From R15 to R17, an article to understand the technological innovation of 5G

From R15 to R17, an article to understand the technological innovation of 5G

In early June 2022, the 96th plenary meeting of the communication standard organization 3GPP was held in Budapest, Hungary as scheduled.
At this meeting, the high-profile 3GPP R17 standard was officially announced to be frozen. This marks that the first stage of 5G evolution has been completed, and the development of 5G technology will enter a new second stage.
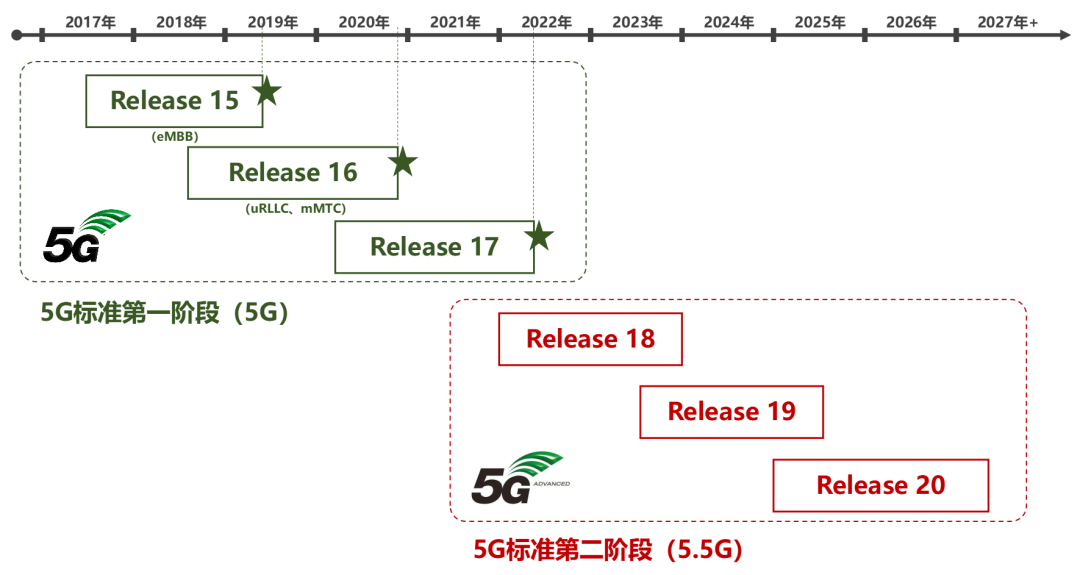
Looking back , about 7 years ago, in September 2015, ITU officially confirmed the three major application scenarios of 5G (eMBB, mMTC and uRLLC). Soon after, in March 2016, 3GPP officially launched the 5G standardization work, aiming to develop a unified and more powerful wireless air interface - 5G NR (New Radio, new air interface).
Today, time flies, and we have witnessed the freezing of 3GPP R15, R16, and R17 versions, as well as the full commercialization and popularization of 5G.
5G, which has high hopes, has experienced a development process from birth to maturity. It is constantly changing our work and life, and subverting the operation mode of the entire society.
So the question is, what revolutionary technological innovations have emerged during the continuous evolution of 5G? What kind of logical thinking lies behind these technological innovations? From R15 to R17, what is the role of each stage?
In today's article, Mr. Xiaozao will lead you to find the answer.
R15: Lay the foundation, lift the veil
First of all, let's take a look at the innovative ideas of R15.
R15 is the beginning of 5G standard formulation. As the saying goes: "A good start is half the battle." In order to take a solid first step, experts in the communication industry have conducted sufficient research and preparation.
At that time, the most important mission of R15 was to formulate standards for eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) scenarios. In this scenario, what is needed is the most important indicator of the communication network - the speed.
The ITU's requirements for eMBB indicators are that the peak downlink rate must reach more than 10Gbps, and the user experience rate must reach more than 1Gbps. In order to realize this requirement, 3GPP adopts two ideas: one is to find more available spectrum resources, and the other is to deeply tap the potential of each MHz frequency resource.
In terms of expanding spectrum resources, 3GPP proposed mobile millimeter wave technology based on the Sub-6GHz frequency band . In other words, the 5G operating spectrum is extended to higher frequency bands, covering the millimeter wave frequency band.
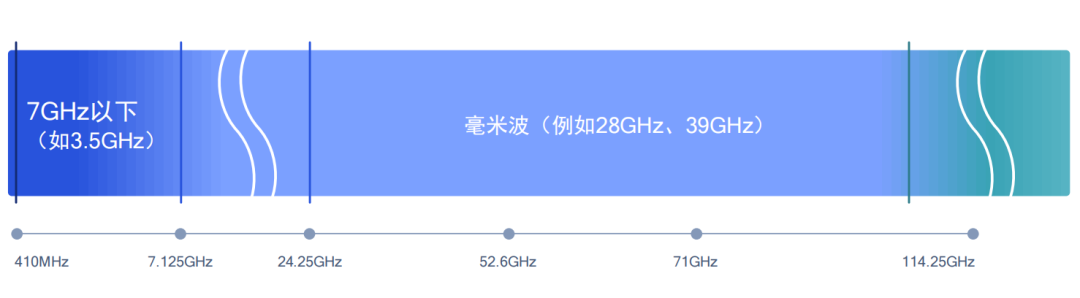
The rate and capacity improvements brought by mobile millimeter waves are very obvious, laying the foundation for 5G high-speed connections.
On the basis of millimeter wave technology, 3GPP has introduced Massive MIMO (large-scale antenna array).
This technology is one of the most iconic innovations of 5G, and it can be said to be a "magic stroke". It forms independent narrow-beam coverage for different users by greatly increasing the number of antennas in the base station, thereby increasing the system throughput by dozens of times and improving the coverage effect of the base station (especially making up for the lack of millimeter wave coverage. ).
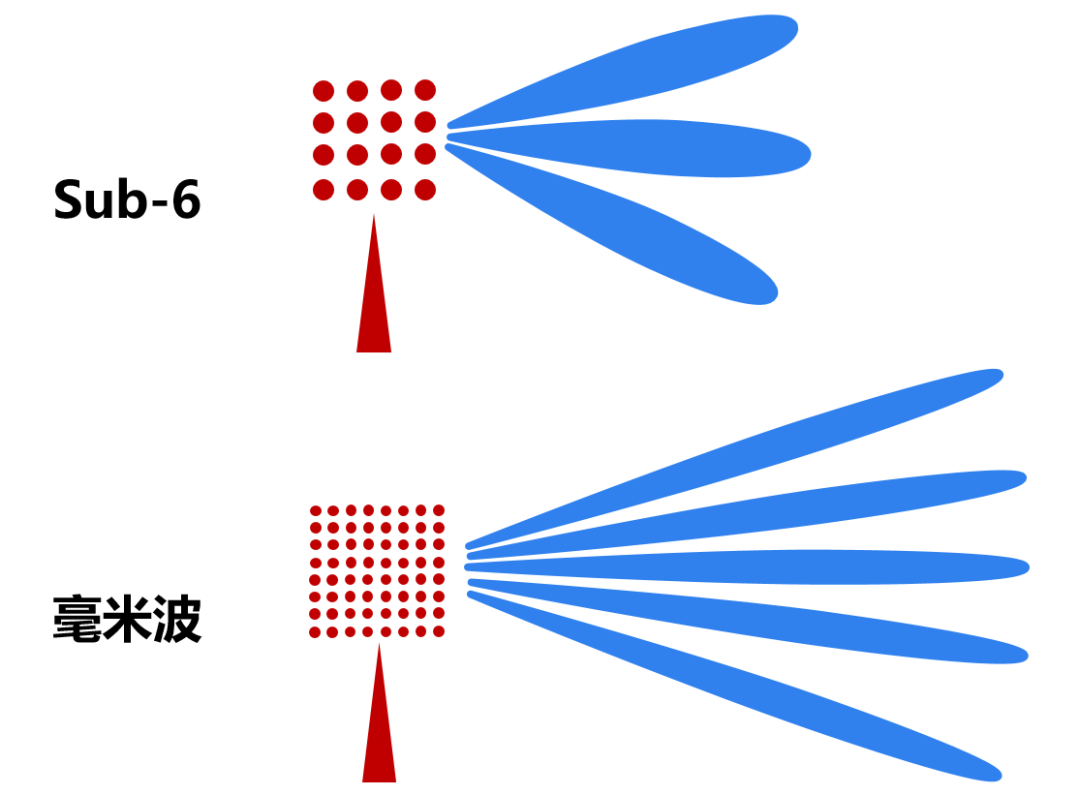 Massive MIMO
Massive MIMO
In terms of deeply tapping the potential of spectrum resources, the technical challenges are even greater. This involves a large number of underlying technology innovations, including multiple access technology, modulation technology, coding technology, physical layer structure, etc., all of which need to be redesigned.
One of the most important decisions in 5G NR design is the choice of radio waveform and multiple access technology.
During the program evaluation process at that time, Qualcomm found through extensive research that the Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system, specifically including cyclic prefix Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (CP-OFDM) and discrete Fourier transform Frequency Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (DFT-S OFDM), is the best choice for 5G eMBB and more other scenarios (it turned out to be true later).
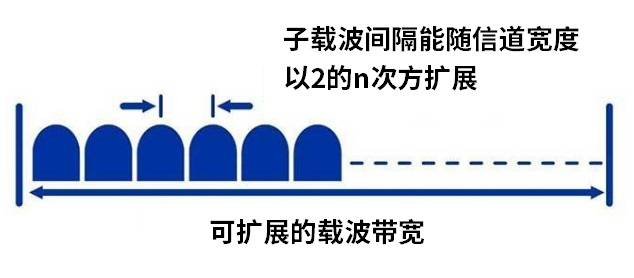
On the basis of existing OFDM applications in 4G LTE, Qualcomm Senior Engineering Director Ji Tingfang designed a unified subcarrier spacing index expansion formula to realize scalable OFDM parameter configuration. This technical invention, known as the "Extensible Parameter Set", is a major highlight of R15.
By using the scalable OFDM parameter configuration, the subcarrier spacing can be extended by the nth power of 2 with the channel width. This allows the FFT point size to expand in larger bandwidth systems without increasing processing complexity.
Another refreshing design of the R15 is the slot-based flexible frame. The key technical invention of this flexible framework is the 5G NR self-contained slot structure . In the new self-contained slot structure, each 5G NR transmission is processed modularly, capable of independent decoding, avoiding static timing relationships across slots.
In June 2018, the 3GPP R15 standard was officially frozen. Now it seems that R15 has successfully fired the first shot of 5G. The many innovations it brings have unveiled the mystery of 5G for people, and also laid a solid foundation for the subsequent iterative evolution of 5G.
R16: Scenario expansion, enabling industries
R15 mainly develops standards for eMBB (enhanced mobile broadband) scenarios. On the basis of R15, R16 further improved the standard specifications of uRLLC and mMTC scenarios, thereby contributing the first complete 5G standard and the first 5G evolution standard.
In essence, supporting and empowering vertical industries is the most important mission of R16.
R16 requires standardized uRLLC (ultra-reliable low-latency communication) scenarios, which are mainly aimed at vertical industries such as industrial Internet and Internet of Vehicles. The indicators proposed by the ITU for the uRLLC scenario include stricter reliability requirements (up to 99.9999% reliability) and millisecond-level latency.
R16 needs to further enhance the basic capabilities of 5G networks and introduce more new network features, so as to better support key business use cases of toB and meet the needs of vertical industries such as smart manufacturing, smart quality inspection, and driverless driving.
In terms of enhancement of basic network capabilities, R16 has specially optimized and enhanced spectrum efficiency, network utilization, and robustness, including large-scale antenna enhancements, carrier aggregation enhancements, and handover technology enhancements, which have greatly improved Availability and perfection of 5G.
In terms of the introduction of new features, the performance of R16 is even more remarkable.
Taking spectrum expansion as an example, R16 adds support for 5G NR license-free spectrum (NR-U), including two modes: license-assisted access (LAA), and independent deployment that does not require any licensed spectrum. This not only brings greater capacity, but also enables more flexible deployment.
For the aforementioned reliability and latency requirements, Qualcomm-led Cooperative Multipoint Communication (CoMP) is one of the key enabling technologies to achieve this goal. In this technological innovation, by adopting multiple transmit and receive points (multi-TRP), create space diversity with redundant communication paths, achieve high reliability and low latency, and build a usable time-sensitive network (TSN).
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) is an important vertical application field of 5G. In this field, the direct-to-connect communication (D2D) promoted by Qualcomm and other companies is an important technological innovation, which can realize V2X support for vehicle formation, semi-autonomous driving, extension sensors, remote driving and other richer car networking application scenarios.
In terms of networking technology, R16 introduces remote interference management, wireless relay, network organization and self-optimization technology, which improves the actual user experience of the network.
Typical examples are new interference measurement and mitigation technologies (such as RIM/CLI), and integrated access and backhaul (IAB).
Integrated Access and Backhaul (IAB) supports millimeter-wave base stations for wireless access and backhaul, which can effectively reduce the need for new fiber deployment when deploying dense networks.
It is particularly worth mentioning that in order to better promote the implementation of 5G in the vertical industry of government and enterprises, R16 has also innovated in the private network deployment mode, and launched support for non-public networks (NPN), which provides support for 5G private network communications. Development points the way.
R16 introduces many new features. In addition to the above technologies, it also includes terminal energy saving, enhanced terminal mobility, and high-precision positioning.
In July 2020, the R16 standard was officially frozen.
If R15 only realizes a "usable" 5G, then the role of R16 is to turn "usable" 5G into "easy-to-use" 5G. It has undergone in-depth enhancements and improvements in cost, efficiency and functionality, paving the way for the full implementation of 5G.
R17: Capability upgrade, application exploration
It's finally R17!
If one word is used to describe the positioning of R17, it is " inheriting the past and ushering in the future ".
As the third major version of the global 5G NR standard, R17 further expands the 5G technical foundation in terms of network coverage, mobility, power consumption, and reliability, and broadens 5G to new use cases, deployment methods, and network topologies.
The keywords of R17 evolution can be divided into "enhancement" and "extension".
- Enhancement of basic network capabilities
R17 is a standard formulated after 5G commercial use. Therefore, it can "check for leaks and make up for gaps" based on the actual deployment experience of 5G in the early stage and the deficiencies found.
R17 brings more enhancements to the basic capabilities of 5G systems such as capacity, coverage, delay, energy efficiency, and mobility, including Massive MIMO enhancements, coverage enhancements, terminal power saving, spectrum expansion, IAB enhancements, and uRLLC enhancements, etc. .
Let's start with the spectrum.
Release 17 extends the spectrum of 5G millimeter waves and defines a new unique frequency range called FR2-2, which pushes the upper limit of millimeter wave spectrum to 71 GHz.
This means that the network capacity of 5G mmWave will become larger, and more use cases and deployment methods will be realized. For example, the millimeter wave enterprise private network that supports communication and positioning functions in the smart manufacturing industry.
Thanks to the 5G NR Scalable Subcarrier Spacing (SCS) scheme and slot-based flexible frame structure, this frequency band extension can directly extend the subcarrier spacing of control and data channels to 480 kHz and 960 kHz (previously low-band mm wave is 120 kHz).
In addition to frequency band expansion, R17 also brings other mmWave enhancements, including support for inter-band uplink/downlink carrier aggregation and enhanced mobility.
IAB (Integrated Access and Backhaul) enhancements come from features such as simultaneous transmit/receive (i.e. full-duplex) and enhanced multi-hop operations, which can further improve deployment efficiency, coverage, and performance. This is especially useful for mmWave deployments, where it is more cost-effective and efficient to rapidly expand coverage.
In terms of terminal capability enhancement, in order to improve user experience, R17 proposes a series of enhanced features.
Examples include support for up to eight antennas and additional spatial streams for higher throughput; advanced MIMO enhancements for increased capacity, throughput, and battery life; new power-saving features for connected and idle modes that extend Battery life; retransmission and higher transmission power can improve the network coverage of the terminal; 5G positioning technology enhancement can improve positioning accuracy and delay; dual card dual standby can support two subscription services of one or two operators concurrent; etc.
- 5G network and terminal application expansion
R17, as a transition between the first and second phases of 5G, not only needs to enhance the existing 5G, but also explores the application possibilities of more 5G scenarios. These possibilities include RedCap, non-terrestrial networks (NTN), extended direct communication, centimeter-level positioning, extended broadcast/multicast, and unbounded XR (extended reality).
The most representative technology introduced by 5G R17 is, of course, RedCap, or NR-Light, for medium and low-speed IoT applications.
RedCap is a simplified version of 5G. By reducing the complexity of the protocol and adopting better energy-saving technologies, it can meet the needs of the Internet of Things such as wearable devices, industrial sensors, and surveillance cameras.
Another new feature of R17 that deserves attention is the non-terrestrial network (NTN).
In recent years, there has been an increased interest in satellite communications. In order to allow 5G to provide ubiquitous connections, 3GPP has also strengthened research on network coverage in non-terrestrial areas. In Release 17, there are two parallel NTN working groups addressing mobile broadband and low-complexity Internet of Things (IoT) use cases.
The first project uses the 5G NR framework for satellite communications, enabling fixed wireless access (FWA) backhaul from the ground to satellites, and providing low-rate data services and voice services directly to smartphones. The second project focuses on supporting satellite access for low-complexity eMTC and NB-IoT terminals, expanding network coverage for key use cases such as global asset tracking.
The last new direction of R17 I want to mention is Unbounded XR.
The Metaverse, which exploded last year, showed us a personalized digital experience that spans the physical world and the virtual world. As the underlying supporting technology of the metaverse, XR extended reality technology represented by VR and AR has received more attention.
The XR project in R17 focuses on researching and defining various types of XR traffic (AR, VR, cloud games). This study defines requirements and assessment methodologies for the identified XR traffic types and supports performance assessments to identify areas for future enhancements.
epilogue
Someone once said that the development process of 5G from R15 to R17 is like a process of building a house:
The R15 version is the "rough room" of the 5G technical standard, which has established the foundation and framework. The R16 version is a "finish decoration" of the 5G standard, making it have the initial "living conditions". The newly released R17 version is "soft decoration" on top of "hardcover", which has the effect of icing on the cake and makes the living experience better.
And it is. The first stage of 5G is a process of dynamic expansion. Mobile communication technology begins to empower the Internet and digital intelligence transformation of the industry.
Through the technological innovations mentioned above, we are constantly challenging the limits of Shannon's theory and exploring the future development direction of communication technology.
Judging from the current phased results, 5G has laid a connection foundation for the digital transformation of the entire society through these highly disruptive technological innovations. A large number of 5G vertical industry landing cases have greatly enhanced people's confidence in 5G and the digital economy.
Looking ahead, we are about to enter the 5G-Advanced era. The first standard version of 5G Advanced, R18, has been fully launched. It will start a new round of wireless technology innovation and escort the prosperity and development of the digital economy.
What kind of excitement is waiting for us? Let us wait and see!