A brief analysis of the application of NAT technology in cloud gateways

A brief analysis of the application of NAT technology in cloud gateways

Introduction to Labs
With the increase of network applications and the increase of home devices, the problem of IPv4 address exhaustion is becoming more and more serious. Although IPv6 can fundamentally solve the problem of insufficient IPv4 address space, currently many network equipment and network applications are mostly based on IPv4. Therefore, before IPv6 is widely used, the use of some transition technologies (such as CIDR, private network addresses, etc.) is the best way to solve this problem. main way of the problem.
Part 01. Introduction to NAT technology
NAT (Network Address Translation) is the process of converting the IP address in the IP data packet header to another IP address. In practical applications, NAT is mainly used to implement the function of private networks accessing public networks. This approach of using a small number of public IP addresses to represent a larger number of private IP addresses will help slow down the depletion of available IP address space.
(1) Types of NAT
Depending on whether NAT conversion converts the source address or the destination address in the packet, NAT can be divided into source NAT, destination NAT and bidirectional NAT. Below we introduce these three NAT types respectively.
1. Source NAT
Source NAT only translates the source address in the packet during NAT translation. It is mainly used in scenarios where private network users access the public network. When the private network user host accesses the Internet, after the packet sent by the private network user host reaches the NAT device, the device converts the private network IPv4 address in the message into a public network IPv4 address through source NAT technology, so that the private network user can normally Access the Internet.
2. Destination NAT
Destination NAT only translates the destination address and destination port number in the packet during NAT conversion. It is mainly used in scenarios where public network users access private network services. When the packet sent by the public network user host reaches the NAT device, the device uses destination NAT technology to convert the public IPv4 address in the packet into a private IPv4 address, so that the public network user can use the public network address to access private network services.
3. Bidirectional NAT
Bidirectional NAT refers to the simultaneous conversion of the source information and destination information of the message during the conversion process. Bidirectional NAT is not a separate feature, but a combination of source NAT and destination NAT. Bidirectional NAT targets the same flow and simultaneously translates the source address and destination address of the packet when it passes through the device. Bidirectional NAT is mainly used in scenarios where external network users access internal servers and private network users access internal servers at the same time.
(2) Special protocols supported by NAT
NAT not only implements general address translation functions, but also provides a complete address translation ALG (Application Layer Gateway, application level gateway) mechanism, so that it can support some special application protocols without any modification to the NAT platform. Has good scalability. The message payloads of these special protocols carry address or port information, and this information may also require address translation. Special protocols that can be supported include: FTP (File Transfer Protocol, file transfer protocol), PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol, point-to-point tunneling protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol, Internet Control Message Protocol), DNS ( Domain Name System, ILS (Internet Locator Service, Internet location service), RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol, real-time streaming protocol), H.323, SIP (Session Initiation Protocol, session initiation protocol), NetMeeting 3.01, NBT (NetBIOS over TCP/IP, network basic input and output system based on TCP/IP) etc.
(3) NAT log
The NAT log is a type of system information generated by the NAT device when performing NAT conversion. This information includes the source IP address, source port, destination IP address, destination port, converted source IP address, converted source port, and operations performed by the user, etc. of the message. It is only used to record the access of internal network users to the external network, and does not record the access of external users to the internal network server. When internal network users access the external network through a NAT device, multiple users share an external network address, making it impossible to locate the user accessing the network. The log function can be used to track and record the access of internal network users to external networks in real time, thereby enhancing network security.
Part 02. Application of NAT technology in cloud gateway
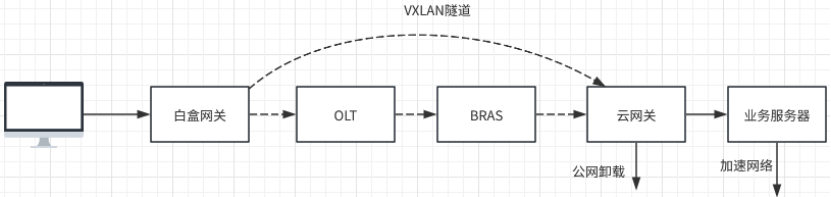
Currently, China Mobile is vigorously promoting the research and development and implementation of cloud gateways. One of the solutions is to deploy the cloud gateway as a network element after BRAS on the mobile cloud.
As shown in Figure 1, the network architecture uses VXLAN tunnels to access and terminate user packets. That is, each white box gateway (ONU) will create a VXLAN tunnel with the cloud gateway and be assigned a unique VNI identifier. The terminal The message is encapsulated in the VXLAN tunnel at the white box gateway (ONU) and forwarded to the cloud gateway. The cloud gateway decapsulates the message to obtain the inner original message, and performs different processing according to the type of the message. The cloud gateway architecture Most of the control plane functions and value-added services of traditional home gateways are moved up to the cloud gateway system behind BRAS for unified processing.
To put it simply, the process of users accessing the Internet in the cloud gateway scenario is:
1. The white box gateway initiates PPPOE dialing and obtains an Internet-enabled IP from the BRAS;
2. Use the IP obtained by PPPOE dial-up as the local IP and the pre-assigned VNI value to create a VXLAN tunnel with the cloud gateway;
3. The user terminal (such as mobile phone, PC, etc.) initiates a DHCP request, and the VXLAN tunnel is encapsulated in the white box gateway and forwarded to the cloud gateway. The VXLAN message is decapsulated at the cloud gateway and the original message is transparently transmitted to the cloud gateway control plane. The DHCP server assigns an intranet address to the terminal;
4. The end user accesses the Internet normally (including DNS), the packet reaches the cloud gateway, and the policy is used to determine whether the value-added service has been ordered:
(4.1) Non-value-added service users use public network IP for NAT to perform public network offloading and forwarding;
(4.2) Value-added service users send the message to the service server for subsequent processing based on the specific ordered service, and perform operations such as discarding, accelerating or reinjecting the message.
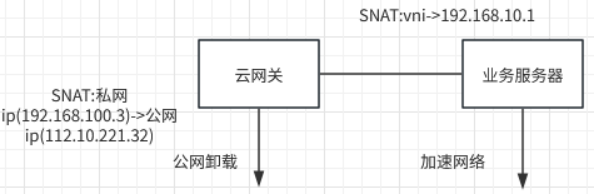
The scenario of cloud gateway using NAT is mainly divided into two parts:
- The cloud gateway directs the traffic to the business server. The cloud gateway performs source NAT based on the user's VXLAN ID (VNI) and converts the source IP and source port into source IP and source port that can be recognized by the business server;
- The cloud gateway is offloaded to the public network. The cloud gateway performs source NAT based on the public IP of the offloaded network port, and converts the source IP and source port to the public IP and port.
Part 03. Summary
The NAT function can be deployed on network hardware devices such as routers, firewalls, and core Layer 3 switches, as well as on various software proxy servers, such as Proxy. Relatively speaking, when NAT is deployed on network hardware devices, it has the characteristics of fast processing speed and high security, and is suitable for large and medium-sized enterprises; when deployed on software proxy servers, it has lower costs and slower conversion speed, and is suitable for small businesses. enterprise. At present, China Mobile Smart Home Operation Center has completed self-research on cloud gateways based on NAT technology and completed pilot deployments in many provinces, forming a complete end-to-end solution.