Using sunlight instead of WiFi signals to connect to the Internet, Saudi scientists have achieved bright results

Using sunlight instead of WiFi signals to connect to the Internet, Saudi scientists have achieved bright results
Is it possible to use sunlight instead of wifi signals to connect to the Internet and transmit data?
Someone did it.
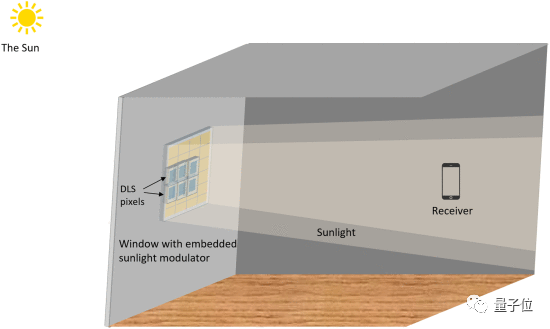
Researchers in Saudi Arabia have designed a smart glass system.
It can use the window as a modem (that is, the "cat" used to surf the Internet at home), and realize information transmission by changing the nature of sunlight.
After the phone camera receives the light signal, it converts it back into binary data.
All it takes is a 1 watt solar cell to make it work.
Currently, the research has been published in IEEE Photonics Journal.

How exactly? look down.
Do you believe in light?
In the past, predecessors generally changed the intensity of light to encode it.
However, when light propagates in the air, its intensity will change continuously due to environmental influences such as air pressure, the transmission efficiency is too low, and the human eye is very sensitive to drastic changes in light intensity.
This time, the researchers turned to the principle of the polarization of light.
We have learned in middle school that light is a transverse wave, if it passes through a specific medium (polarizer), only part of the light wave in a specific direction will be retained.
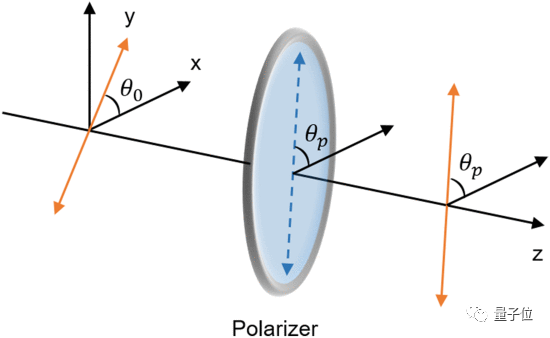
Based on the above principles, the researchers designed a system that carries information into sunlight by changing the polarization of light waves, and the changes are not easily detectable by the human eye.
Specific changes need to be achieved through liquid crystal materials. Under different voltages, the molecular arrangement of such materials will change, which in turn affects the polarization of the light in the medium.
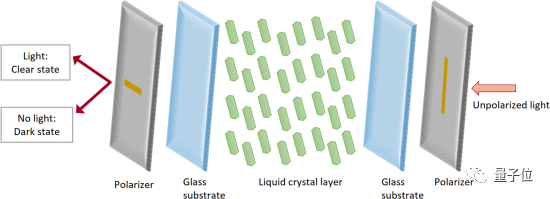
But this is not enough.
In order to improve the encoding efficiency, the researchers also referred to the time response function of the liquid crystal shutter, and considered issues such as the birefringence of the light-transmitting medium, and stacked two reversed liquid crystal (LC) units together.
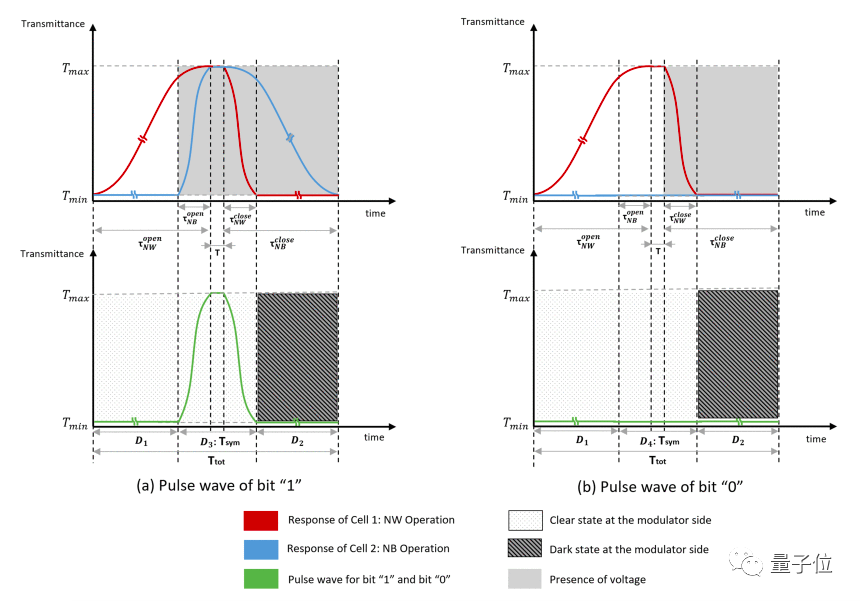
Finally, the entire modulation system consists of 3 polarizers, 2 reverse liquid crystal layers (one normally white and one normally black)——
The researchers call it a dual-cell liquid crystal shutter (DLS).
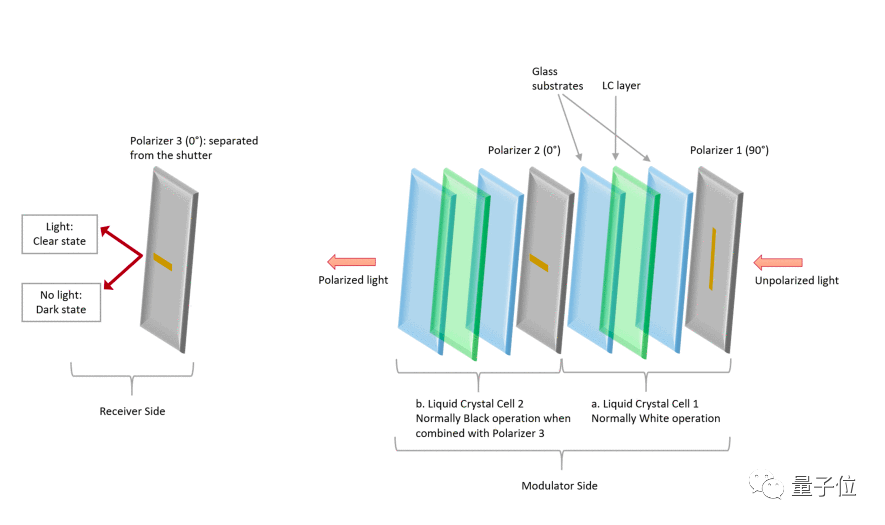
The benefits of this design are:
Compared with a single-layer liquid crystal polarization system, it can change the polarization of light waves faster, reduce encoding errors, and at the same time reduce the impact on the "flicker effect" of random fluctuations in the intensity of light during propagation.
As can be seen from the figure below, the red line is the output of signal 1 in normally white mode, and the blue line is in normally black mode. When the two are stacked, the pulse (green curve) of signal "1" is shorter and changes more rapidly. More efficient in coding.
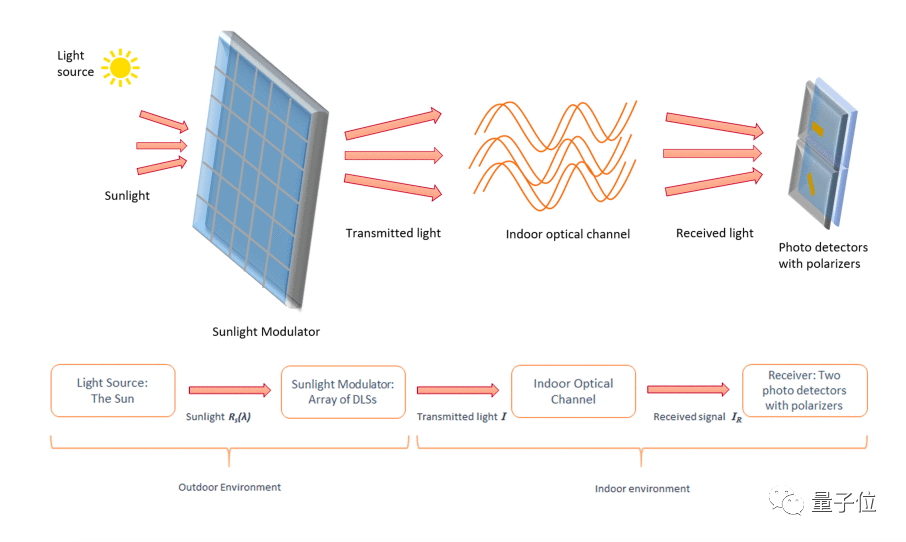
Using DLS as the basic modulation unit, the researchers designed a complete information transmission system to replace wifi:
Let the sunlight shine through the smart glass window first, the window itself is a modulator, and the polarization of the light wave is changed by DLS, and then modulated and coded.
The light waves loaded with information continue to enter the room, and then are received by terminal cameras such as mobile phones, which are demodulated and converted back into binary data.
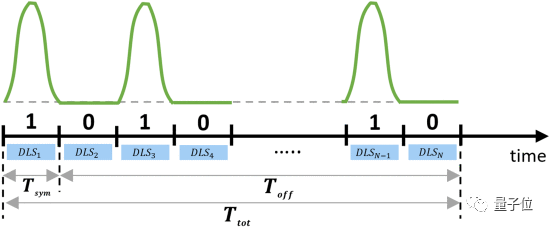
In order to further increase the transmission rate, the researchers also used time division multiplexing (TDM).
Simply put, this technology is to cut the transmission time in a channel, and allocate the transmission reception time to different devices in a certain order. When it is the turn of a certain device, the device will start the transmission, and the transmission of other devices will be cut off at the same time.
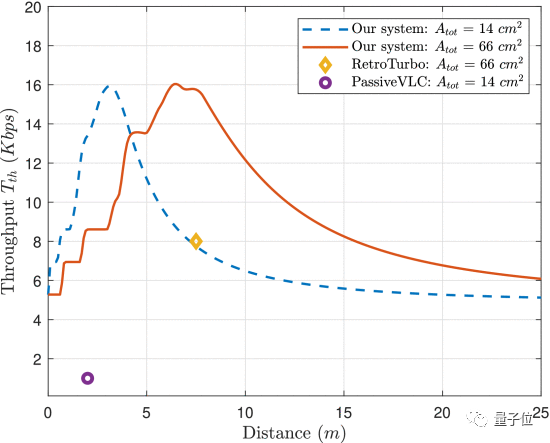
Finally, the research team observed the transmission performance of the system they built through modeling.
At present, the more mainstream optical modulation and direct transmission communication method will use semiconductor optical amplifier (SoA). The researchers selected two modulation modes for comparison: RetroTurbo with a modulation area of 66 square centimeters, and PassiveVLC with a modulation area of 14 square centimeters.
The results show that their systems are superior to the most advanced methods at present with the same modulation area and the same transmission distance, and the maximum transmission rate can reach 16Kbps.
In terms of energy consumption, only 1W of solar panels are needed to drive the entire system.

Although the current information transmission rate is limited, the team believes that this achievement indicates that sunlight is not only an energy resource, but also an information resource, which will help us transmit information with lower energy consumption.
Regarding follow-up research planning, the team stated:
Their next step is to increase the transmission rate to megabits per second, or even gigabits, for which they will apply for ordering relevant test hardware.
team introduction
Get to know the members of the research team.
The first is Sahar Ammar from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Department of Electrical and Mathematical Science and Engineering (CEMSE), whose main research direction is optical communication;
Second author Osama Amin, also from the Department of Electrical and Mathematical Sciences and Engineering (CEMSE) at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology;
The instructor, Basem Shihada, is mainly engaged in wireless and wired communication, and is also involved in network security and cloud computing.