Application of SRv6 technology in home network

Introduction to Labs
In order to adapt to the development of emerging digital home services such as cloud games, high-definition video calls, and AR/VR, China Mobile's home network capabilities need to provide mutually isolated and service quality-guaranteed slicing networks based on business characteristics to provide users with a good business experience. Based on the computing power network infrastructure, China Mobile builds a home computing power network capability layer focusing on "lightweight equipment + containerized plug-ins + deterministic network" to support home business applications and achieve lightweight home terminals and home business deployment Flexibility and high-quality home broadband network.
1. SRv6 concept
Segment Routing (SR) is a source routing technology that assigns Segment IDs to each node or link. The head node combines these Segment IDs to form a Segment sequence (Segment List), which directs packets to be forwarded according to the Segment sequence. Implement network programming capabilities.
Currently, Segment Routing technology mainly has two implementations: SR-MPLS and SRv6. Among them, SR-MPLS is a Segment Routing implementation based on the MPLS data plane, and its SID is the MPLS label (Label); SRv6 (Segment Routing over IPv6, segment routing based on IPv6) is a Segment Routing implementation based on the IPv6 data plane, and its SID is an IPv6 address.
SRv6 combines the source routing advantages of Segment Routing with all the characteristics of IPv6, and has multiple network programming spaces, conforming to the SDN (Software Defined Network) idea.
2. SRv6 implementation principle
2.1 SRH package
SRv6 implements segment routing by inserting a routing extension header SRH (Segment Routing Header) into the IPv6 packet header to carry segment transmission information. The SRH contains a Segment List represented by a SID list with IPv6 address characteristics. The destination address of the message will be updated segment by segment based on the Segment List, thereby completing segment-by-segment forwarding.
The message format of SRv6 is shown in Figure 1.
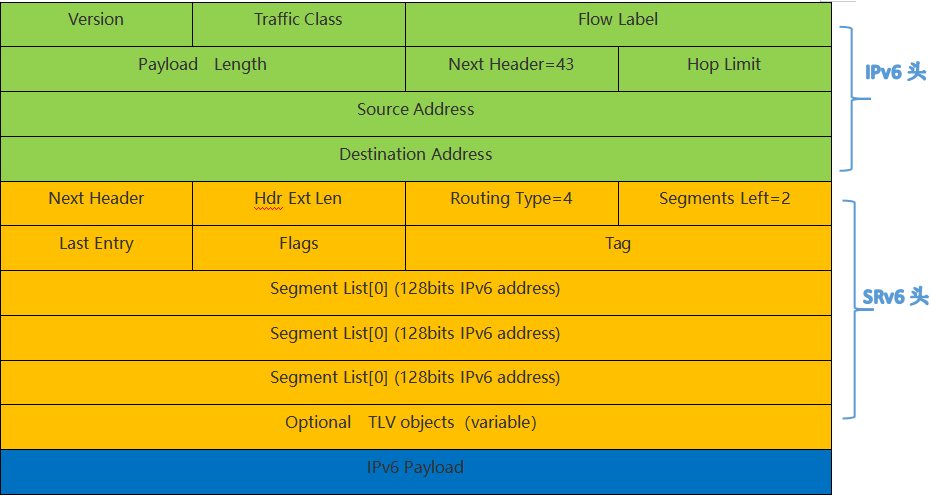
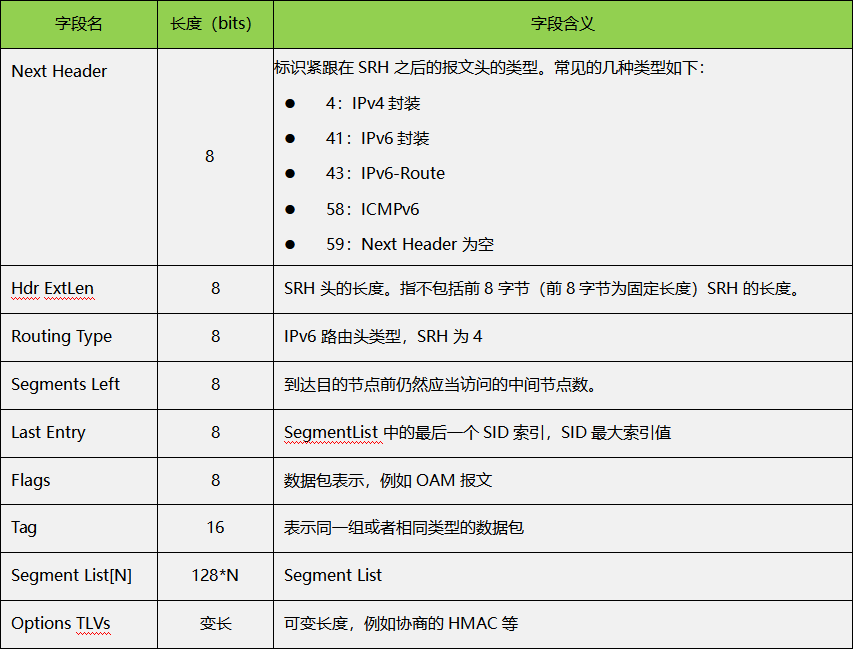
The fields included in SRH are explained as follows:
2.2 SID definition
The routable 128-bit SID is usually divided into three parts: Locator, Function and Arguments. The respective lengths of the three parts are flexibly defined according to actual needs.
- Locator is a network location identifier assigned to a network node and is used for routing and forwarding data packets.
- Function is used to express the forwarding behavior to be performed by the SID. In SRv6 network programming, different forwarding behaviors are expressed by different Functions.
- Arguments are optional parameters that can carry parameters required for instruction execution. For example, user ID, application type, quality requirements and any other relevant information.

2.3 Segment type
SRH directly uses IPv6 addresses to represent segments, which can flexibly support many types. Different types of segments can be used together to complete specific functions. Generally speaking, Segments can be divided into two categories: Segments representing path information; Segments representing business information.
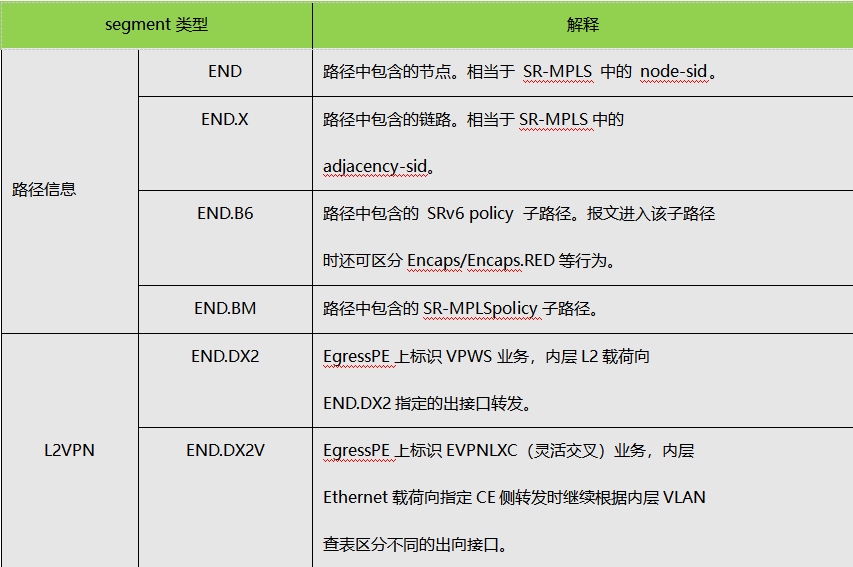
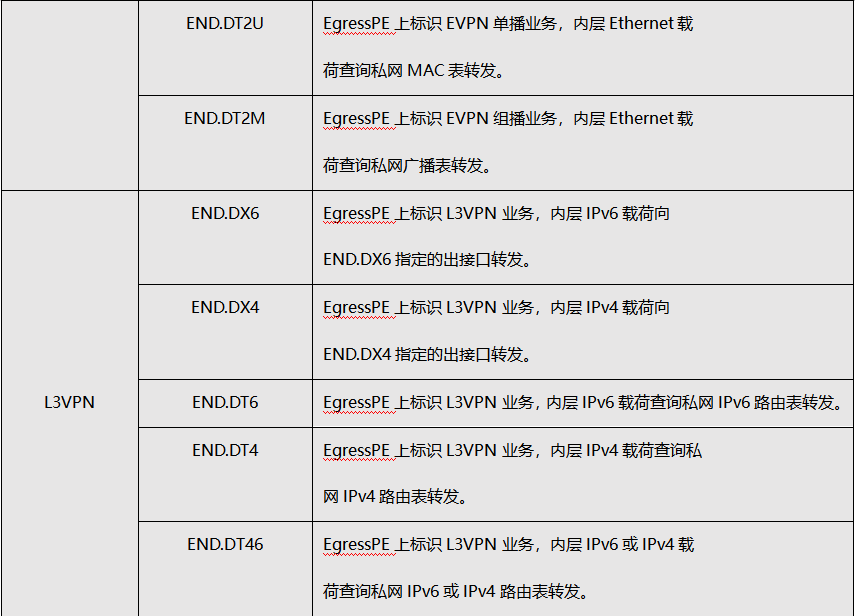
3. SRv6 forwarding process
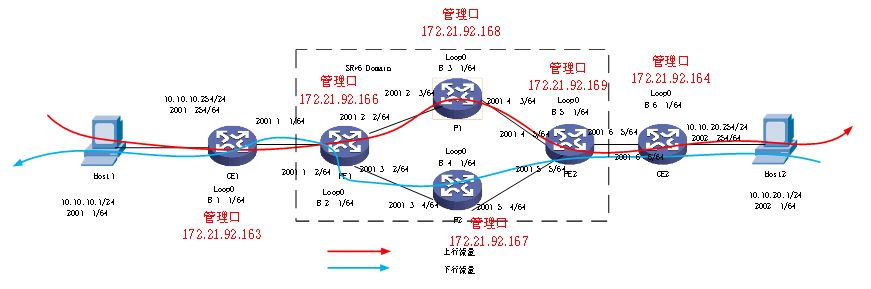
P1 and P2 simulate backbone network equipment, PE1 and PE2 simulate backbone network edge equipment, and CE1 and CE2 customer access devices Host1 and Host2 act as clients and servers. During the forwarding process, changes in destination IP, Segment list encapsulation, SL, Last Entry and other fields can be seen in the pcap packet.
3.1 Client accesses the server upstream path
Host1->CE1->PE1->P1->CE2->Host2
CE1:
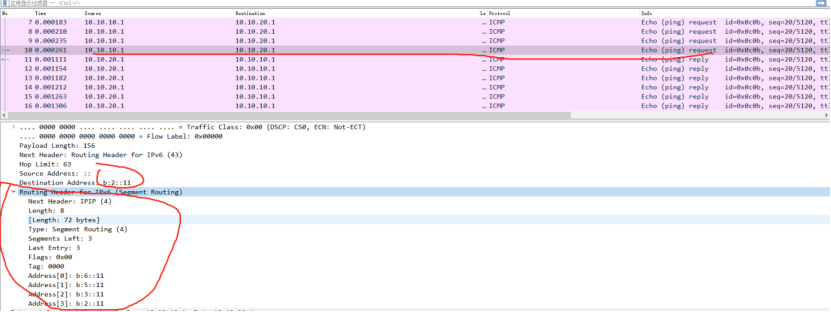 picture
picture
PE1:
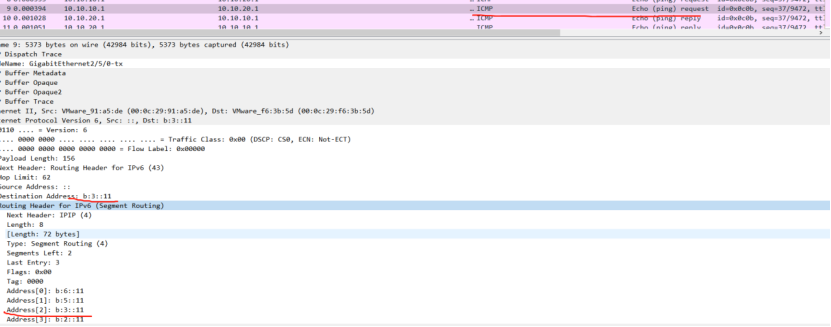 picture
picture
Q1:
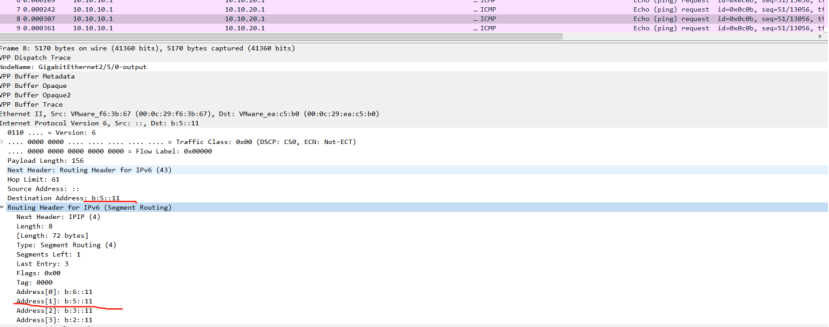 picture
picture
PE2:
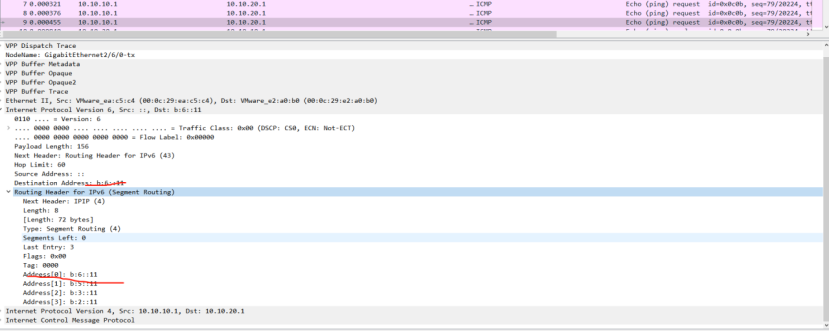 picture
picture
CE2:
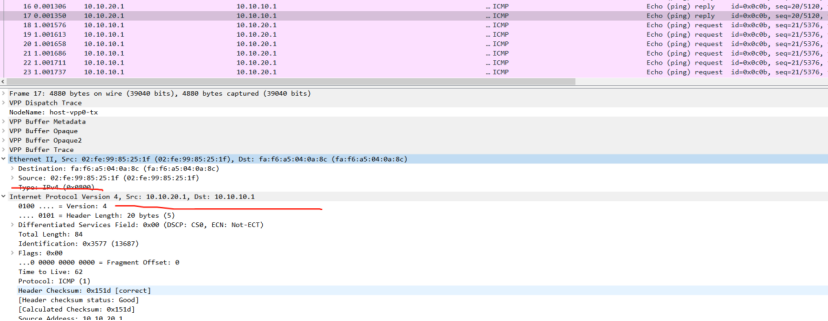 picture
picture
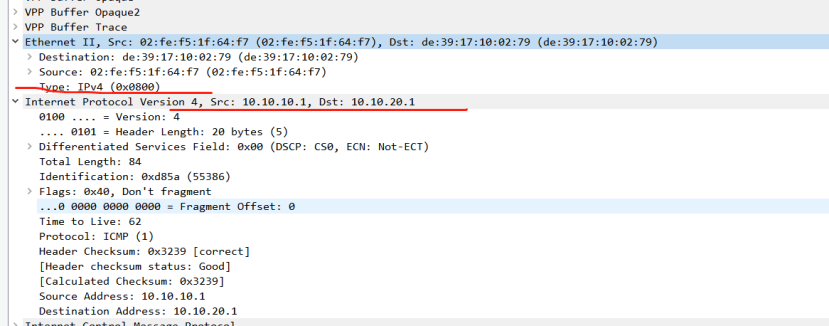 picture
picture
3.2 Client accesses the server downstream path
Host2>CE2->PE2->P2->CE1->Host1
CE2:
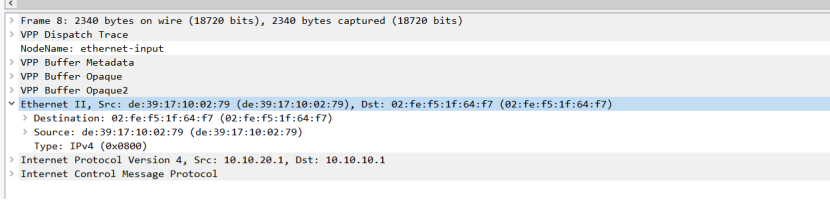 picture
picture
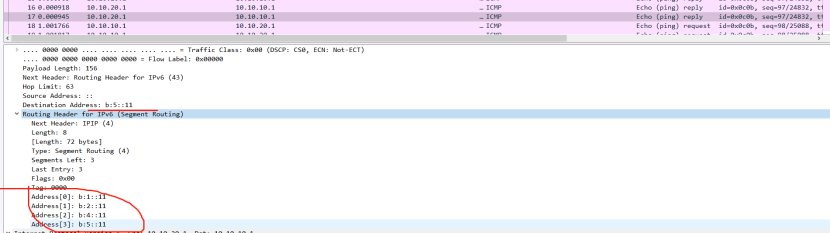 picture
picture
PE2:
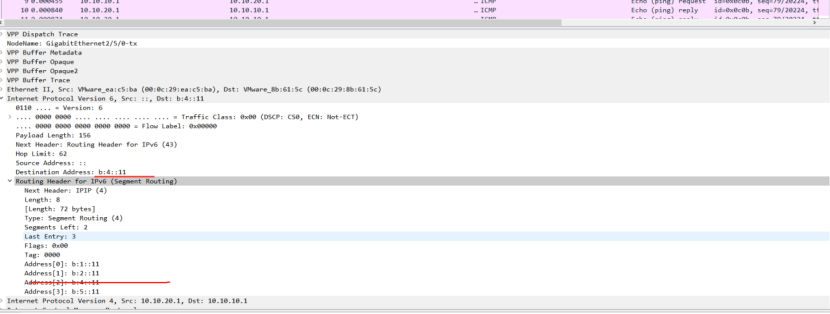 picture
picture
P2:
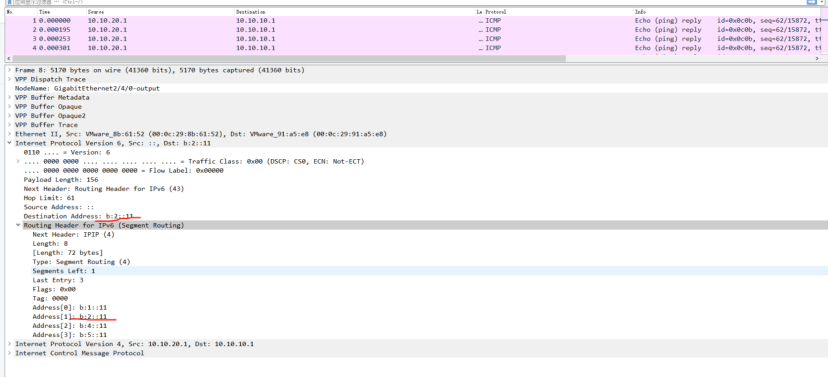 picture
picture
PE1:
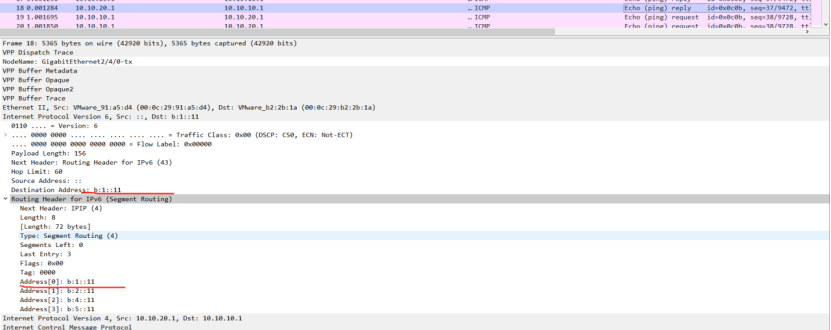 picture
picture
CE1:
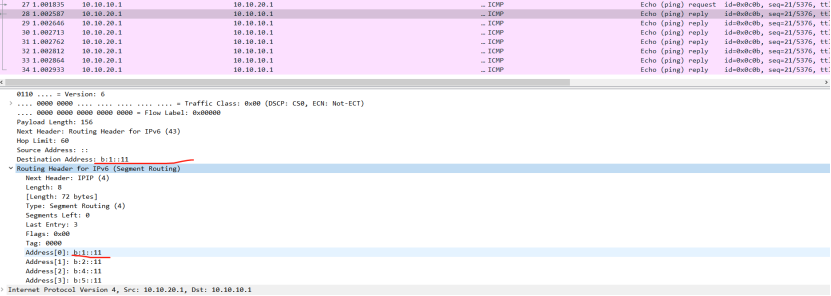 picture
picture
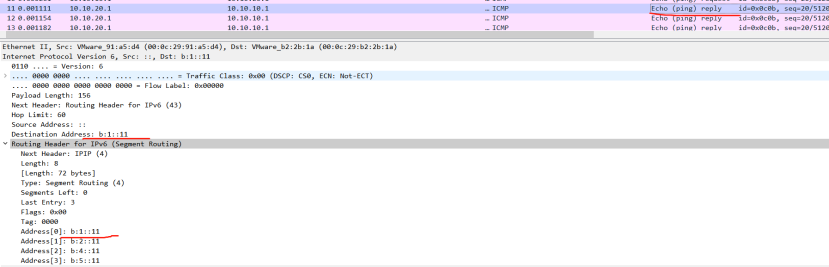 picture
picture
4. Advantages of SRv6
- Simple deployment: only need to deploy SRv6 policies end-to-end, without operating intermediate transmission nodes.
- Intelligent: By interacting with the SDN controller through the MP-BGP protocol, the entire network can be automatically scheduled intelligently.
- Programmable: Segments can be programmed according to business needs.
- Aware applications: Bring application information into the network so that the network can sense application types and needs in real time to provide intelligent and customized services.
- Multiple tunnel capabilities: can support SRv6 BE, L2VPN, L3VPN
5. SRv6 application scenarios
5.1 Main application scenarios of SRv6
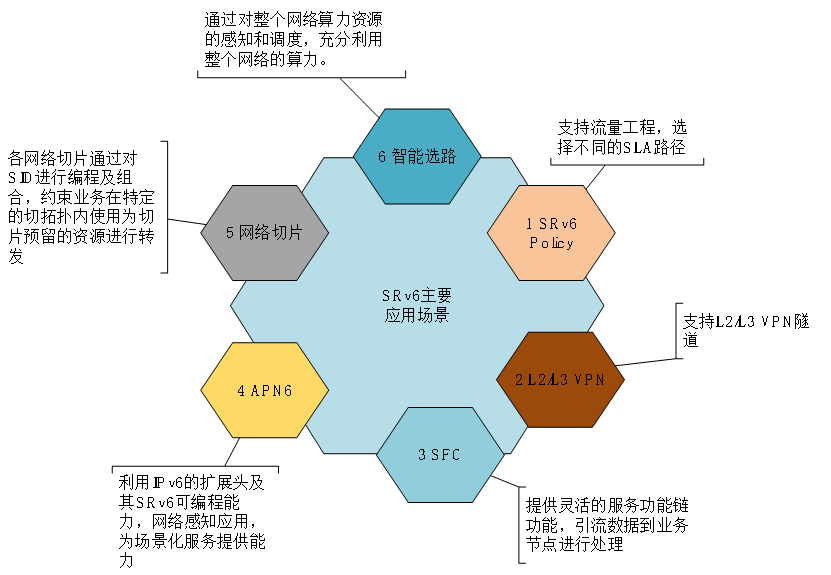
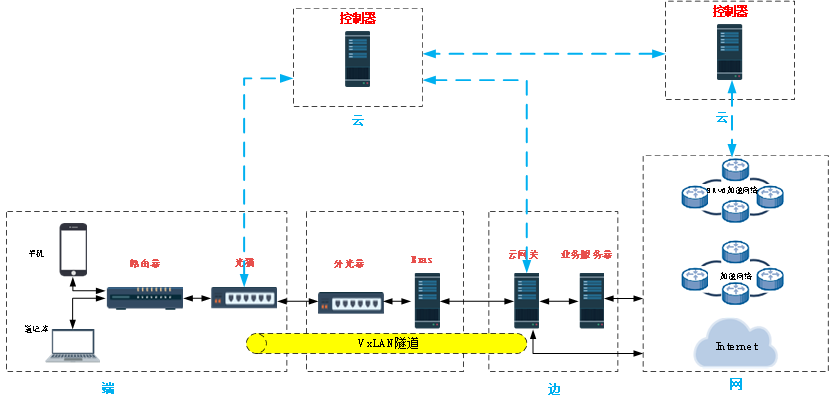
5.2 SRv6 home application scenario
The traffic is APN6 encapsulated through the cloud gateway, and the customized service traffic is imported into the SRv6 acceleration network through the traffic diversion policy to realize intelligent scheduling of home broadband services.
6. Summary and Outlook
IPv6 has always been an issue of great concern to various countries. It is also the basis for the development of the next generation of the Internet. It is also an important new technological application of the new generation of information technology in my country's strategic emerging industries. As SRv6 technology matures, the application and deployment of IPv6 in existing networks will be accelerated.
As a new generation IP bearer protocol, SRv6 can simplify and unify traditional complex network protocols and will be widely used in home broadband business scenarios in terms of computing power networks, intelligent network scheduling, and service orchestration.