Smart Manufacturing: Ensuring a Smart Future for Manufacturing

Smart Manufacturing: Ensuring a Smart Future for Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing has the potential to improve the entire manufacturing industry.
The Internet of Things (IoT), combined with broadband connectivity, enables us to create smart factories, where every aspect of the manufacturing process can be monitored and optimized using artificial intelligence and predictive analytics. However, as the number of connected devices increases, so does the potential security risk, making cybersecurity a key consideration in smart factory design and implementation. In this article, we discuss the advantages of smart manufacturing, the role of 5G in enabling smart manufacturing, and the importance of cybersecurity to protect digital assets and prevent cyber threats.

YuHelenYu invited industry thought leader Dez Blanchfield as a guest to host AT&T Business Talk, and together they explored the exciting world of smart manufacturing, IoT, 5G, the benefits of MEC in making informed decisions, predicting demand and preventing downtime while prioritizing Consider strong network security.
The following is a summary of the discussion:
Q1. What does a smart factory look like in practice? What is the best case scenario?
YuHelenYu: A smart factory means applying smart technology to manufacturing operations. With connected solutions like IoT, video intelligence, and 5G, we can use predictive analytics to make informed decisions, anticipate demand, and prevent downtime. My ideal factory would also have an effective cybersecurity strategy that extends from the factory to remote workers, third-party vendors and suppliers to help protect vulnerabilities that hackers could target.
Dez Blanchfield: I use infographics to illustrate the key components of a smart factory. The key drivers of smart manufacturing are digital technology and fast telecommunications, both of which are drivers of innovation and digitization.
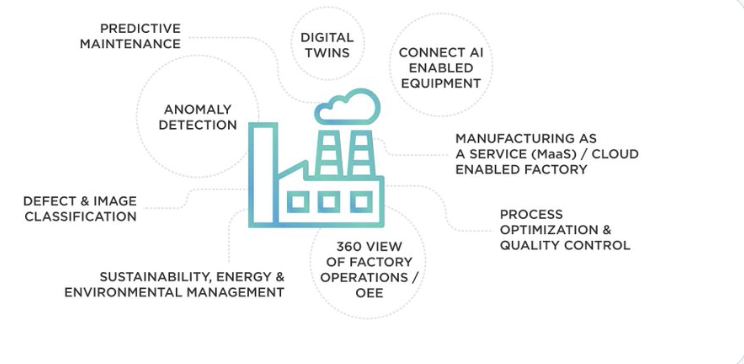
Maryson W.: Smart factories maximize edge computing by enhancing cybersecurity. Industry 4.0 requires more frameworks than just checklists, strategies or plans. As digital transformation finally turns into a race for digital survival, the toughest will come Industry 5.0.
Q2. Why is 5G considered a catalyst for "smart factories"?
YuHelenYu: 5G is the catalyst because it provides higher bandwidth and lower latency, and enables real-time communication between machines, sensors, cameras, and people. It allows more machines to connect to the network and communicate with each other, optimizing production processes in real time. 5G enables manufacturers to use sensors to track the location and condition of inventory in the supply chain and help prevent delays and reduce waste. It can use augmented reality technology in manufacturing. Technicians can use AR to visualize and solve problems.
Dez Blanchfield: Industry 4.0 is only possible in a high-speed, trusted, secure, low-latency, high-data-throughput network like 5G, because data is the catalyst for smart manufacturing.
Maryson W.: The touchstone has already begun. If we want artificial intelligence to manage everything one day, now is the time to act. At a time when factories have less manual surveillance on real estate, 5G could open the door for 4K security cameras. 5G can be summarized as the backbone of the Internet of Things, Industrial IoT devices, and simplifying digital twin operations.
Q3. What is the difference between 5G and fiber? How can they help create a more reliable network?
YuHelenYu: Advanced wireless technologies such as 5G, edge or Wi-Fi can maximize the flexibility of connecting data collection endpoints. Advanced Internet solutions, such as commercial fiber optics, create the backbone for building advanced wireless technologies at the speeds needed for real-time decision-making.
Dez Blanchfield: The key points here, one is wireless (5G) and the other is "fixed wireline" (fibre) technology. They offer distinct yet powerful and valuable solutions to the manufacturing floor.
Q4. What expertise do companies need to build a reliable manufacturing network?
YuHelenYu: It all starts with business priorities. It starts with what business outcome you want to achieve, and then the technology you need to achieve it, so you can identify the expertise you need. Some of the priority areas I see are artificial intelligence, machine learning, IoT, big data and analytics. Selecting the right partner with the required expertise is critical.
Dez Blanchfield: Successful smart manufacturing companies will choose the right partners to design, deploy and manage their future networks while focusing on their core business.
Maryson W.: The probability of not needing a blockchain is less than 50%.
Q5. What is the role of cybersecurity in the digital revolution in manufacturing?
YuHelenYu: Cybersecurity plays a vital role in the digital revolution in manufacturing. As manufacturing facilities increasingly adopt industrial IoT devices, automation systems, and cloud computing, the attack surface for cyber threats expands. Cybersecurity measures are key to protecting digital assets. Implement firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, access control mechanisms, and encryption protocols to prevent unauthorized access, data leakage, and other cyber threats. Cybersecurity in manufacturing also involves securing supply chains, as many manufacturers rely on third-party suppliers for components and services.
Dez Blanchfield: Security or cybersecurity, which has always played a key role in the evolution of manufacturing, is now a key element of the digital revolution.
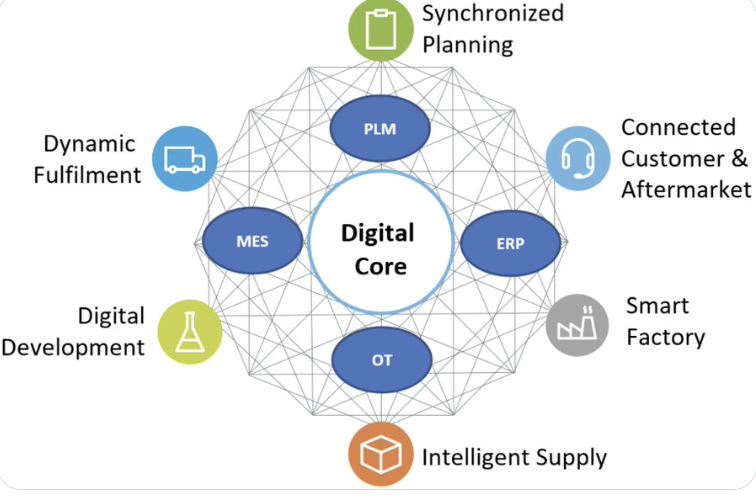
Q6. What are the biggest barriers to cybersecurity and reliability for manufacturers?
YuHelenYu: The biggest barriers to cybersecurity are the lack of awareness and expertise, and the increasing complexity of manufacturing networks with the adoption of more digital technologies and the interconnection of various devices and systems. Manufacturers may prioritize meeting production goals over safety due to perceived cost or lack of understanding of potential risks. In addition, network attacks are increasingly frequent and complex, posing a major challenge to network security and reliability.
Dez Blanchfield: The early barriers to digital transformation are often education or awareness, and intelligent design and implementation of the right tools and systems to make them happen.
Q7. What is MEC and what role does it play in manufacturing network security and reliability?
YuHelenYu: MEC is a type of multi-access edge computing, a managed service that enables enterprise customers to differentiate specific data traffic in a private wireless network campus environment and route it to designated customer application. It allows factories to put decision intelligence in this edge computer that can decide what to keep on the network. It prioritizes inherent security capabilities. This is a device that makes intelligent decisions within the factory.
It brings edge computing closer to the manufacturer than to the edge of the cloud provider's network. It brings the benefits of cloud networking directly to the facility. It reduces complexity because it makes distributed decisions about what to keep.
Dez Blanchfield: MEC has proven to be a powerful enabler of digital technologies, telecommunications, data analytics and manufacturing insights.
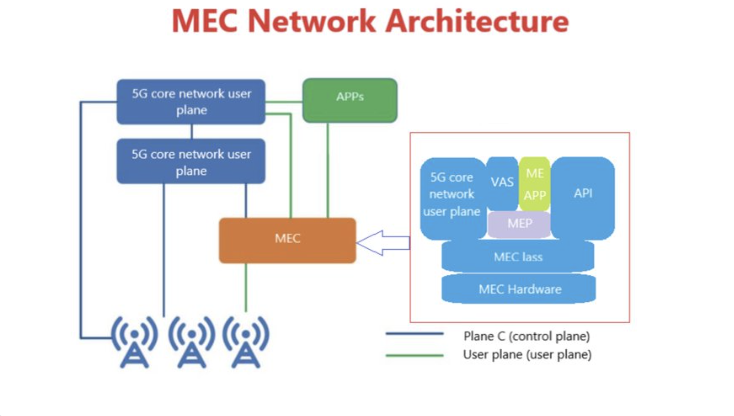
Maryson W.: Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) helps connect smart factories to the cloud, and of course a resilient network is required, as there are plenty of automation technologies to choose from.
The smart factory of the future requires secure networks and reliable connections. This includes security at the device level, network level, edge and cloud. These overlapping layers of protection from AT&T help reduce risk and identify threats as they arise:
- Cybersecurity strategy, planning and assessment services.
- DDoS Defense and Application Layer Security
- Managed Firewall Service
- AT&T Global Security Gateway
- Cloud Security Strategy and Assessment
- Threat Detection and Response Solutions
The complexity of the modern security environment requires cybersecurity experts - and it is easier to manage security services than to train or hire in-house experts. Choose a provider with a trusted history of enterprise-grade service.
As we continue to embrace the evolution of smart manufacturing, it is critical to prioritize safety and connectivity to ensure a successful future. With AT&T's expertise in cybersecurity and reliable networks, smart factories can operate efficiently, sustainably and safely. Let's work towards a future where data-driven insights and technological advancements drive innovation and success.