The website built by Alibaba Cloud is a fool's way to prohibit foreign IP access

The website built by Alibaba Cloud is a fool's way to prohibit foreign IP access
1 Introduction
The solution is suitable for technical novices, and the content publishing of blog websites is aimed at domestic groups.
Access to foreign IP addresses can be intercepted through domain name resolvers.
For example: This site is mainly for domestic Chinese groups to share relevant knowledge.
Recently, through the logs in nginx, it was found that there are a large number of attack visits from foreign IPs. If we use a firewall to intercept ip, it will be more cumbersome.
No matter what kind of manual protection, it cannot avoid being attacked.
Finally, sum it up. There are also various automatic attacks in China. But more is the access of foreign ip.
So, just think about whether there is a way to directly ban it?
Yes, and the method is relatively simple.
2. Alibaba Cloud DNS resolution
First, through the Alibaba Cloud workbench, access the DNS function of Cloud DNS. Then find the domain name you need to restrict and add the resolution configuration
Click the: Add Record button in the image above.
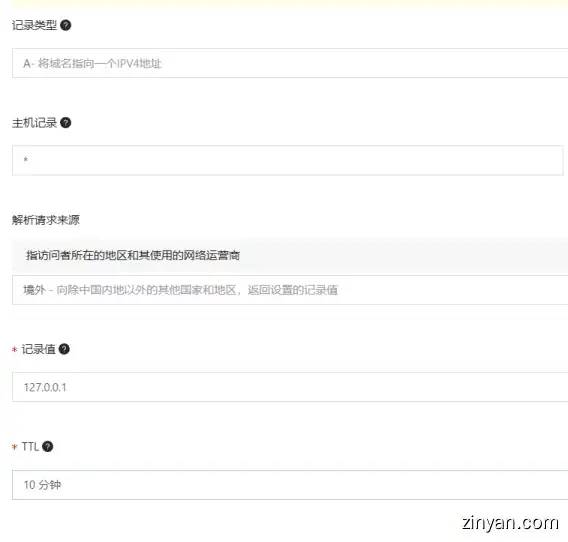
First, configure the record type: A, host record: * represents all the sub-domain names under the domain name and so on.
The most important thing is to parse the two parameters of request source and record value.
We choose: Overseas
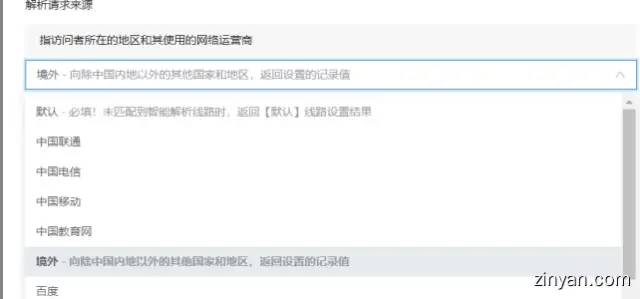
When all regions and countries other than mainland China visit our domain name, they will directly point to the address of the record value filled in below.
2.1 Explanation
Explain a little bit about the relationship between the request source and the record value.
All domain name addresses are ultimately pointed to a specific IP address through the DNS server.
And the various parameters we configure here are telling the DNS server if someone visits our domain name. So what ip should you return to it.
The record value is the ip to be returned.
For example, when configuring access to all overseas IPs, we assign the domain name to the IP address 127.0.0.1. This ip address is the local ip address of all computers.
That is to say, all foreign visitors to our domain name will eventually visit its local machine.
PS1: You can also allow visitors to access other servers through this. Adjust according to your actual needs.
When we are done configuring, save it. That's it.
PS2: After the configuration is complete, according to the actual use experience. Not 10 minutes later, all the IPs accessed outside the world point to the address we defined.
Instead, there will be a gradual update process. After all, it takes time for the server to update and synchronize. Especially the refreshing of this dns configuration. So, wait a little longer,
As far as my personal experience is concerned, after two days, nginx logs will still receive visits from foreign ip. But it can be clearly felt that it has been reduced.
3. Other
When we configure foreign ip to access the domain name to prohibit it. Please note that if the other party can still access our server directly through ip.
At this time, we can filter through nginx and directly return 404 or 444 for all ip address visits. For details, please refer to my article:
Nginx configuration prohibits direct access to web services through ip addresses
3.1 Record Type
To expand, when we add dns record types, we have many options:
You only need to grasp one core point, no matter what kind of records, the goal is to guide users to specific servers for processing when they visit our domain name.
And different record types, it affects the type of record value and parameter format.
- A: Point the domain name to an IPV4 address. That is, after configuring this record type, when we add the record value below, we can only fill in an ipv4 address
- CNAME: Point the domain name to another domain name. Usually it is a CDN service, etc. The other party accesses our domain name address, but the actual data needs to be provided by a third-party service provider, such as oss, CDN, etc.
- AAAA: Point the domain name to an IPv6 address. If we have an ipv6 server address, then we need to configure this option to direct the domain name to the ipv6 server.
- NS: Point the subdomain name to other DNS servers for resolution. We can specify the second-level domain name and other sub-domain names to be resolved by the DNS server of the giant group. (personal use is relatively small)
- MX: Point the domain name to the mail server address. It is usually used when building a mail server, but it is rarely used by individuals now.
- SRV: A server that provides a specific service. In fact, the service information provided by the server is recorded through this logo, which is generally used when setting up Microsoft's active directory. (There are more special server configurations and fewer individuals)
- TXT: Text record type, the length limit is 512, usually as SPF record. A common situation is that when various manufacturers need to verify whether our domain name belongs to them, they add txt records. It will not affect the normal access of the domain name.
- CAA: CA certificate authority authorization verification. It is similar to txt, but it is used by CA certificate for domain name authentication detection. (Individuals can ignore it temporarily, it does not affect)
- Explicit URL: Redirects the domain name to another address. For example, if we want to redirect all requests to access a second-level domain name to other domain names, we can use this configuration directly. Instead of going through the redirection function of software such as nginx.
- Stealth URL: Redirects the domain name to another address, but hides the real target address. Unlike the explicit URL, when redirecting, it will not tell the visitor which URL you are visiting now.