VoNR vs. ViNR, are you really differentiated?

In the sea of stars of 5G, there are two technical terms that are quietly changing our call experience - VoNR (Voice over New Radio) and ViNR (Video over New Radio).
VoNR and ViNR represent voice calls and video calls in the 5G era, respectively. They greatly enrich our daily lives and further enhance our calling experience.
Have you ever wondered how phone calls will be made in the future? Is it the seamless handover of VoNR, or the efficient innovation of ViNR? Let's demystify them together and explore the new trend of communication!
 Image
Image
VoNR: A new chapter in 5G voice calling
Concept demystified
VoNR, i.e., the direct processing of voice calls over the 5G New Radio (NR) network, without the need to fall back to the 4G network.
How it works
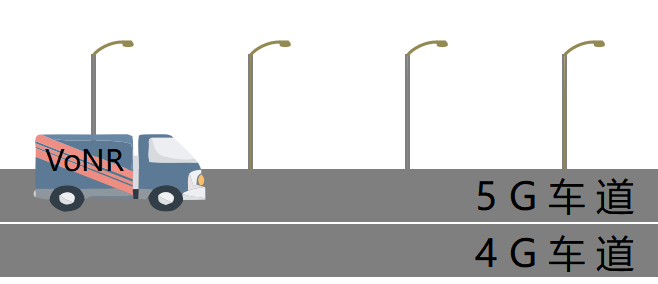
Driving on the highway, VoNR allows your voice calls to drive on the 5G lane all the way, avoiding the delay caused by "lane change".
 Image
Image
History
- In the 2G/3G era, CS (circuit switching) technology is used for voice services.
☛ Require the mobile phone to establish a line that monopolizes resources before the call, and dismantle it after the call ends.
☛ It has the disadvantages of low efficiency, complex networking, and resource consumption.
- Initial 4G: CSFB (Circuit Switched Fallback) is used. When the mobile phone initiates a voice call in the 4G network, it will automatically fall back to the 2G/3G network, use CS technology to complete the voice call, and return to the 4G network after the call ends.
- 4G era: VoLTE is used.
☛ Implement IP-based voice services on 4G networks.
☛ High-resolution voice codec technology using AMR-WB. Provide clearer and wider voice frequencies to improve transmission efficiency and voice quality.
- 5G Era: Using VoNR.
☛ Voice services implemented directly on 5G pure IP networks.
☛ A more efficient architecture and technology is used to shorten the call setup time, and the voice quality and voice coding rate are further improved.
merit
- In terms of efficiency: The call setup time is shorter, improving network efficiency, reducing network O&M costs, reusing high-quality low-frequency resources, and improving the security of voice calls.
- In terms of application: support 5G voice and 5G data service concurrency: you can make calls while high-speed 5G Internet access; It also supports new 5G applications, such as AR/VR, holographic, etc., which are inseparable from real-time high-definition audio and video calls.
ViNR: A new experience for 5G video calls
Basic Understanding:
ViNR, which provides high-quality video calls over 5G new wireless (NR) networks.
History
- 4G era: ViLTE is an extension of VoLTE.
- 5G era: ViNR is used on 5G networks.
merit
- In terms of efficiency: improve network efficiency.
- In terms of application: support new 5G applications: such as AR/VR, holographic, etc., are inseparable from real-time high-definition audio and video calls.
What is the difference between VoNR and ViNR?
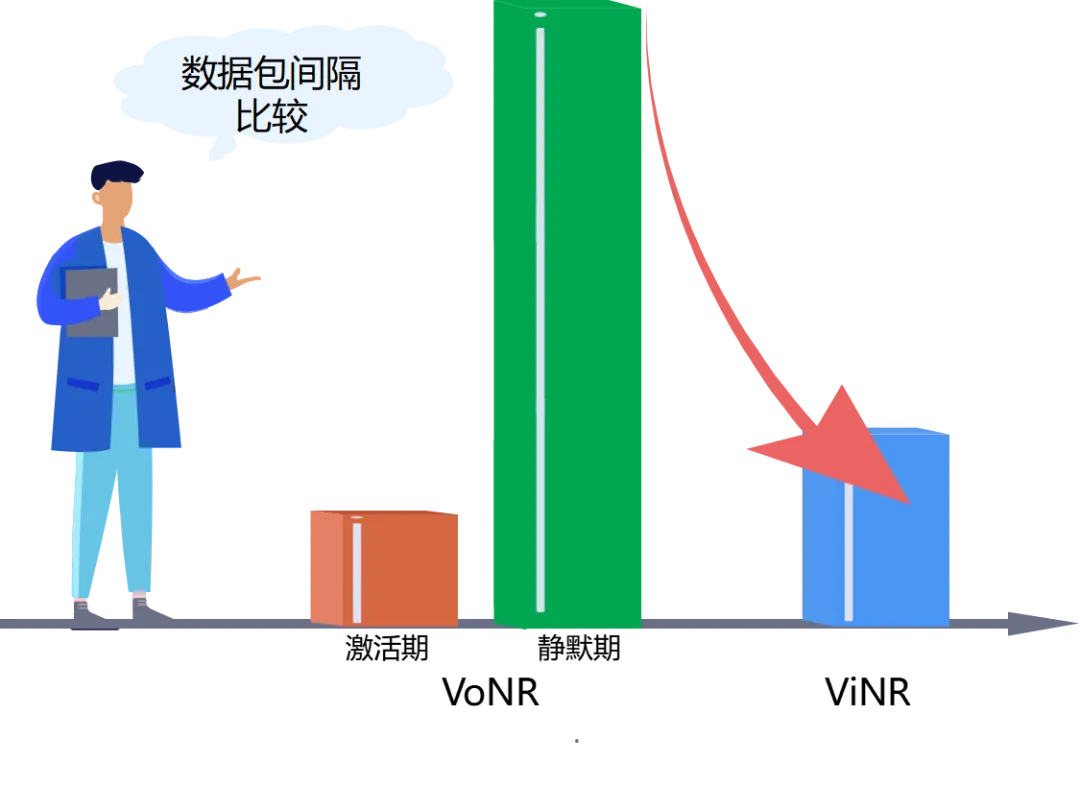
Packet interval
- VoNR: The interval between adjacent RTP packets during the activation period of voice services is 20 ms, and the quiescent period is fixed at 160 ms.
- ViNR: The interval between video call packets is distributed in the range of 0ms~40ms. (VoNR has a higher packet interval than ViNR!) )
 Image
Image
Packet size
- VoNR: The length of the AMR-WB23.85RTP packet is 73 bytes during activation and 19 bytes during quiescent period.
- ViNR: The length of RTP packets for video calls is 1,153 bytes (about 70%). (ViNR packet size is much higher than VoNR!) )
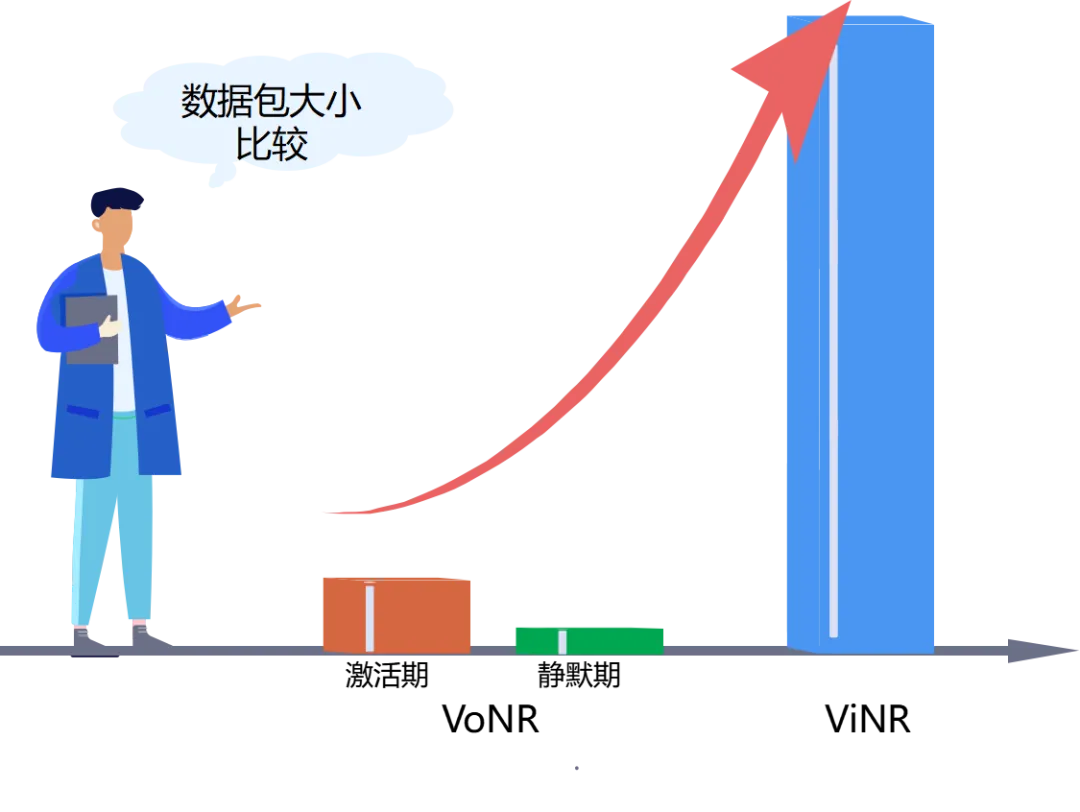 Image
Image
Bandwidth requirements
- VoNR:
☛ RTP packets are fixed at a fixed interval of 20ms, and 50 RTP packets per second. Each voice packet is about 86 bytes (byte aligned, 688 bits).
☛ So: VoNR voice rate = 688 × 50 / 1024 ≈ 34.4 kbps
- ViNR:
☛ Each pixel of the video is 2 bytes, that is, 16 bits (YUV samples according to 4:2:2); The amount of data per frame = resolution × 16bit; The frame rate is 30, 30 frames per second.
☛ The compression ratio, the mainstream is H.264 video coding, the compression ratio is roughly 1/150, that is, 150M data can actually be transmitted using 1M data.
☛ So: ViNR video rate = resolution × 16 × 30 × compression / 1024 kbps
☛ Take a resolution of 720P as an example: ViNR video rate = 720 × 1280 × 16 × 30 × 1 / 150 / 1024 = 2880 kbps (ViNR requires much more bandwidth than VoNR!). )
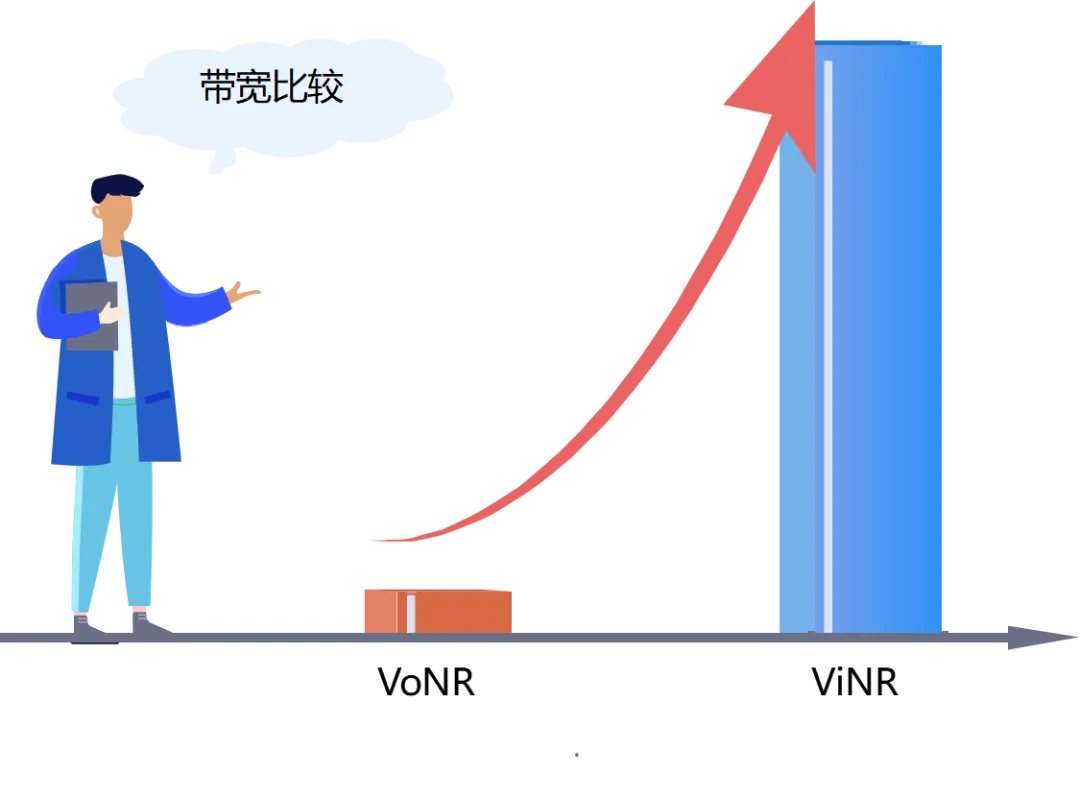 Image
Image
summary
This article takes you through the style of VoNR and ViNR, and understands the concepts and differences between the two, both of which are important parts of communication technology in the 5G era.
At present, the use of voice calls in daily life is still the mainstream, and video calls are still active among some users as an auxiliary means of calling. VoNR and ViNR allow us to enjoy a smarter and more convenient communication life.
In the future, with the popularization and improvement of communication networks, let us wait and see how high the development of voice call and video call technology will be.