Whose encryption key is written in the code?

Whose encryption key is written in the code?

System design, protocol first.
Most people do not understand the design details of the protocol, and use the existing protocol for application layer design, such as:
- Use HTTP, design get/post/cookie parameters, and json package format;
- Use dubbo instead of delving into the details of the binary header package inside;
In any case, understanding the principles of protocol design is very helpful for a deeper understanding of system communication.
First, the layered design of the protocol
The so-called "agreement" is the rule that both parties abide by, such as divorce agreement, truce agreement. The protocol has three elements: syntax, semantics, and timing:
- syntax, i.e. the structure or format of data and control information;
- semantics, i.e. what control information needs to be sent, what actions need to be done, and how to respond;
- Timing, i.e. a detailed description of the order in which events are implemented;
Voiceover: The following text focuses on grammatical design.
Protocol design is generally divided into three layers: application layer protocol, security layer protocol, and transport layer protocol.
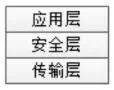
Let's take a look at how the protocols of these three layers should be selected.
Second, application layer protocol design
There are three common application layer protocol types: text protocol, binary protocol, and streaming XML protocol.
(1) Text Agreement
Text protocol refers to the communication transmission protocol "close to human written language expression", the typical protocol is HTTP protocol, an HTTP protocol request message sample such as the following:
GET / HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: curl
Host: musicml.net
Accept: */*- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
The characteristics of the text protocol are:
- Good readability, easy to debug;
- Good scalability, can be extended through key:value;
- The parsing efficiency is not high, read line by line, split according to the colon, parse the key and value;
- Not binary friendly, such as voice/video, etc.;
(2) Binary Protocol
The binary protocol is the binary protocol, typically the IP protocol, the following is a diagram of the IP protocol:
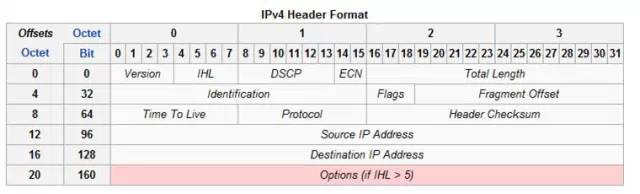
Binary protocols generally include: Generally include:
- Fixed length baotou;
- Expandable variable-length package;
- Generally, each field has a fixed meaning, taking the IP protocol as an example, the first 4 bits represent the protocol version number (Version);
The features of the binary protocol are:
- poor readability and difficult to debug; Voiceover: Journaling generally requires a toString() function to enhance readability.
- The extensibility is not good, if you want to extend the field, the old version of the protocol is not compatible, so there will generally be a Version field when designing;
- The parsing efficiency is super high, there is almost no parsing cost, and each field of the binary stream represents a fixed meaning;
- Natural support for binary streams, such as voice/video;
Here is a typical example of a 16-byte binary fixed-length header:
//sizeof(cs_header)=16
struct cs_header {
uint32_t version;
uint32_t magic_num;
uint32_t cmd;
uint32_t len;
uint8_t data[];
}__attribute__((packed));- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
Thereinto:
(1) The first 4 bytes indicate the version number version;
(2) The next 4 bytes represent the magic number magic_num, which is used to solve the problem of data misalignment or packet loss;
Voiceover: For example, agree that the magic number is 0x01020304, the received message, the magic number matches, it is considered a normal message, otherwise it is considered an abnormal message and disconnected.
(3) The next 4 bytes indicate the command number command, and different command numbers correspond to different variable-length packages;
(4) The last 4 bytes indicate the length of the packet body to determine how many bytes the variable-length packet is;
Here is an actual binary variable-length package:
message CUserLoginReq {
optional string username = 1;
optional string passwd = 2;
}
message CUserLoginResp {
optional uint64 uid =1;
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
It uses Google's Protobuf protocol and is easy to see:
- The user name and password are passed in the request packet;
- The response packet returns the user's UID;
PB is a popular binary variable-length packet protocol, and its advantages are:
- Universal, can generate C++, Java, PHP and other multilingual code;
- Built-in compression function;
- Binary friendly;
- It has been widely used in the industry; Voiceover: Produced by Google, it must be a boutique.
Streaming XML Protocol Streaming XML seems to be a special case of text protocols and can be used as a separate class. For example, xmpp is a typical streaming XML protocol, and the following is a typical message of the xmpp protocol:
<message
to=’romeo@example.net’
from=’juliet@example.com’
type=’chat’
xml : lang=’en’>
<body>Wherefore art thou, Romeo?</body>
</message>- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
From the XML tag, you can roughly tell that this is a chat message sent by Romeo to Juliet.
The XML protocol has several features:
- Good readability and good extensibility, which is a feature of XML;
- The analysis cost is super high, and DOM tree analysis is required;
- The effective data transfer rate is ultra-low, with a large number of tags;
- Not binary friendly, such as voice/video, etc.;
Third, the security layer protocol design
Security layer protocol design, in addition to the use of SSL, self-implementation, there are three common solutions.
Voice over: SSL key management is a problem.
(1) Fixed key
The server and the client agree on a key, and at the same time agree on an encryption algorithm (for example, AES), each time before the client sends a packet, the agreed algorithm and the agreed key are encrypted and then transmitted, and after the server receives the packet, it uses the agreed algorithm and the agreed key to decrypt it.
Voiceover: Low security, security based on the programmer's professional ethics.
(2) One person, one secret
Simply put, a person's key is fixed, but it is different from person to person. Common implementations are:
- Fixed encryption algorithm;
- The encryption key uses "a special attribute of the user", such as the user's UID, mobile phone number, QQ number, user password, etc.;
(3) One secret at a time
That is, the dynamic key, one session and one key have higher security, and the key is negotiated before each session. The process of key negotiation goes through 2 random generation of asymmetric keys and 1 random generation of symmetric encryption keys, the specific details are not expanded here.
Fourth, the design of transport layer protocol
Optional protocols are TCP and UDP, now basically use TCP, with epoll and other technologies, multi-connection is not a bottleneck, single hundreds of thousands of links are no problem.