How does the famous CDN acceleration service perform access acceleration and content distribution?

How does the famous CDN acceleration service perform access acceleration and content distribution?
Hello everyone, I am Bernie, an IT pre-sales engineer.
This article briefly talks about the well-known CDN content distribution service, and how CDN realizes service acceleration. Welcome to read~
We assume that in a certain corner of the earth, there is a website service provider Inernet Content Provider. In another place thousands of miles away, a brother wants to visit the website business on a whim.
Then, an astonishing scene happened: Due to the long communication distance, the web page was stuck to death, and even a picture took 2 or 3 seconds to load, let alone a video.
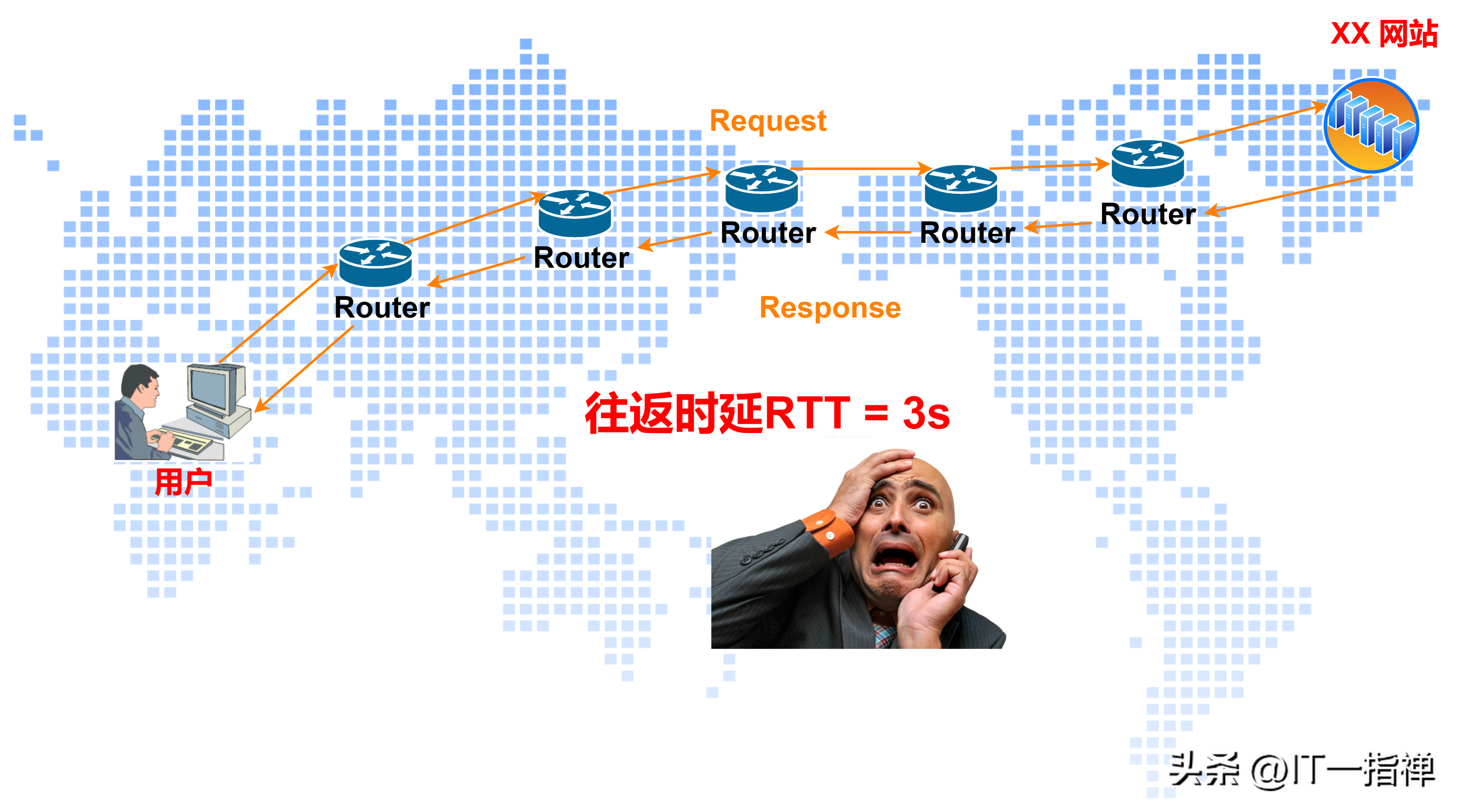
Just ask, can such a website still provide business access services to global users?
It is estimated that it can only serve users who are relatively close to each other, which is similar to the operation of local services in the metropolitan area network.
So what if the ambitious boss does not give up and wants to serve more users and earn more money?
Some people may say: "Then build more resource pools, at least one central node, subordinate to multiple edge nodes." Similar to the following.
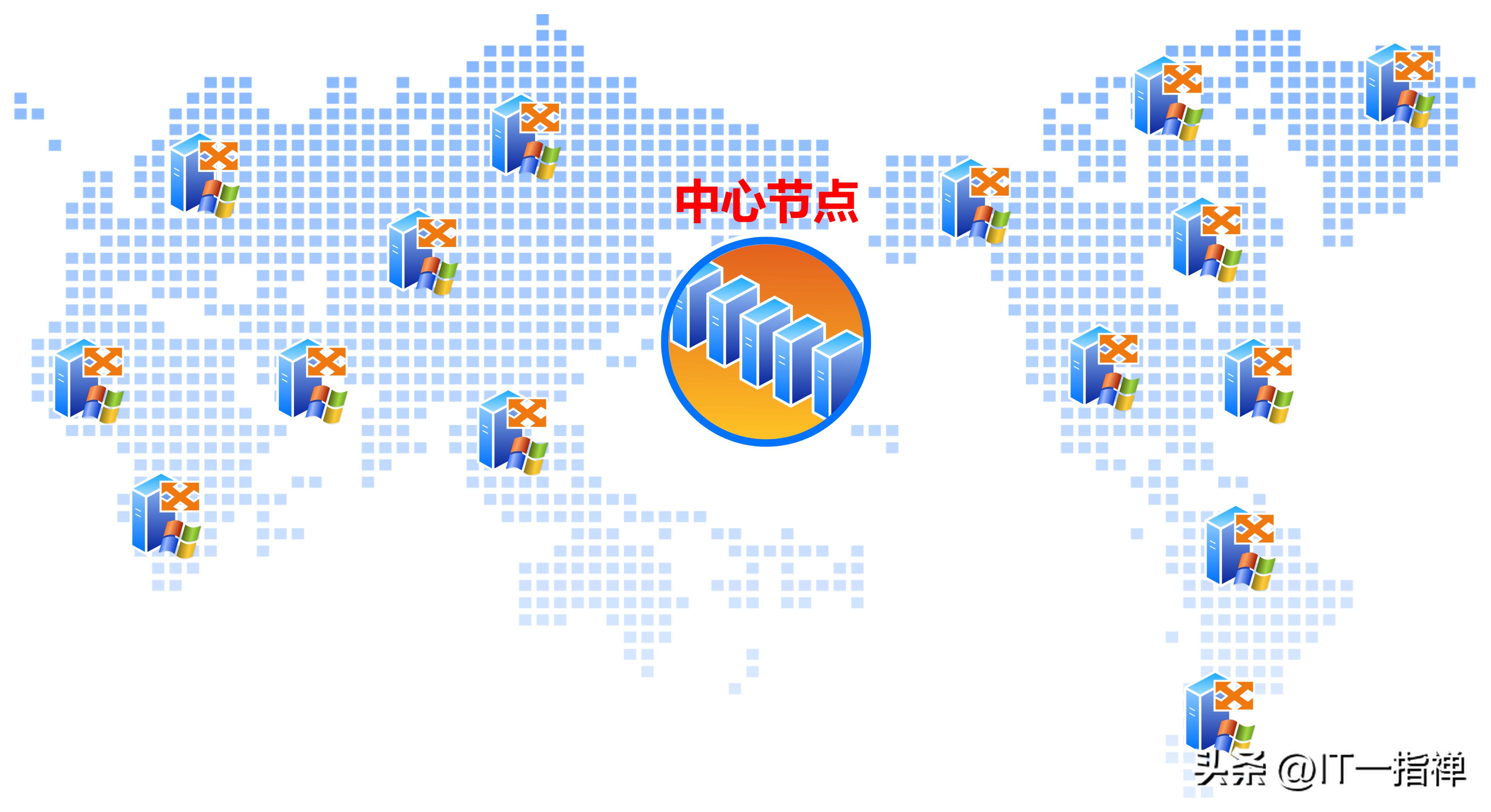
The idea is good, but what about the money?
The cost of resource pool construction is very huge, a single server is about 100,000 (more than good), network cables, switches, routers, IDC computer rooms, racks, electricity, operation and maintenance manpower...
It will cost a lot of money!
However, the business still needs to develop. If there are difficulties, you have to go up, if there are no difficulties, you have to go up to create difficulties!
At this time, you need to know a little about CDN.
What are CDNs?
There are a group of wealthy patrons who have taken a fancy to the business opportunity of server leasing. Therefore, a lot of money has been spent to build many resource pools in many countries around the world, or in multiple places in a certain country. Then, some servers in these resource pools are leased to bosses who need to expand their business but do not have enough funds to build edge nodes.
These rich and powerful financial owners are CDN service providers.
The full English name of CDN is Content Delivery Network, content distribution network. Simply put, it is to distribute the content of the central node to many edge nodes close to users, so that users can access certain services nearby, speed up the access speed, and improve the service efficiency of the Internet Content Provider.
In CDN services, the central business node is often owned by an Internet company, and many edge nodes are owned by CDN service operators.
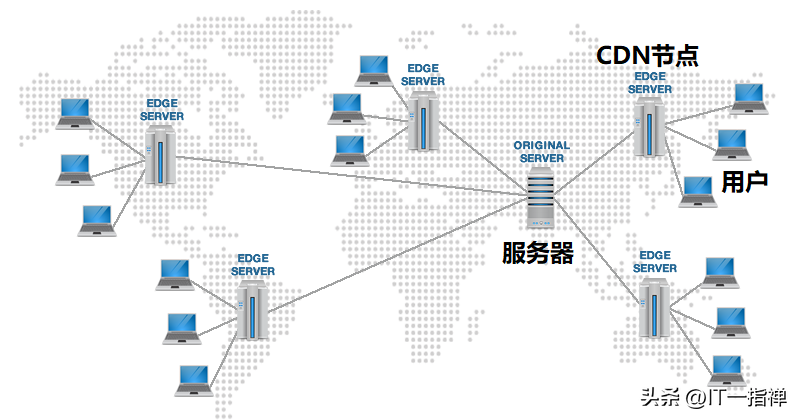
What can a CDN do?
The core purpose of CDN is: relying on the natural advantage of being close to the user, when the user needs to request a certain service, first request the nearest edge node.
Usually, Internet service providers deploy dynamic resources on CDN. The so-called dynamic resources are resources that often change and often receive requests, such as server time. In contrast, there are static resources, which are those resource types that are almost "unchanged for thousands of years".
For example, for a certain business, the central resources are deployed in Shanghai. If users in Lanzhou, Gansu want to access the network, they must first access nodes near Lanzhou. If the Lanzhou node has the resource it wants, it will process it and return the result as soon as possible.
If not, then ask the central node for data and return it to the client; at the same time, the Lanzhou node will store the accessed data locally so that it can be directly read and returned to the user when it receives a request next time.
Who are the CDN operators?
As mentioned earlier, CDN operators need to build edge resource pools all over the country or around the world, and also provide professional operation and maintenance teams. It is said that it is a rich man's game, and the threshold is extremely high.
Who are the well-known CDN operators?
In China, there are Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, UCloud, Baidu Cloud, Lanxun, Wangsu, etc., as well as the three major communication operators (China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom).
Foreign CDN giants include CloudFlare, StackPath, Akamai, Fastly, CloudFront, Edgecast, CDNetworks, CacheFly, Keycdn, and CDN77, etc. You can find detailed information on Baidu.
Summarize
The above is a brief introduction to the CDN network. The application of CDN is very extensive. It can be used in large picture files, small file downloads, live streaming media, video and audio on demand, site-wide acceleration, and security acceleration.
In addition, the CDN network also has load balancing and disaster recovery strategies. For example, if an edge node stops running due to an accident, it will automatically switch to another edge node that is relatively close to the user to provide efficient network services.
The article comes from: IT One Finger Zen , if you want to reprint this article, please contact [IT One Finger Zen] Toutiao account.