How does DNS affect your surfing speed?

How does DNS affect your surfing speed?
This article introduces DNS-related knowledge in detail, including the working principle of DNS, how to improve the speed of domain name resolution, and DNS records and messages.
1. Domain name and domain name server
In everyday surfing, people prefer to type a website's domain name into their browser rather than an IP address for memorable reasons. For example, if you want to visit Baidu, you will enter www.baidu.com instead of 202.108.22.5 (or other IP of Baidu website).
However, the identification identified in computer network communication is not a domain name, but an IP address, because it can provide the location information of the host in the Internet, and it is of fixed length, which is easier for devices such as routers to handle.
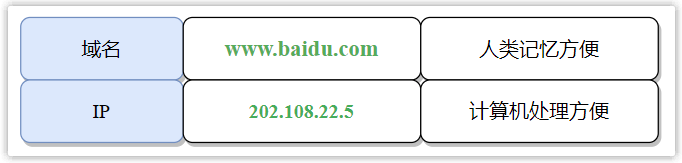
In order to compromise the different preferences of humans and computers, DNS (Domain Name System, Domain Name System) appeared, and its main task is to find out the corresponding IP address based on the domain name.
Let's first introduce domain names and domain name servers, and then introduce how DNS works.
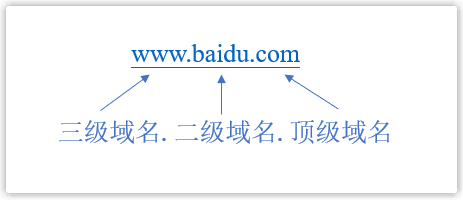
The domain name is composed of several English character strings (case-insensitive), and the character strings are separated and connected by dots ".". The closer to the right, the higher the domain name level.
For example, Baidu's domain name is www.baidu.com, where com is the top-level domain name (first-level domain name), baidu is the second-level domain name, and www is the third-level domain name.
The domain name server (also called DNS server) is responsible for storing the mapping relationship between domain names and IP addresses. When we need to obtain the IP address corresponding to a domain name, we only need to query from the domain name server.

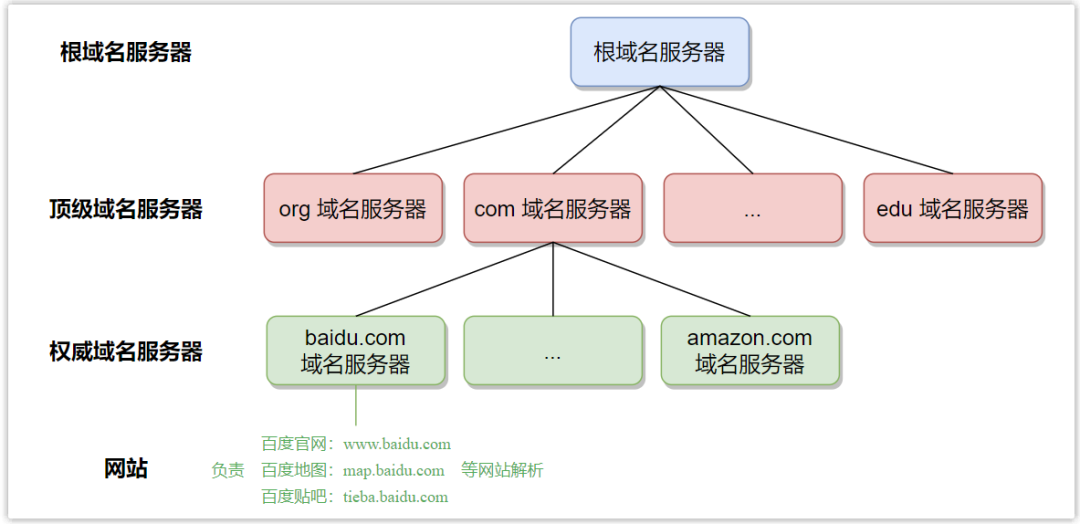
Since there are so many domain names, if they are all stored in one domain name server, not only will the query speed be slow, the server will be under heavy pressure, and it will be difficult to guarantee the reliability of the service. Therefore, DNS adopts a distributed design scheme, and a large number of domain name servers are organized hierarchically and distributed all over the world.
In general, domain name servers can be divided into the following four categories:
- Root domain name server: the highest-level domain name server, there are 13 root domain name servers on the Internet (named in sequence from English letters A to M, the format is [a~m].root-servers.net), each root domain name server Everyone knows the IP addresses of all top-level domain name servers, such as the IP address of the top-level domain name server responsible for com domains.
- Top-level domain name server: For each top-level domain name, such as com, org, edu, etc., there is a corresponding top-level domain name server. The top-level domain name server knows the IP addresses of all the authoritative domain name servers it manages. For example, the top-level domain name server responsible for the com domain knows the IP address of the authoritative domain name server responsible for the baidu.com domain.
- Authoritative domain name server: A website needs to register its domain name and IP address to the corresponding authoritative domain name server. For example, the domain name and IP address of the website www.baidu.com are stored in the authoritative domain name server responsible for the baidu.com domain.
- 本地域名服务器:本地域名服务器不属于上述域名服务器的层次结构,但是它对域名系统非常重要。每个 ISP(如一个大学、一个公司)都有一个本地域名服务器(也叫默认域名服务器)。具体在下一节中介绍。
2. 域名解析流程
知道了域名和域名服务器的基础知识后,我们来了解一下域名解析的具体流程,以输入百度域名为例,看看我们的主机是如何得到 www.baidu.com 的 IP 地址的。
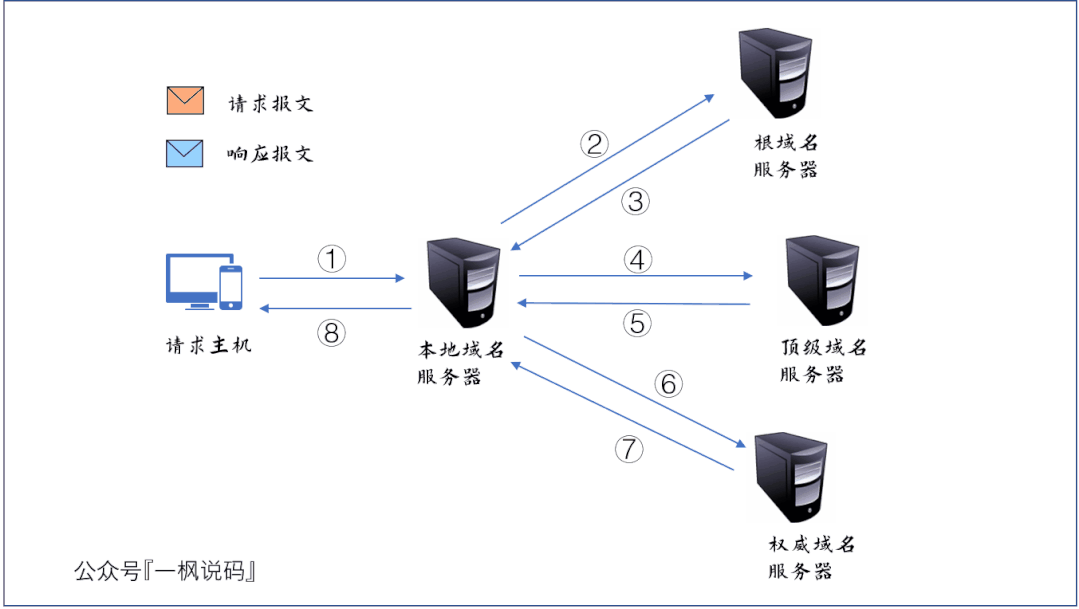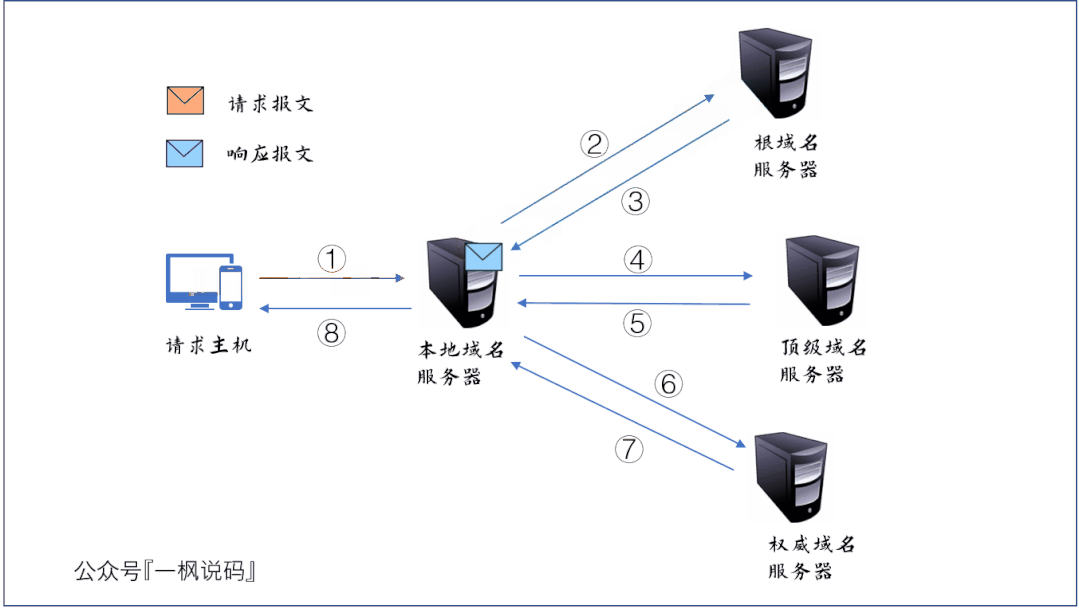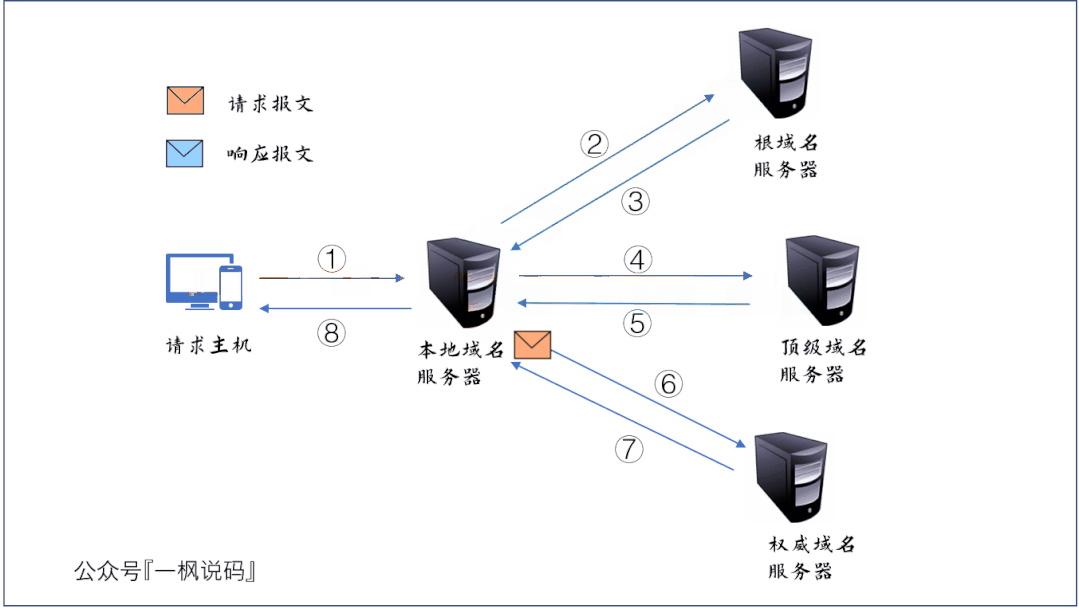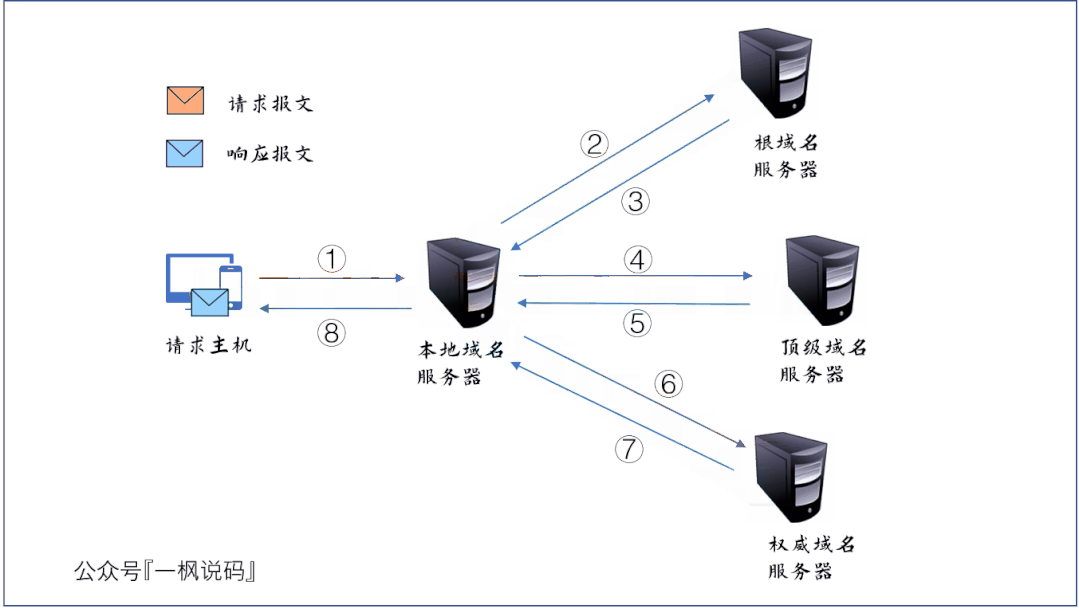
- 请求主机向本地域名服务器发送 DNS 查询报文,询问 www.baidu.com 的 IP 地址是什么;
- 本地域名服务器转发此查询报文到根域名服务器;
- 根域名服务器发现要查询的顶级域名为 com,于是向本地域名服务器发送响应报文,报文中封装了负责 com 域的顶级域名服务器的 IP 地址列表;
- 本地域名服务器收到根域名服务器响应的报文后,选择其中一个顶级域名服务器的 IP 地址,并向其发送查询报文;
- 顶级域名服务器发现要查询的二级域名为 baidu,于是向本地域名服务器发送响应报文,报文中封装了负责baidu.com 域的权威域名服务器的 IP 地址列表;
- 本地域名服务器收到顶级域名服务器响应的报文后,选择其中一个权威域名服务器的 IP 地址,并向其发送查询报文;
- 权威域名服务器通过查询数据库,找到 www.baidau.com 的 IP 地址,并将此信息封装为一个响应报文,发送给本地域名服务器;
- 本地域名服务器将响应报文发送给原请求主机。我们的主机就知道了百度的 IP 地址,DNS 查询过程结束。
在此过程中,请求主机与本地域名服务器之间的交互称为递归查询,而本地域名服务器与域名服务器层次结构中相关服务器的交互称为迭代查询。
请求主机是如何知道本地域名服务器的 IP 地址的?
当用户插上网线或者连上 WIFI 后,电脑会通过 DHCP 协议分配一个 IP 地址,与此同时,也会获取到本地域名服务器的 IP 地址!
本地域名服务器是如何知道根域名服务器的 IP 地址的?
因特网上一共有 13 个根域名服务器,它们的 IP 地址是固定不变的,因此被集成在了操作系统中,每台电脑都知道!
为了解析出百度域名的 IP 地址,一共发送了 8 份 DNS 报文。用户本来只是想和百度的服务器进行交互,却耗费了大量的时间进行域名解析,如果每次都这样搞,岂不是得慢死?因此就需要有一些提升域名解析速度的方式。
3. 提升域名解析速度
(1)TCP or UDP
我们都知道,TCP 相较于 UDP 更可靠,但是速度更慢。
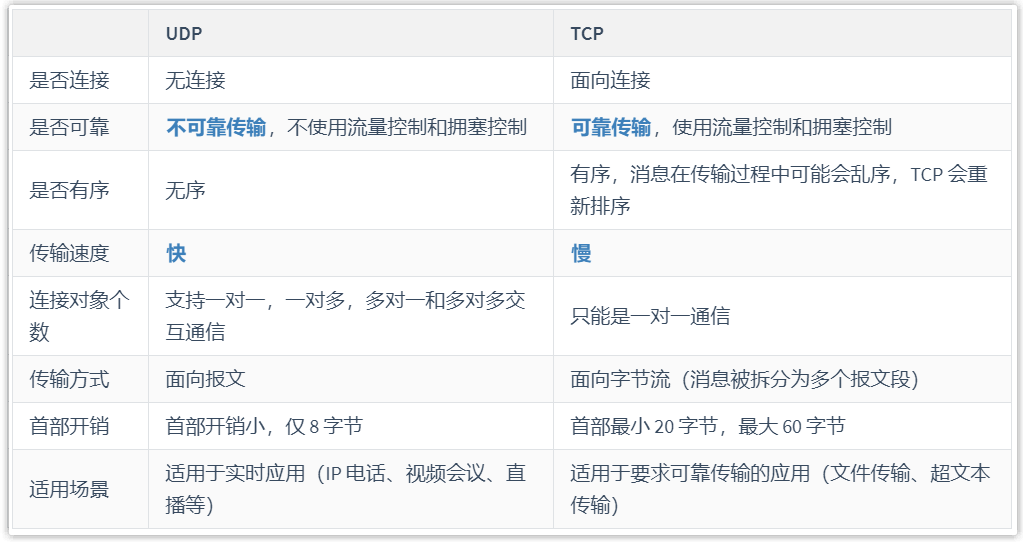
DNS 应该采用哪个传输层协议呢?
- 如果采用 TCP 协议,不仅需要三次握手建立连接,而且需要进行拥塞控制等,那么域名解析速度将慢成龟速,不利于用户体验。
- 如果采用 UDP 协议,万一丢包了怎么办?如果解析不出来 IP,怎么访问目标网站?不利于用户体验。
实际上,DNS 主要使用 UDP,在特殊情况下,也会使用 TCP,端口号都是 53。
一般情况下,DNS 报文都比较小,只需要一个包就能承载所有信息。既然只有一个包,就无需考虑哪个包未送达,直接重发一个包即可,因此无需使用 TCP 那样复杂的协议,直接使用 UDP 协议,DNS 协议自己处理超时和重传问题,以提供可靠性服务。
当然有的时候 DNS 报文比较大,比如响应报文中可能一个域名包含有很多 IP 记录。当服务器响应时,会将报文中的 TC 标志位设置为 1,表示响应长度超过了 512 字节,此报文仅仅返回前 512 字节。当我们的主机收到响应后,就会使用 TCP 协议重发原来的查询请求,以获取完整报文。
此外,为了防止本地域名服务器(主域名服务器)宕机而导致无法对域名进行解析,本机还需要设置一个辅助域名服务器。当主域名服务器宕机后,由辅助域名服务器继续提供域名解析的服务。辅助域名服务器会定时(通常是每隔 3小时)向主服务器发送查询请求以实现同步,此时传输数据较多,因而使用 TCP 协议。
(2)DNS 缓存
即使采用 UDP 协议,但是如果每次都需要从根服务器开始一层一层的查询,仍然很慢,且处于层级结构中的域名服务器将会接收到大量的请求,处理速度进一步降低!
为了提升域名解析速度并减轻域名服务器的压力,DNS 广泛使用了缓存技术。
当用户访问了某个网站后,本地域名服务器会将解析出的域名和 IP 地址的映射关系缓存一定时间。在缓存过期前,用户再访问相同网站时,本地域名服务器就可以直接返回查询结果,而无需再去询问根域名服务器、顶级域名服务器等,这样就能大大减少传输的 DNS 报文数量!
实际上,不仅在本地域名服务器中设置了高度缓存,用户主机也有缓存。对于 Windows 电脑,可以通过命令ipconfig/displaydns查询当前 DNS 缓存,比如当我访问了百度后,本机就会缓存以下信息:
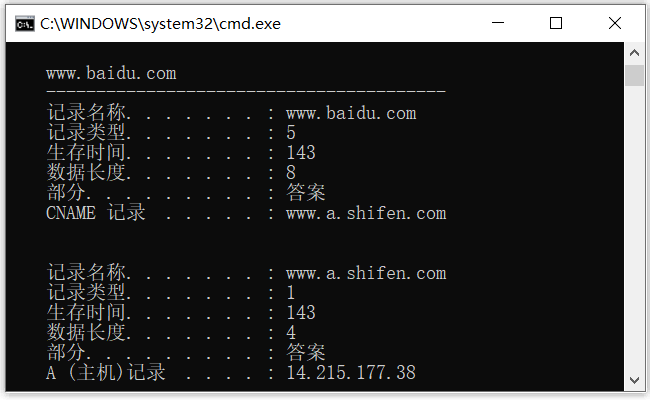
缓存虽然提升了 DNS 解析速度,但并不能保证一致性,因为一个网站的域名和 IP 地址的映射关系并不是永久不变的,可能缓存的解析结果已失效,因而 DNS 缓存时间不能设置太大!
Windows 电脑也可以通过命令ipconfig/flushdns清空本机缓存。
(3)切换本地域名服务器
前面提到,在进行域名解析时,主机会向本地域名服务器发起递归查询,如果本地域名服务器的性能较差,或者未正确配置缓存,那么我们上网的速度将会变得非常慢,因此选择一个好的本地域名服务器将有助于提升冲浪速度!
默认情况下,本机在联网时会通过 DHCP 协议自动获得一个 DNS 服务器地址,那么如果此服务器性能不好,该如何更换呢?
以 Windows 为例,可以通过控制面板—>网络和 Internet—>网络连接—>Internet 协议版本4(TCP/IPv4)修改本地域名服务器的 IP 地址。
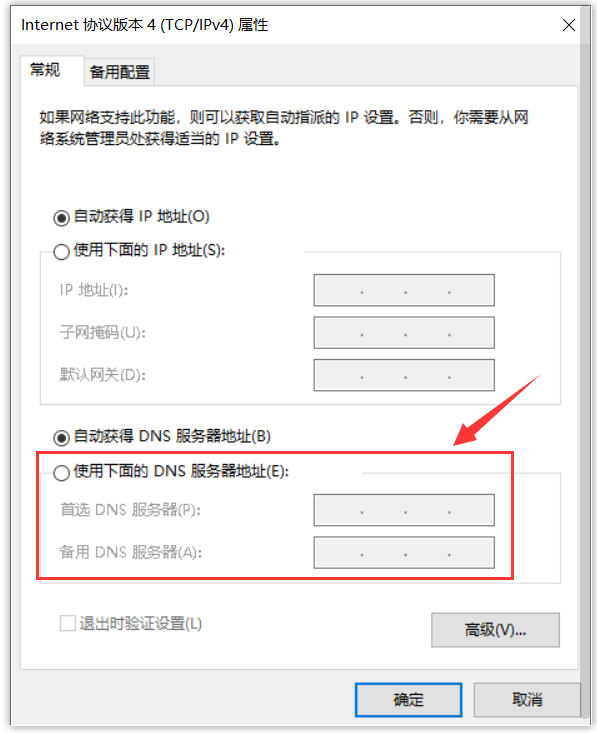
互联网上常见的公共 DNS 服务器的 IP 地址如下:
首选 DNS 服务器地址 | 备用 DNS 服务器地址 | |
阿里 | 223.5.5.5 | 223.6.6.6 |
腾讯 | 119.29.29.29 | 182.254.116.116 |
百度 | 180.76.76.76 | 114.114.114.114 |
谷歌 | 8.8.8.8 | 8.8.4.4 |
114DNS | 114.114.114.114 | 114.114.115.115 |
一般情况下,自动获取的本地域名服务器与主机位于同一个子网中,速度都挺快的。但是如果在上网过程中,发现打开网页的速度很慢,也可以尝试使用上面的公共 DNS 服务器,说不定速度会有所改善。
4. DNS 记录和报文
实际上,域名服务器中保存并不仅仅是域名和 IP 地址,而是保存了一个资源记录(Resource Record,RR)。
一个资源记录包含四部分内容,分别是 Name,Value,Type,TTL。
TTL 指的是记录的生存时间,以秒为单位,它决定了缓存此记录的过期时间。
Name 和 Value 的含义随着 Type 的不同而不同,举几个常见例子:
- 当 Type = A 时(A 是 Address 缩写,也可用编号 1 表示),Name 表示域名,Value 表示对应的 IP 地址,如(www.example.com,93.184.216.34,A,86400)。
- 当 Type = NS 时(NS 是 Name Server 缩写,也可用编号 2 表示),Name 表示一个域,Value 为负责该域解析的域名服务器的域名,如(baidu.com,ns1.baidu.com,NS,172800),此记录用于沿着层级结构查询链来路由 DNS 查询。
如果一台域名服务器是用于某特定域名的权威域名服务器,那么其将会有一条包含该域名的 A 记录。
如果一台域名服务器不是用于某特定域名的权威域名服务器,那么其将包含一条 NS 记录,该记录用来指定该域名由哪个域名服务器来进行解析;除此之外,它还将包含一条 A 记录,该记录提供了在 NS 记录中 Value 字段中的域名服务器的 IP 地址。

接下来介绍一下 DNS 报文的具体内容。DNS 报文分为两类:查询报文和回答报文,二者有着相同的格式,如下图所示:
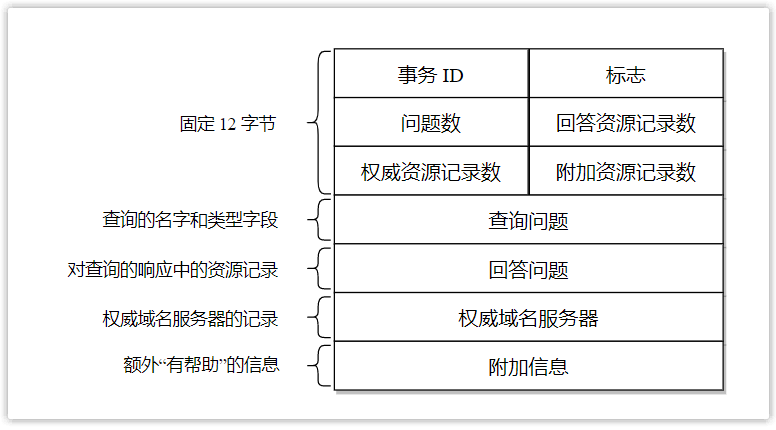
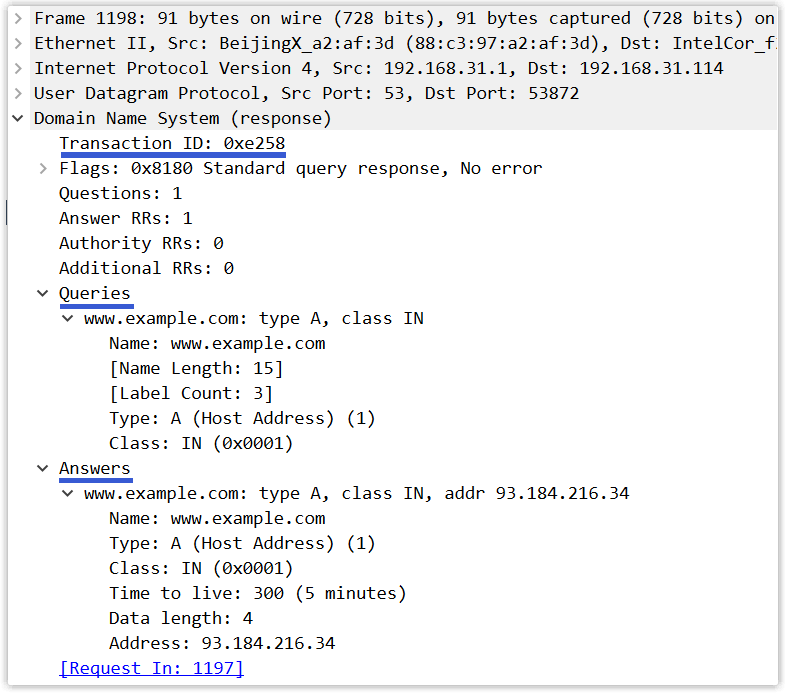
- 事务 ID:用于标识 DNS 查询的标识符。查询报文和其对应的回答报文有着相同的事务 ID,因此通过它可以区分 DNS 回答报文是对哪个请求进行响应的。
- 标志:此字段中含有若干标志,比如有一个『QR』标志位用于指出此报文是查询报文(0)还是回答报文(1),再比如有一个『TC』标志位用于指出此报文长度是否大于 512 字节。
- 问题数:对应于下面查询问题的数量(支持同时查询多个域名,通常为一个)。
- 回答资源记录数:对应于下面回答问题相关资源记录的数量(一个域名可能有多个 IP 对应,那么将会有多个回答记录)。
- 权威资源记录数:对应于下面权威域名服务器相关资源记录的数量。
- 附加资源记录数:对应于下面附加信息相关资源记录的数量。
- 查询问题:此区域为查询内容,包含查询域名和查询类型(如 www.example.com,A)。
- 回答问题:此区域为查询结果,包含一到多条资源记录(如 www.example.com,93.184.216.34, A,300)。
- 权威域名服务器:此区域为其他权威域名服务器的记录,即含有指向权威域名服务器的资源记录,用以继续解析过程。(如 baidu.com,ns1.baidu.com,NS,172800)。
- 附加信息:此区域为其他有帮助的信息,比如提供权威域名服务器所对应的 IP 地址。
最后,使用 Wireshark 抓一个 DNS 查询报文和回答报文:
查询报文:
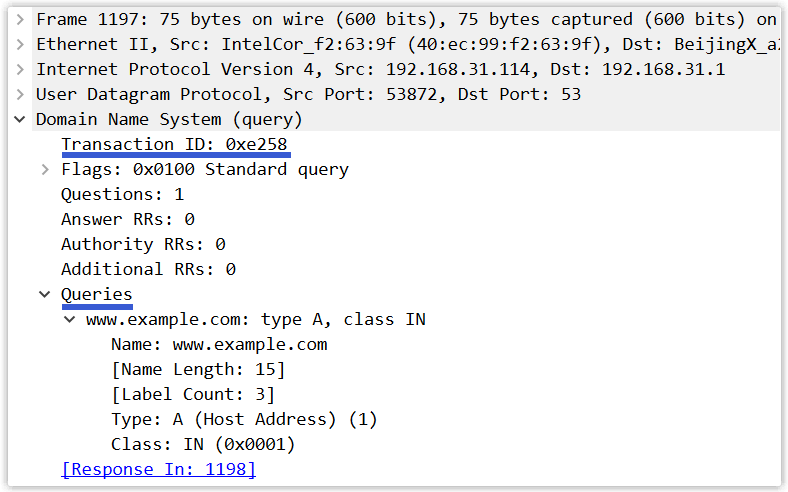
回答报文:
本文转载自微信公众号「 一枫说码」,作者「一枫说码」,可以通过以下二维码关注。

转载本文请联系「 一枫说码」公众号。