How is the overlay network formed?


With the development of network technology, the layer 2 networking structure of the data center has undergone periodic architectural changes. The data center network is divided into two parts: Underlay and Overlay, and the network has entered the stage of Overlay virtualization. So how is the Overlay network formed? How is it different from Underlay? What problem are you trying to solve?
Underlay Network
The underlay network is a physical network responsible for transmitting data packets. It consists of switches and routers and other devices, driven by Ethernet protocols, routing protocols, and VLAN protocols. All network components of Underlay must use routing protocols to determine IP connectivity.
For Underlay networks, a well-designed L3, including campus edge switches, etc., needs to be established to ensure network performance, scalability, and high availability.
Underlay protocol: BGP, OSPF, IS-IS, EIGRP.
Overlay network
Overlays are logical networks connected on top of physical infrastructure using network virtualization. Compared with UnderLay network, Overlay realizes the separation of control plane and forwarding plane, which is also the core concept of SDN.
The VXLAN protocol is one of the most popular overlay network tunneling protocols. It is one of the NVO3 (Network Virtualization over Layer 3) standard technologies defined by the IETF. It adopts the L2 over L4 (MAC-in-UDP) packet encapsulation mode. By encapsulating Layer 2 packets with Layer 3 protocols, the Layer 2 network can be expanded within the scope of Layer 3, and the “Layer 2 domain” can break through the scale limitation to form a “large Layer 2 domain”.
Through the OverLay technology, one or more logical networks can be created on the existing physical network through the tunnel technology without any modification of the physical network, which effectively solves many problems existing in the physical data center and realizes the data center automation and intelligence.
Overlay protocols: VXLAN, NVGRE, GRE, OTV, OMP, mVPN.
Some limitations of the Underlay network
Traditional routing protocols build a list of routing prefixes, with each routing entry pointing to the IP address of the next hop. This means that each packet is forwarded hop-by-hop through the network to its destination according to the routing table. This hop-by-hop routing behavior has many inefficiencies, such as:
(1) Network segmentation and network slicing are difficult to implement on a large scale:
- The hop-by-hop transmission of segment labels in the network requires complex control plane interactions between VRF, MPLS, and MP-BGP.
- Network slicing and multi-tenancy are not possible.
(2) Multi-path forwarding is cumbersome, and it is impossible to integrate multiple underlying networks to achieve load balancing.
(3) Service chaining does not scale efficiently because it requires manual configuration on multiple devices.
(4) The Internet cannot guarantee the security requirements of private communications.
Underlay network has many of the above limitations, and Overlay brings flexibility that Underlay cannot provide. So how is the Overlay network formed?
How is the overlay network formed?
Overlay is software based and not transport dependent, it is like a virtual network on top of a physical network.
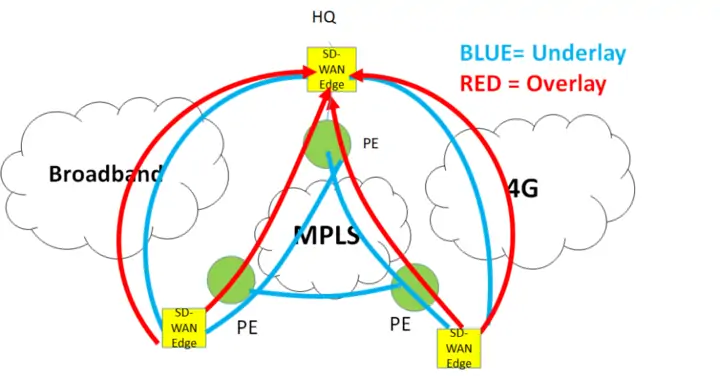
A typical example of an overlay network is an Internet VPN, which builds a virtual closed network on the Internet. Communication of private IP addresses is made possible by building virtual networks using protocols such as IPsec. In addition, SDN and SD-WAN also adopt the concept of overlay network.
However, to build an overlay in SD-WAN, a special CPE, called the SD-WAN edge device, is required.
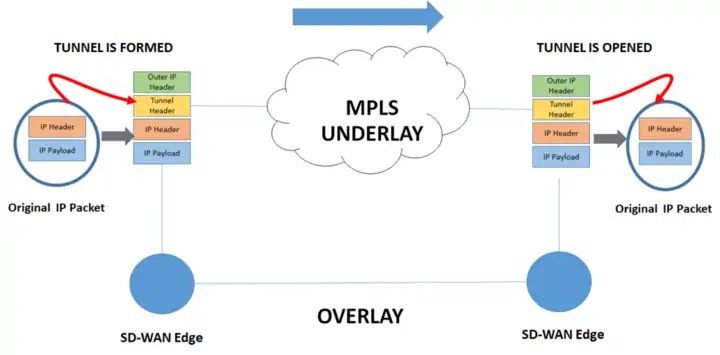
The following uses an SD-WAN edge device to establish a GRE tunnel as an example for description. A tunnel is established between the connected SD-WAN edge devices. When the packet is ready to be transmitted, the device adds a new IP header and tunnel header to the packet, and isolates the inner IP header from the MPLS domain. MPLS forwarding is based on the outer IP. head on.
Once the packet reaches its destination, the SD-WAN edge device removes the outer IP header and tunnel header, resulting in the original IP packet. During the whole process, the Overlay network does not perceive the Underlay network.
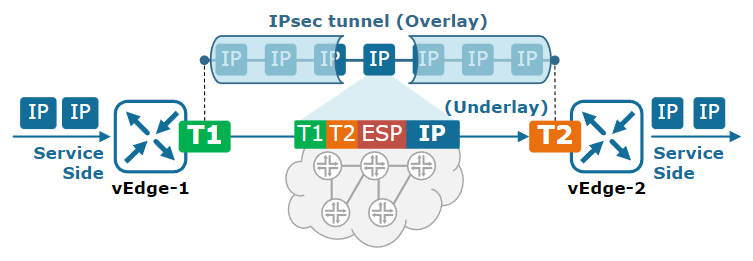
The same process can also be used for Internet Underlay, but requires encryption with IPSec.
How does the overlay network solve the problem?
(1) The use of encryption technology can protect the communication of private traffic on the Internet.
2) Traffic transmission does not depend on a specific line. The overlay network uses tunnel technology, which can flexibly select different underlying links and use various methods to ensure stable traffic transmission.
(3) Support multi-path forwarding. In an overlay network, traffic can be transmitted from the source to the destination through multiple paths, so as to achieve load balancing and maximize the utilization of the line bandwidth.
4() Supports network slicing and network segmentation. By dividing different services, the optimal allocation of network resources can be achieved.
Overlay vs UnderlaySummary
