Outlook 2023: 5G, private LTE and eSIM

Outlook 2023: 5G, private LTE and eSIM
Looking ahead to the rest of 2023, we review what customers and our ecosystem are learning about how device manufacturers are using eSIM and iSIM technology for innovative connectivity solutions.
eSIMs are very important
Let's start by taking a look at the recent and upcoming product launches related to eSIM technology:
With Apple's iPhone shifting to eSIM-only models in the US market, eSIM has entered The Economist's important (technical) vocabulary for 2023. The adoption of eSIM lays the foundation for the acceleration of consumer and industrial digital transformation.
Samsung revealed that during CES 2023, the company will focus on connectivity innovation and sustainable development. During the show, the South Korean company will likely show off a new and expanded SmartThings experience that more seamlessly integrates the home ecosystem with systems supported by enhanced security. eSIM may not be in the news, but it promises to lead to wider interoperability and more independent devices that work together.
From an industrial IoT perspective, the Trusted Connections Alliance reports that eSIM technology will see continued double-digit growth. Earlier in 2022, GSMA Intelligence published research showing that 83% of businesses believe eSIMs are critical to the success of their IoT efforts.
Why should device manufacturers and OEMs care about eSIMs?
According to IMC IoT Buyer Research, almost one-third of product manufacturer or ODM deployments in 2022 will involve more than 10,000 devices, indicating that IoT solutions are scaling. Many companies starting to adopt or scale IoT begin their journey by talking to a system integrator (SI) firm.
According to IMC IoT Buyer research, almost one-third of product manufacturer or ODM deployments in 2022 will involve more than 10,000 devices, which shows that the scale of IoT solutions is already built. --Kigen UK Limited
Product manufacturers are more likely to make their first port of call equipment manufacturers. With scale a key requirement for the next phase of their IoT deployments, they identified a lack of interoperability as one of the biggest hurdles, and this trend has been increasing over time. Furthermore, according to McKinsey research, interoperability is critical in high-end scenarios of the fastest growing IoT markets:
"74% of IoT value requires interoperability for maximum impact." -- McKinsey, November 2021 IoT Value Survey Results
Here's a quick primer on eSIM technology from Kigen's second edition of Wiley's for Dummies guide on eSIM and iSIM:
Embedded SIM cards (ESIMs) are an evolution of SIM cards designed to address the limitations of traditional SIM cards. They went a step further, introducing new capabilities needed to enable trusted IoT devices. An ESIM is typically a physical SIM card soldered into a device, capable of storing and remotely managing multiple network operator profiles (remote SIM provisioning), offering the following advantages:
- Seamless Global Connectivity: Easily switch networks anywhere in the world without physical handling.
- Size: Since eSIMs are about half the size of Nano SIMs and don't require a socket, they fit easily into very small devices.
- Durability: The eSIM card cannot be touched by the user, so it cannot be damaged or lost.
- Physical security: SIM cards soldered inside enclosed devices are difficult to locate, remove and reuse.
- Cost: eSIMs reduce the total cost of ownership of devices as they optimize and eliminate costly supply chain and management costs.
There are two flavors of Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP) services, as shown below (and Figure 2-1 in the RSP-dedicated section here). The first is a consumer solution that enables a smartphone device to request or pull the desired profile based on the user's needs. The second flavor is an M2M (machine-to-machine) solution where fleet owners can push SIM profiles and required data to unattended devices in the field. This applies to many cellular IoT deployments.
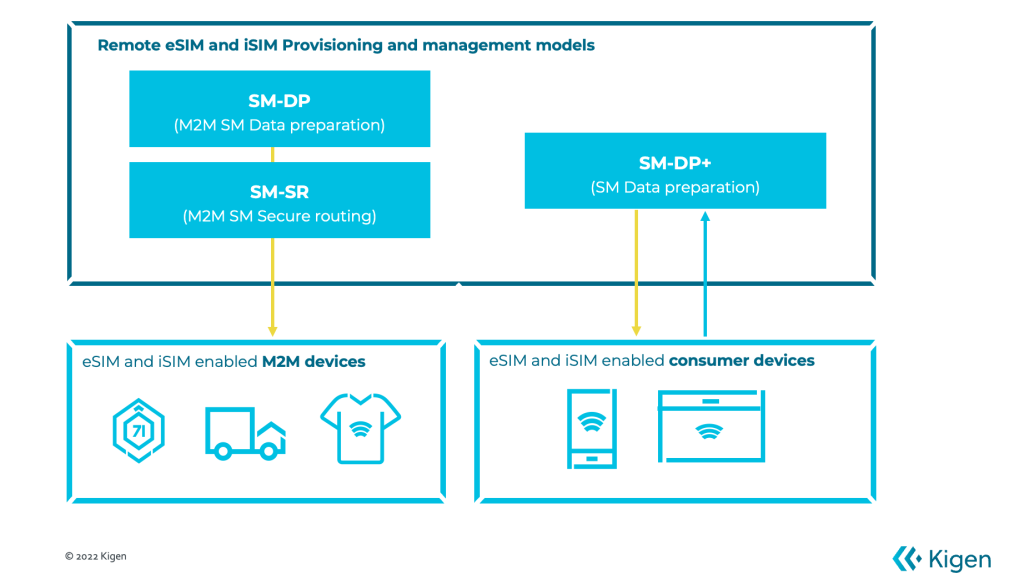
Remote eSIM and iSIM configuration and management mode
Given that leading OEMs are targeting eSIM-only devices, the technical advantages of eSIM itself should be enough to push device manufacturers to adopt the technology. However, eSIM combined with the remote SIM provisioning feature has more favorable factors.
The combination of eSIM and remote SIM provisioning enables manufacturers to dramatically simplify procurement arrangements. It will enable devices to be connected remotely and wirelessly and securely delivered globally throughout the device's lifetime.
Trends in eSIM innovation this year and beyond
Device manufacturers should pay attention to five key aspects of eSIM innovation:
1. Make full use of 5G technical standards through low-power network LPWAN
NB-IoT and LTE-M were originally developed for the 4G LTE standard. However, 3GPP, the standards body responsible for 5G as well as NB-IoT and LTE-M standards, has included NB-IoT and LTE-M as part of the 5G standard.
2. Utilize terrestrial and non-terrestrial network designs for enhanced coverage
With 3GPP release 17 and upcoming release 18 defining the Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) for NB-IoT as part of the next 5G standard, device manufacturers can now take advantage of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and Geostationary Orbit (GEO) Satellite constellations provide additional service and support. Only 30% of the Earth's surface has terrestrial network coverage. With the advent of asset tracking, logistics, emergency services and value-added solutions, enhancing coverage without changing current designs can provide a radical approach to creating a unique customer experience.
3. Improve reliability and simplify SIM inventory for your production
OEMs or device manufacturers managing a large number of customers can now receive the eSIMs they require in discrete, soldered or integrated form factors and transfer ownership of their subscriptions to their customers' Control Center accounts.
4. The remote supply function greatly prolongs the service life of the product
Many IoT devices are designed for the long term. For example, utility device designers and smart city planners hope to create connected devices that can share data within the next 10-15 years. Remote SIM configuration allows you to change user profiles and networks to extend on-site availability.
5. Further reduce electrical bill of materials and total cost of ownership (TCO) with iSIMs
Fewer components means less upstream production to combine three different components into an integrated SoC. The reduction in BoM cost provides significant benefits for devices with low average retail price per unit (ARPU). When one considers devices with higher ARPU, the focus of most device manufacturers and end customers shifts to lifetime operating costs using total cost of ownership (TCO) as a metric.
Build differentiation through savings and new revenue opportunities
In addition to the cost savings already discussed above, eSIM and iSIM technologies offer device manufacturers new revenue-generating opportunities – both for themselves and to pass on to customers.
To this end, another benefit of eSIM and iSIM technology is the proof of root of trust, which becomes the basis for end-to-end security. This ROT must comply with GSMA standards, specifically GSMA's IoT Security.
As an associate member and active contributor to the GSMA IoT Security Standard, Kigen has launched a multi-award-winning open IoT security standard to simplify zero-touch provisioning and trusted service creation. Device manufacturers can simplify how devices register and configure cloud infrastructure, and speed up the delivery of new services. Examples of such services include digital asset brokerage and digital wallet services – we expect to see more in 2023.