Don’t let hackers sneak into your network: in-depth analysis of DHCP Snooping

Don’t let hackers sneak into your network: in-depth analysis of DHCP Snooping
1. Overview of DHCP working principle
Before learning DHCP Snooping, we need to review how DHCP works. Let’s analyze the working principle of DHCP from two scenarios:
1.DHCP without relay scenario
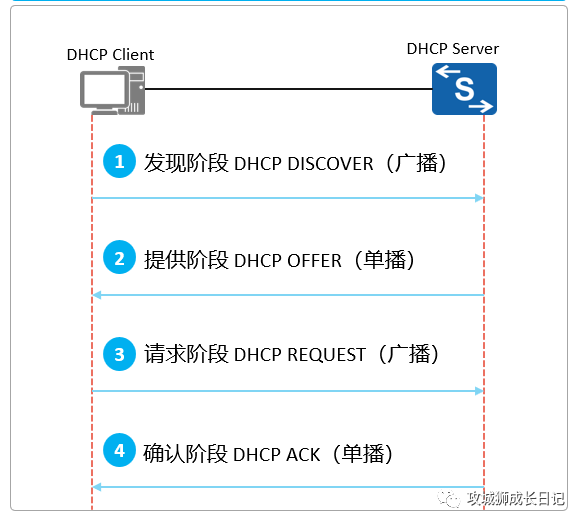
DHCP non-relay scenario
(1) Discovery stage
The DHCP client requests services from the DHCP server in the LAN by broadcasting DHCP Discover messages.
(2) Provision stage
The DHCP server responds to the client through a DHCP Offer message based on its own configured IP address pool, corresponding subnet mask, gateway and other information.
(3) Request stage
If the configuration in the DHCP Offer message is accepted, the DHCP client broadcasts a DHCP Request message to notify the DHCP server and other hosts in the LAN of its effective IP address.
() Confirmation stage
When the DHCP client receives the DHCP ACK message, it will broadcast and send gratuitous ARP messages to detect whether other terminals in this network segment use the IP address assigned by the server.
2.DHCP relay scenario
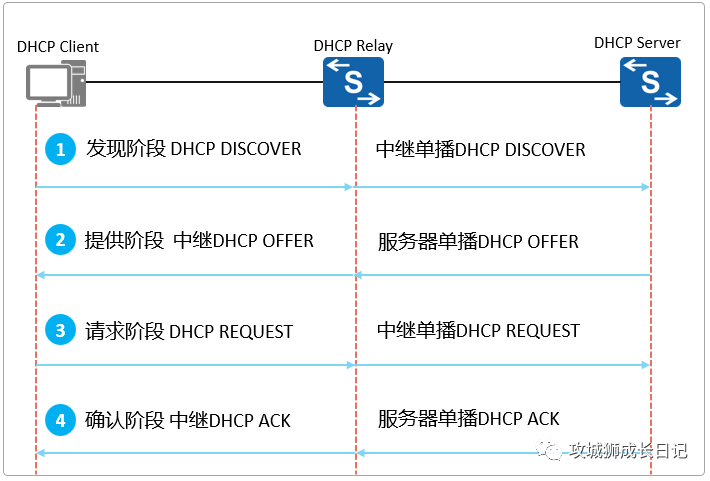
DHCP has relay scenario
(1) Discovery stage
After receiving the DHCP DISCOVER message broadcasted by the DHCP client, the DHCP relay performs the following processing:
- Step 1: Check the hops field in the DHCP message. If it is greater than 16, discard the DHCP message; otherwise, add 1 to the hops field (indicating that it has gone through a DHCP relay), and continue with step 2.
- Step 2: Check the giaddr field in the DHCP message. If it is 0, set the giaddr field to the IP address of the interface that receives the DHCP DISCOVER message. If it is not 0, do not modify this field and continue with step 3.
- Step 3: Change the destination IP address of the DHCP message to the IP address of the DHCP server or next-hop relay, change the source address to the interface address of the relay connecting to the client, and unicast the DHCP message to DHCP through routing forwarding. Server or next hop relay.
(2) Provision stage
After receiving the DHCP DISCOVER message, the DHCP server selects an address pool in the same network segment as the giaddr field in the message, allocates IP addresses and other parameters to the client, and then unicasts a DHCP OFFER message to the DHCP relay identified by the giaddr field. arts.
After receiving the DHCP OFFER message, the DHCP relay will perform the following processing:
- Step 1: Check the giaddr field in the message. If it is not the address of the interface, discard the message; otherwise, continue with the following operations.
- Step 2: The DHCP relay checks the broadcast flag of the message. If the broadcast flag bit is 1, the DHCP OFFER message is broadcast to the DHCP client; otherwise, the DHCP OFFER message is unicast to the DHCP client.
(3) Request stage
The processing process when the relay receives the DHCP REQUEST message from the client is the same as the "discovery phase".
(4) Confirmation stage
The processing process when the relay receives the DHCP ACK message from the server is the same as the "provision phase".
2. Overview of DHCP Snooping
In order to ensure the security of network communication services, DHCP Snooping technology is introduced to establish a firewall between DHCP Client and DHCP Server to resist various attacks on DHCP in the network.
DHCP Snooping is a security feature of DHCP that is used to ensure that DHCP clients obtain IP addresses from legitimate DHCP servers. The DHCP server records the correspondence between the DHCP client's IP address and MAC address and other parameters to prevent DHCP attacks on the network.
Currently, the DHCP protocol encounters many security issues during its application. There are some attacks against DHCP in the network, such as DHCP Server bogus attacks, DHCP Server denial-of-service attacks, and counterfeit DHCP message attacks.
DHCP Snooping mainly implements DHCP network security through the DHCP Snooping trust function and the DHCP Snooping binding table.
DHCP Snooping trust function
The trust function of DHCP Snooping can ensure that the client obtains an IP (Internet Protocol) address from a legitimate server.
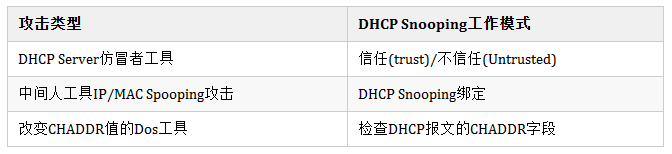
As shown in the figure below, if there is a privately installed DHCP Server counterfeiter in the network, it may cause the DHCP client to obtain the wrong IP address and network configuration parameters, and cannot communicate normally. The DHCP Snooping trust function can control the source of DHCP server response messages to prevent possible DHCP Server counterfeiters in the network from allocating IP addresses and other configuration information to DHCP clients.
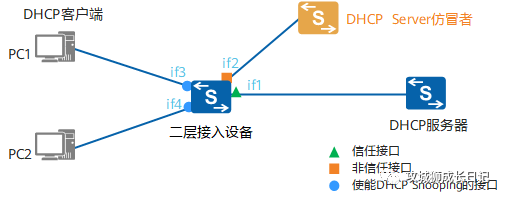
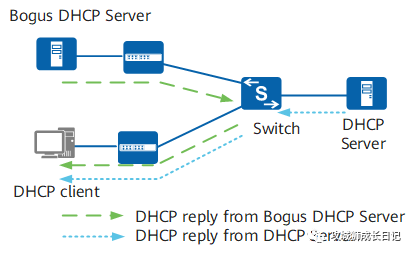
DHCP Snooping trust function diagram
The DHCP Snooping trust function divides interfaces into trusted interfaces and untrusted interfaces:
- The trusted interface normally receives the DHCP ACK, DHCP NAK, and DHCP Offer messages responded by the DHCP server.
- The DHCP OFFER, DHCP ACK, and DHCP NAK messages sent by the DHCP Server received by the untrusted interface will be directly discarded.
- The interface configured with the dhcp snooping enable command will forward the DHCP request message to all trusted interfaces after receiving it; discard the DHCP response message after receiving it.
- The interface configured with the dhcp snooping trusted command will forward the DHCP request message to all trusted interfaces after receiving the DHCP request message. If there are no other trusted interfaces, the DHCP request message will be discarded; after receiving the DHCP response message, it will only be forwarded to the connection corresponding The client's interface is configured with the dhcp snooping enable command. If the above interface cannot be found, the DHCP response message is discarded.
3. DHCP Snooping binding table
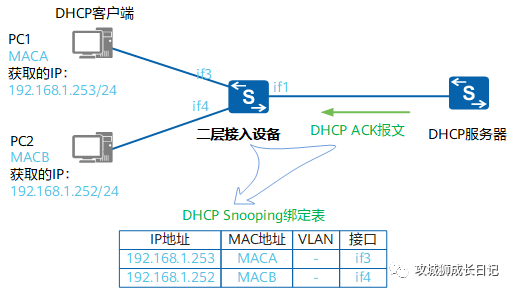
DHCP Snooping binding table function diagram
After the Layer 2 access device enables the DHCP Snooping function, it extracts key information (including the MAC address of the PC, the obtained IP address, and the address lease) from the received DHCP ACK message, and obtains the enablement of connection with the PC. The interface information of the DHCP Snooping function (including the interface number and the VLAN to which the interface belongs) is used to generate a DHCP Snooping binding table based on this information.
Since the DHCP Snooping binding table records the correspondence between the DHCP client IP address and MAC address and other parameters, attacks by illegal users can be effectively prevented by matching the packets with the DHCP Snooping binding table.
The DHCP snooping binding table ages based on the DHCP lease period or automatically deletes the corresponding entries based on the DHCP Release message sent when the user releases the IP address.
4. The role of DHCP Snooping
The DHCP Snooping function is used to prevent:
- DHCP Server Bogus Attack
- Man-in-the-middle attack and IP/MAC Spooping attack
- DoS attack that changes CHADDR value
According to different attack types, DHCP Snooping provides different working modes, as shown in the following table:
1.DHCP Server counterfeit attack
(1) Attack principle:
Since the DHCP request message is sent in broadcast form, DHCP Server counterfeiters can listen to this message. The DHCP Server counterfeiter responds to the DHCP Client with counterfeit information, such as wrong gateway address, wrong DNS server, wrong IP, etc., to achieve the purpose of DoS (Deny of Service).
(2) Solution:
- To prevent DHCP Server bogus attacks, you can use the "Trusted/Untrusted" working mode of DHCP Snooping.
- Set a physical interface or VLAN interface to "Trusted" or "Untrusted".
- All DHCP Reply (Offer, ACK, NAK) messages received from the "Untrusted" interface are directly discarded, which can isolate DHCP Server bogus attacks.
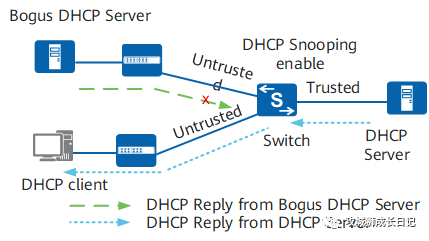
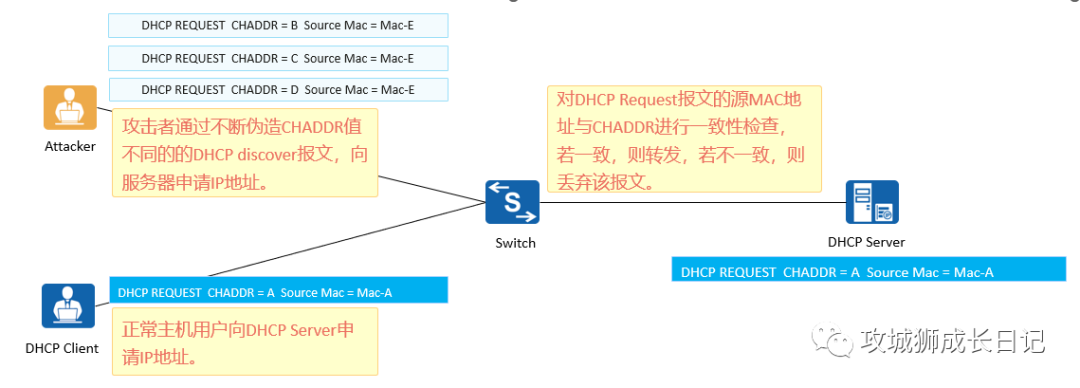
2.DoS attack that changes CHADDR value
(1) Attack principle:
The attacker continues to apply for a large number of IP addresses from the DHCP Server until the IP addresses in the DHCP Server address pool are exhausted, causing the DHCP Server to be unable to allocate them to normal users.
(2) Solution:
To avoid being attacked by attackers who change the CHADDR value, you can configure the DHCP Snooping function on the device to check the CHADDR field in the DHCP Request message. If this field matches the source MAC in the header of the data frame, the packet is forwarded; otherwise, the packet is discarded. This ensures that legitimate users can use network services normally.
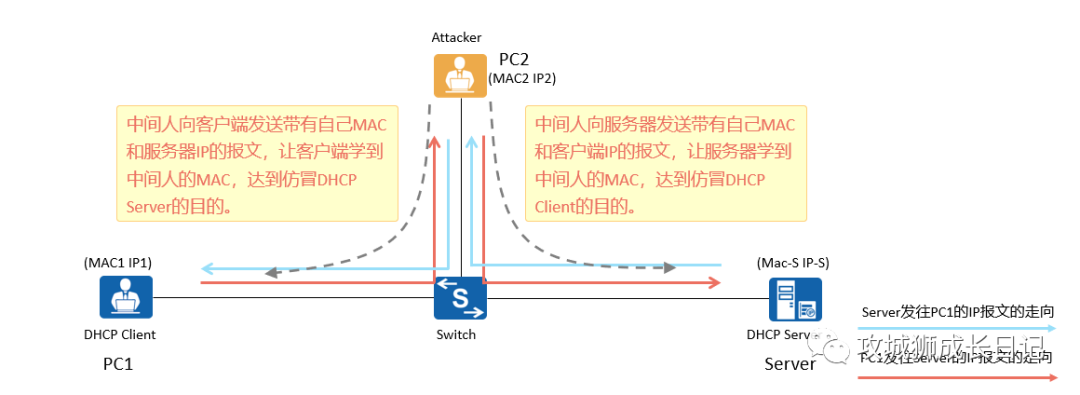
3.DHCP man-in-the-middle attack
(1) Attack principle:
The attacker uses the ARP mechanism to let the client learn the mapping relationship between the DHCP Server IP and the Attacker MAC, and also allows the Server to learn the mapping relationship between the Client IP and the Attacker MAC. As a result, the IP packets exchanged between the Client and the Server will be relayed by the attacker. In essence, a man-in-the-middle attack is a spoofing IP/MAC attack. The man-in-the-middle uses a false mapping relationship between IP addresses and MAC addresses to deceive both DHCP clients and servers.
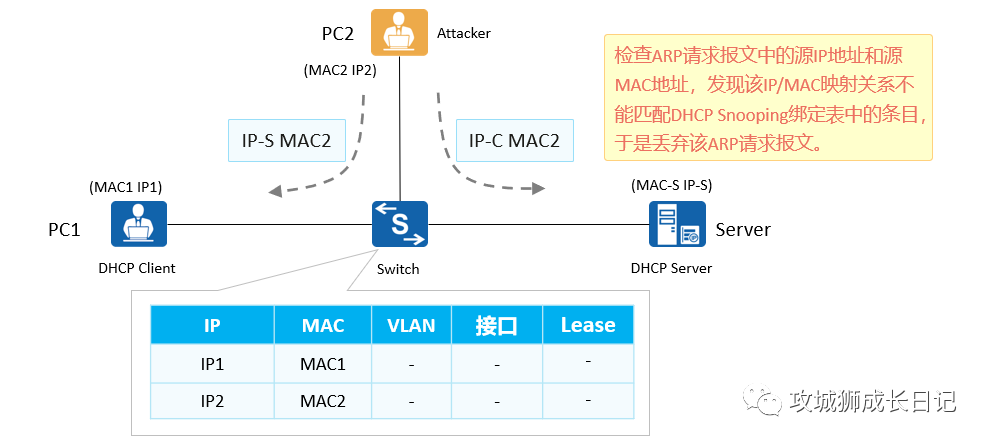
(2) Solution:
To defend against man-in-the-middle attacks and IP/MAC spoofing attacks, you can use the binding table working mode of DHCP Snooping. When the interface receives an ARP or IP message, it uses the "source IP + source MAC" in the ARP or IP message to match the DHCP Snooping binding table. Fixed schedule. If they match, they are forwarded; if they don't, they are discarded.
5. Introduction to DHCP Snooping configuration commands
(1) Globally enable the DHCP Snooping function:
[Huawei] dhcp snooping enable [ ipv4 | ipv6 ]- 1.
(2) Enable the DHCP Snooping function in VLAN view:
[Huawei-vlan2] dhcp snooping enable- 1.
Executing this command in VLAN view will take effect on DHCP packets belonging to the VLAN received by all interfaces of the device.
(3) Configure the interface to "trust" status in VLAN view\
[Huawei-vlan2] dhcp snooping trusted interface interface-type interface-number- 1.
If you execute this command in VLAN view, the command function will only take effect on the DHCP packets belonging to this VLAN received by the interface that joins this VLAN.
(4) Enable DHCP Snooping function in interface view
[Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping enable- 1.
(5) Configure the interface to "trust" status in the interface view
[Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping trusted
- 1.
By default, the device interface is in an untrusted state.
(6) (Optional) Configure to discard DHCP messages with non-zero GIADDR field
[Huawei] dhcp snooping check dhcp-giaddr enable vlan { vlan-id1 [ to vlan-id2 ] }- 1.
Enable the function of detecting whether the GIADDR field in the DHCP Request message is non-zero. This command can also be configured in VLAN view or interface view. If you execute this command in the VLAN view, the command function will take effect on the DHCP packets belonging to the VLAN received by all interfaces of the device; if you execute this command on the interface, the command function will take effect on all DHCP packets under the interface.
6. DHCP Snooping configuration example
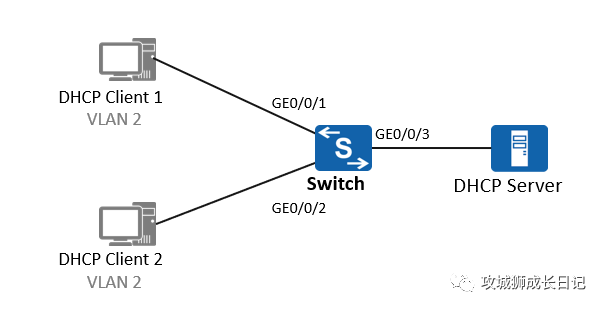
As shown in the figure, the basic configuration of DHCP and VLAN has been completed, and the DHCP Snooping function is configured on the Switch.
(1) Configuration method one: interface view
[Switch] dhcp snooping enable ipv4
[Switch] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1
[Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping enable
[Switch] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2
[Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] dhcp snooping enable
[Switch] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/3
[Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] dhcp snooping enable
[Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] dhcp snooping trusted- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
(2) Configuration method two: VLAN view
[Switch] dhcp snooping enable ipv4
[Switch] vlan 2
[Switch-vlan2] dhcp snooping enable
[Switch] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/3
[Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] dhcp snooping trusted - 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
To verify the configuration, execute the display dhcp snooping interface command to view the DHCP Snooping running information on the interface.
[Switch]display dhcp snooping interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/3
DHCP snooping running information for interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 :
DHCP snooping : Enable
Trusted interface : Yes
Dhcp user max number : 1024 (default)
Current dhcp user number : 0
Check dhcp-giaddr : Disable (default)
Check dhcp-chaddr : Disable (default)
Alarm dhcp-chaddr : Disable (default)
Check dhcp-request : Disable (default)
Alarm dhcp-request : Disable (default)
----- more ------