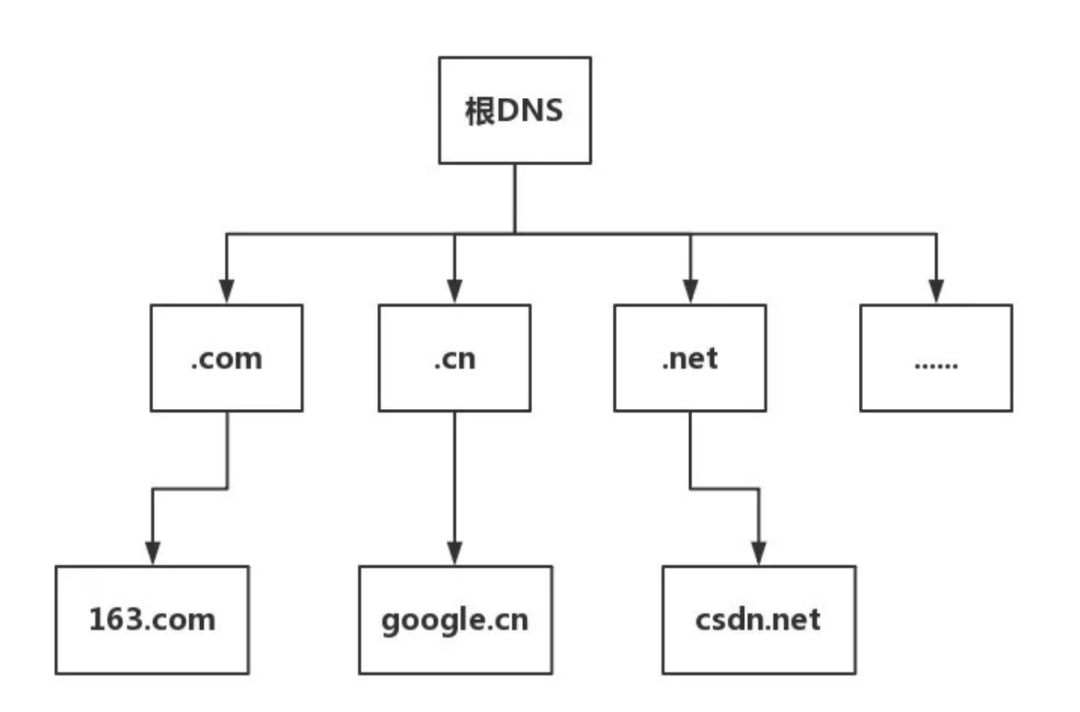
- 如果本地 DNS 服务器没有相应的记录,就会去根域名服务器查询了,目前全球一共有 13 组根域名服务器(这里并不是指 13 台服务器,是指 13 个 ip 地址,按字母 a-m 编号),为了能更高效完成全球所有域名的解析请求,根域名服务器本身并不会直接去解析域名,而是会把不同的解析请求分配给下面的其他服务器去完成,下面是 DNS 域名系统的树状结构图:
在网络中定位是依靠 IP 进行身份定位的,所以 URL 访问的第一步便是先要得到服务器端的 IP 地址。而得到服务器的 IP 地址需要使用 DNS(Domain Name System,域名系统)域名解析,DNS 域名解析就是通过 URL 找到与之相对应的 IP 地址。
PS:为什么不直接访问 IP 地址来请求服务器?因为 IP 地址很长,不方便记忆,而 URL 地址好记很多,所以会使用 URL 来替代 IP 地址,而 URL 就像 IP 地址的别名一样,用它可以定位到相应的 IP 地址。
DNS 域名解析的大致流程如下:
- 先检查浏览器中的 DNS 缓存,如果浏览器中有对应的记录会直接使用,并完成解析;
- 如果浏览器没有缓存,那就去查询操作系统的缓存,如果查询到记录就可以直接返回 IP 地址,完成解析;
- 如果操作系统没有 DNS 缓存,就会去查看本地 host 文件,Windows 操作系统下,host 文件一般位于 "C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts",如果 host 文件有记录则直接使用;
- 如果本地 host 文件没有相应的记录,会请求本地 DNS 服务器,本地 DNS 服务器一般是由本地网络服务商如移动、电信提供。通常情况下可通过 DHCP 自动分配,当然你也可以自己手动配置。目前用的比较多的是谷歌提供的公用 DNS 是 8.8.8.8 和国内的公用 DNS 是 114.114.114.114。
- 如果本地 DNS 服务器没有相应的记录,就会去根域名服务器查询了,目前全球一共有 13 组根域名服务器(这里并不是指 13 台服务器,是指 13 个 ip 地址,按字母 a-m 编号),为了能更高效完成全球所有域名的解析请求,根域名服务器本身并不会直接去解析域名,而是会把不同的解析请求分配给下面的其他服务器去完成,下面是 DNS 域名系统的树状结构图:

2.封装 HTTP 请求数据包
一个 HTTP 请求对象包含 4 部分内容:
- 请求行
- 请求报头
- 空行
- 请求正文
它的基本格式如下:

在得到了服务器 IP 之后,紧接着会将本地的请求封装成一个 HTTP 数据包,如上图所示。
一个 HTTP 请求对象包含 4 部分内容:
- 请求行
- 请求报头
- 空行
- 请求正文
它的基本格式如下:

在得到了服务器 IP 之后,紧接着会将本地的请求封装成一个 HTTP 数据包,如上图所示。
3.封装 TCP 请求数据包
HTTP 底层是依赖 TCP/IP 协议实现的,所以在底层数据传输时,会将 HTTP 请求包进一步封装成 TCP 数据包。
HTTP 底层是依赖 TCP/IP 协议实现的,所以在底层数据传输时,会将 HTTP 请求包进一步封装成 TCP 数据包。
4.建立 TCP 连接(3 次握手)
HTTP 通讯的基础是 TCP 连接,TCP 连接需要 3 次握手,3 次握手就是为了验证客户端的发送能力和接收能力,以及服务器端的发生能力和接收能力,就像打电话一样,通常的通话是这样开头的:
- _我_:喂,能听到吗?
- _对方_:能听到,你能听到吗?(证明了对方的接收能力和我的发送能力)
- _我_:我也能听到,咱们聊正事吧。(证明了对方的发送能力和我的接收能力)
经过以上 3 次握手就可以证明客户端的发送能力和接收能力,以及服务器端的发生能力和接收能力,这样就可以正式开始通讯了。
HTTP 通讯的基础是 TCP 连接,TCP 连接需要 3 次握手,3 次握手就是为了验证客户端的发送能力和接收能力,以及服务器端的发生能力和接收能力,就像打电话一样,通常的通话是这样开头的:
- _我_:喂,能听到吗?
- _对方_:能听到,你能听到吗?(证明了对方的接收能力和我的发送能力)
- _我_:我也能听到,咱们聊正事吧。(证明了对方的发送能力和我的接收能力)
经过以上 3 次握手就可以证明客户端的发送能力和接收能力,以及服务器端的发生能力和接收能力,这样就可以正式开始通讯了。
5.服务器端获取到 HTTP 请求参数
数据在经过 TCP 传到到服务器程序之后,又会将 TCP 的数据包转换成 HTTP 数据包(这一切都是 TCP/IP 协议的功劳),这样服务器端就可以得到客户端发送的请求数据了。
数据在经过 TCP 传到到服务器程序之后,又会将 TCP 的数据包转换成 HTTP 数据包(这一切都是 TCP/IP 协议的功劳),这样服务器端就可以得到客户端发送的请求数据了。
6.服务器端执行业务处理,并返回数据
服务器端拿到了客户端的请求参数之后,会进行相应的业务处理,处理完成之后,再将处理的结果返回给客户端。返回的流程和发送的流程类似,先将结果封装成 HTTP 数据包,HTTP 数据包可分为以下 4 部分:
- 状态行
- 响应报头
- 空行
- 响应正文
它的基本格式如下:
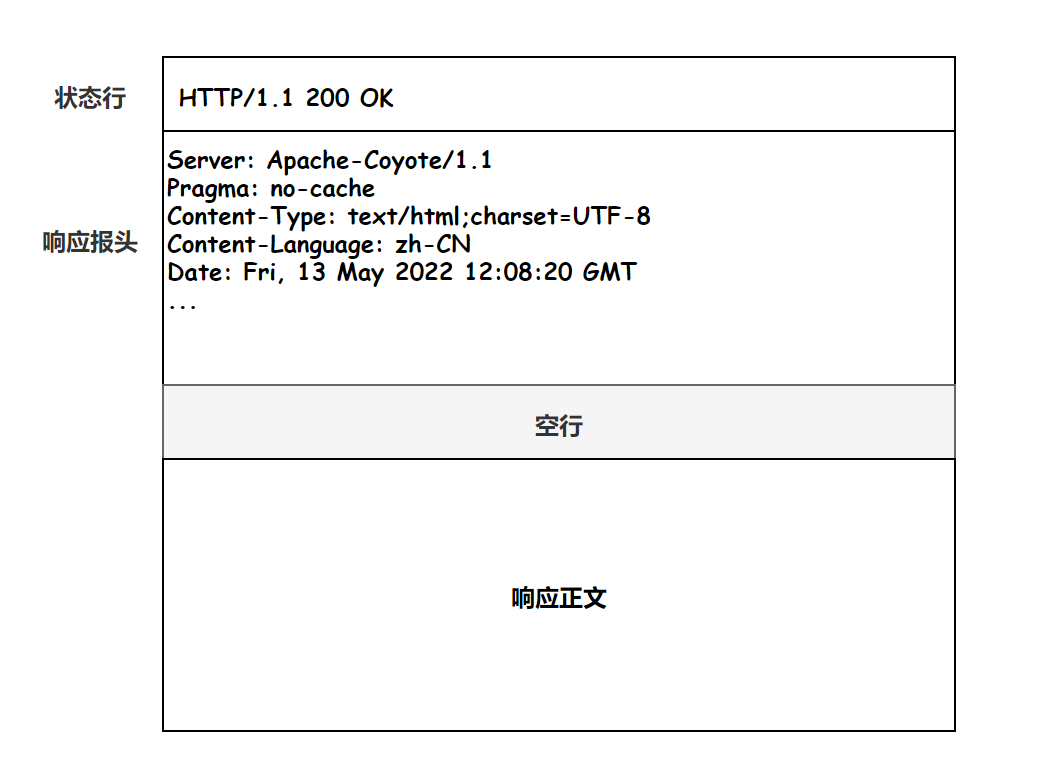
The status line is used to describe the return status of the server, and it consists of 3 parts:
- HTTP version number, such as HTTP/1.1;
- Status code, such as 200;
- Status description information, such as OK;
The common status codes are as follows:
- 200: return success;
- 301: permanent redirection;
- 302: Temporary redirection;
- 404: page not found;
- 500: Server program error.
The response body is all the data returned to the client.
服务器端拿到了客户端的请求参数之后,会进行相应的业务处理,处理完成之后,再将处理的结果返回给客户端。返回的流程和发送的流程类似,先将结果封装成 HTTP 数据包,HTTP 数据包可分为以下 4 部分:
- 状态行
- 响应报头
- 空行
- 响应正文
它的基本格式如下:

The status line is used to describe the return status of the server, and it consists of 3 parts:
- HTTP version number, such as HTTP/1.1;
- Status code, such as 200;
- Status description information, such as OK;
The common status codes are as follows:
- 200: return success;
- 301: permanent redirection;
- 302: Temporary redirection;
- 404: page not found;
- 500: Server program error.
The response body is all the data returned to the client.
7. Disconnect the TCP connection (4 waves)
After a request and a response, the "communication" between the client and the server is over, and the process of disconnecting the TCP connection can be performed at this time, which requires 4 waved hands:
- _Client_: Let’s break up;
- _Server_Side_: Okay, let me get it ready.
- _Server Side_: I'm ready, let's break up.
- _client_: OK.
After going through the above process, the TCP connection is disconnected.
After a request and a response, the "communication" between the client and the server is over, and the process of disconnecting the TCP connection can be performed at this time, which requires 4 waved hands:
- _Client_: Let’s break up;
- _Server_Side_: Okay, let me get it ready.
- _Server Side_: I'm ready, let's break up.
- _client_: OK.
After going through the above process, the TCP connection is disconnected.
8. The browser renders and displays the result
After the TCP interaction, the client also gets the data returned by the server, and then uses the browser's own execution engine to display the final result to the user, and the entire execution process is over.
After the TCP interaction, the client also gets the data returned by the server, and then uses the browser's own execution engine to display the final result to the user, and the entire execution process is over.