Networking in Illustrated: What is Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol VRRP?

VRRP is a commonly used fault-tolerant protocol, which can improve the reliability of the network. Today, Ruige and you will introduce the VRRP protocol in detail.
Let's jump right in!
What is VRRP?
- English full name: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
- Chinese name: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
- Protocol: IETF - RFC 3768
- Multicast address: 224.0.0.18
- network layer protocol
- Agreement number: 112
VRRP terminology
- VRRP router: A router running VRRP, which may belong to one or more virtual routers.
- Virtual IP address: The IP address is assigned as a virtual IP address from the local subnet.
- Virtual MAC address: Use the last 8 bytes of hexadecimal as the VRRP group number to automatically generate a virtual MAC address.
- Master router: The master router is elected based on priority, if a member of a VRRP group has a higher priority than other group members, it will be elected as the master router.
- Backup router: Only one of the VRRP group members becomes the master router, the other members will become backup routers, and if the master router fails, one of the backup routers will become the master router.
How VRRP works
VRRP uses virtual routers to control which physical routers are assigned to the access network. A VRRP group consists of a primary router and one or more backup routers that share a virtual IP address. If the primary router fails, VRRP will automatically assign one of them Backup router without affecting network traffic. When the failed router is up again, it will become the primary router again. VRRP provides this redundancy without requiring user intervention or additional configuration of any device on the network.
The VRRP master router sends a VRRP advertisement message to the backup router. When the VRRP master router fails to send the advertisement message, the backup router with the highest priority takes over as the master router.
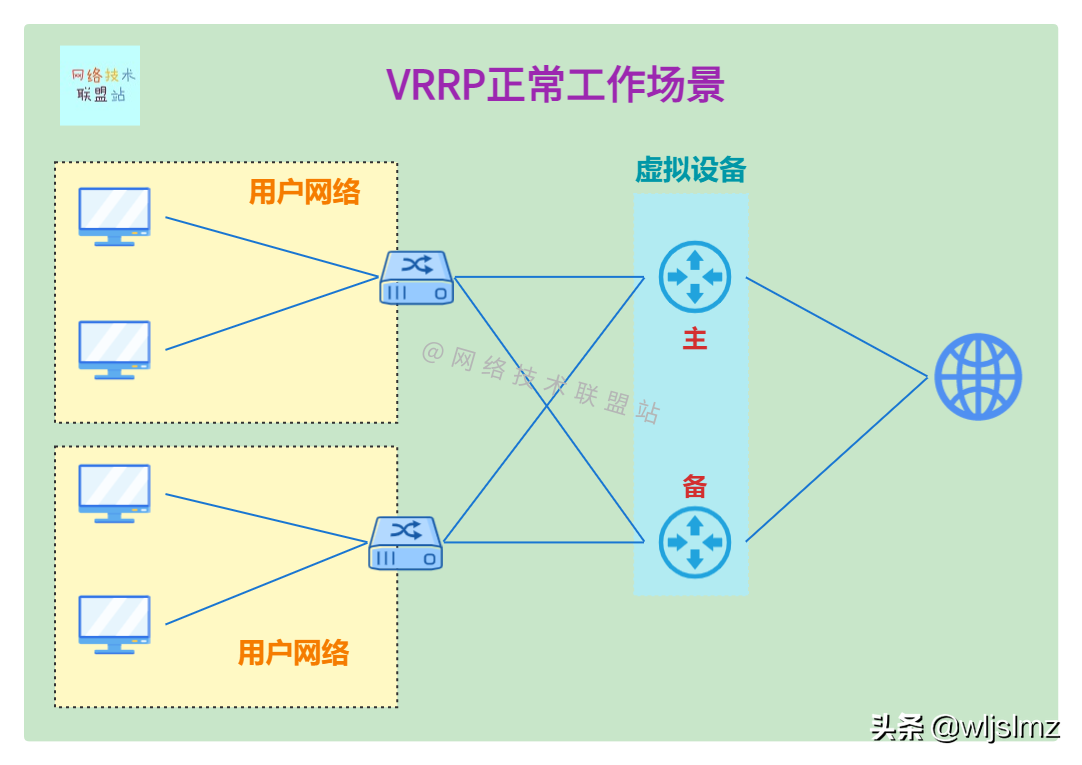
VRRP normal working scenario
As shown in the figure below, there are two virtual devices, the upper one is the main router, and the lower one is the backup router. Now traffic normally goes to the main router:
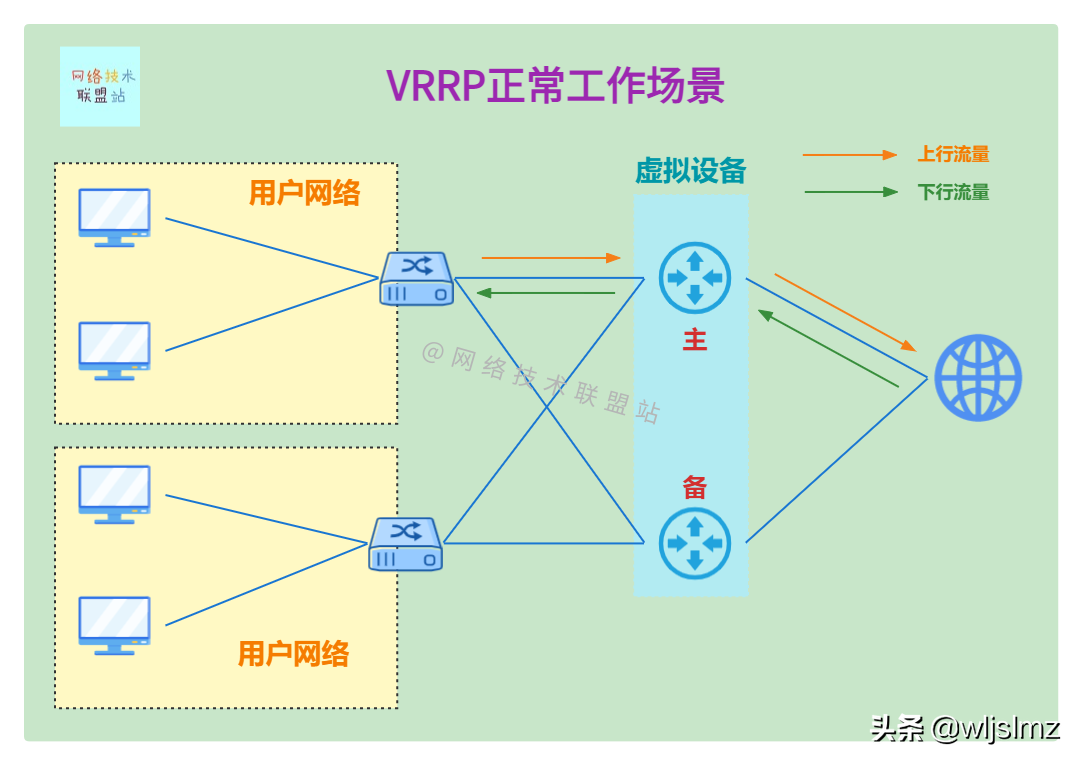
VRRP normal working traffic flow
When the main router fails and goes down:

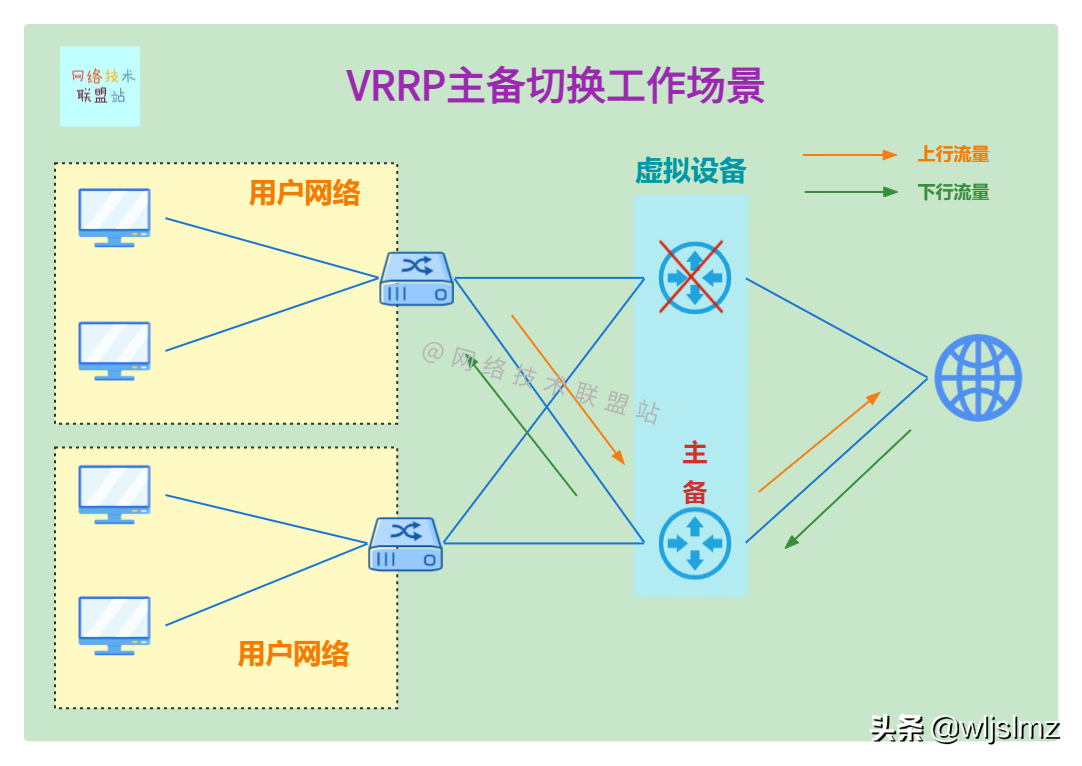
VRRP active/standby switchover working scenarios
At this time, the original backup route quickly becomes the main router, and the traffic is also switched to the backup router. This is the power of VRRP!
Three states of VRRP
VRRP has the following three states:

Initialize initial state
- The Initialize state indicates that VRRP is unavailable, and the device in the Initialize state cannot process VRRP advertisement packets.
- When the VRRP process starts or the device is in the active/standby state and a fault is detected, it enters the initialization state.
Master activity status
- The router obtains the virtual address.
- Responsible for traffic forwarding.
Backup Backup status
- The router is starting up or getting ready to acquire a virtual address in case the primary device fails.
- Traffic forwarding will not be undertaken.
VRRP election mechanism
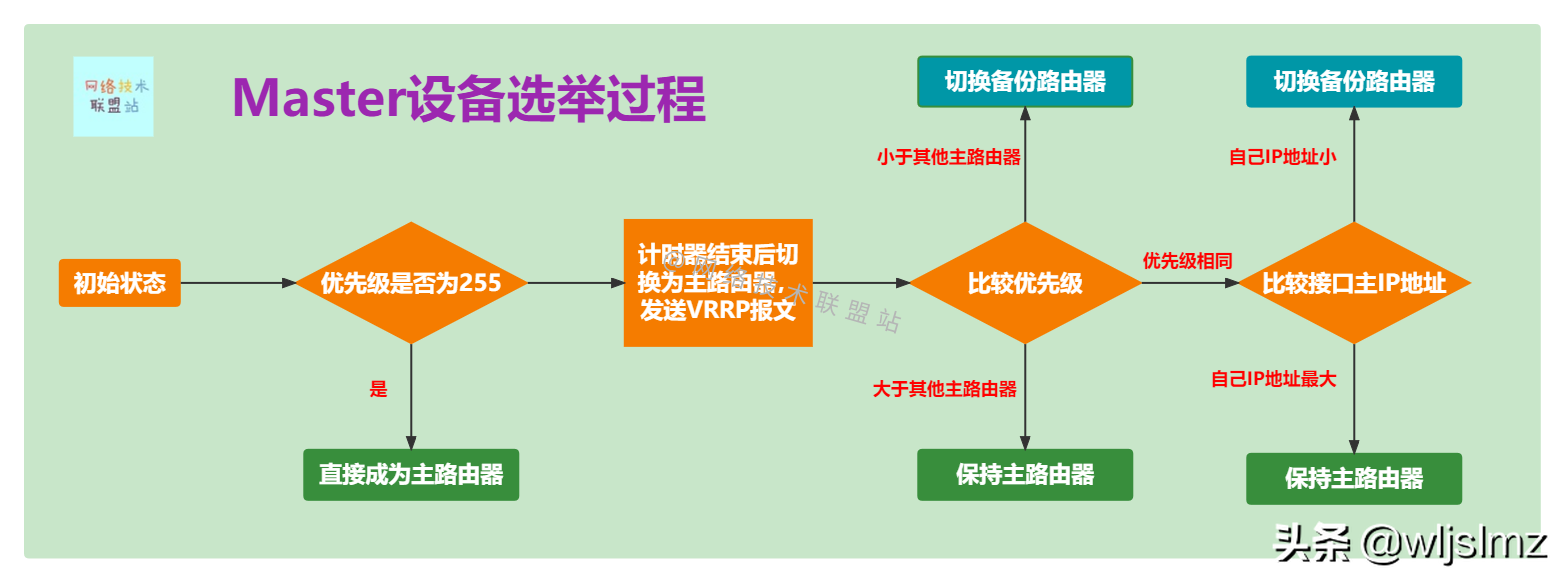
As shown in the picture, no matter how difficult the technology is, as long as the picture is drawn, it is very clear and clear!
The main thing is to pay attention to the selection of the main router according to the priority: the router with high priority is selected as the main router.
If two routers have the same priority, the interface IP addresses are compared and the router with the larger interface IP address will be elected as the primary router.
Other routers serve as backup routers and monitor the status of the Master router at any time.
If the backup router in the group does not receive the message from the master router within the Master_Down_Interval time, it will switch to the master router. In a VRRP group with multiple backup routers, multiple master routers may be generated in a short time, and then The priority in the received VRRP packet is compared with the local priority, and the router with the highest priority is selected as the master router.
case
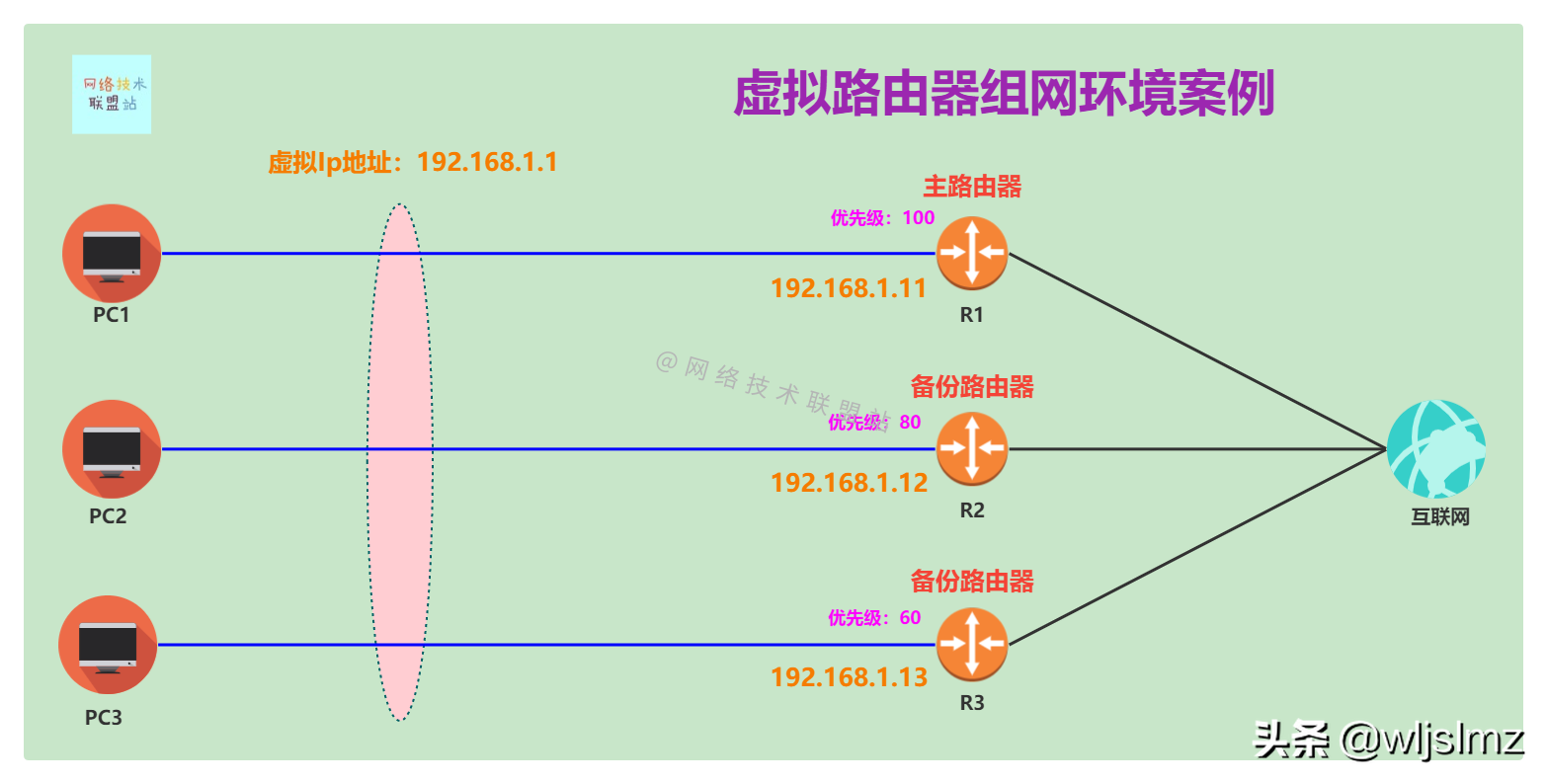
Virtual Router Networking Environment Case - Master Router Election
As shown in the figure, routers R1, R2, and R3 form a virtual router VRRP. The virtual IP address of VRRP is 192.168.1.1. Since the priority of R1 is 100, which is higher than 80 of R2 and 60 of R3, R1 is the master router, that is The main router has an IP address of 192.168.1.11, and R2 and R3 serve as backup routers, with the IP addresses of 192.168.1.12 and 192.168.1.13, respectively.
The default gateways of hosts PC1, PC2, and PC3 in the LAN are set to the VRRP virtual IP address 192.168.1.1. Under normal circumstances, R1, as the main router, is responsible for forwarding packets in the LAN to the external network. When router A is shut down or fails , Router B or Router C (according to the priority) as the backup router will become the main router, and forward the packets of the LAN to the external network, so as to maintain the communication between the LAN and the external network and improve the network reliability.
There are several situations now:
R1 fails, R2 and R3 have different priorities
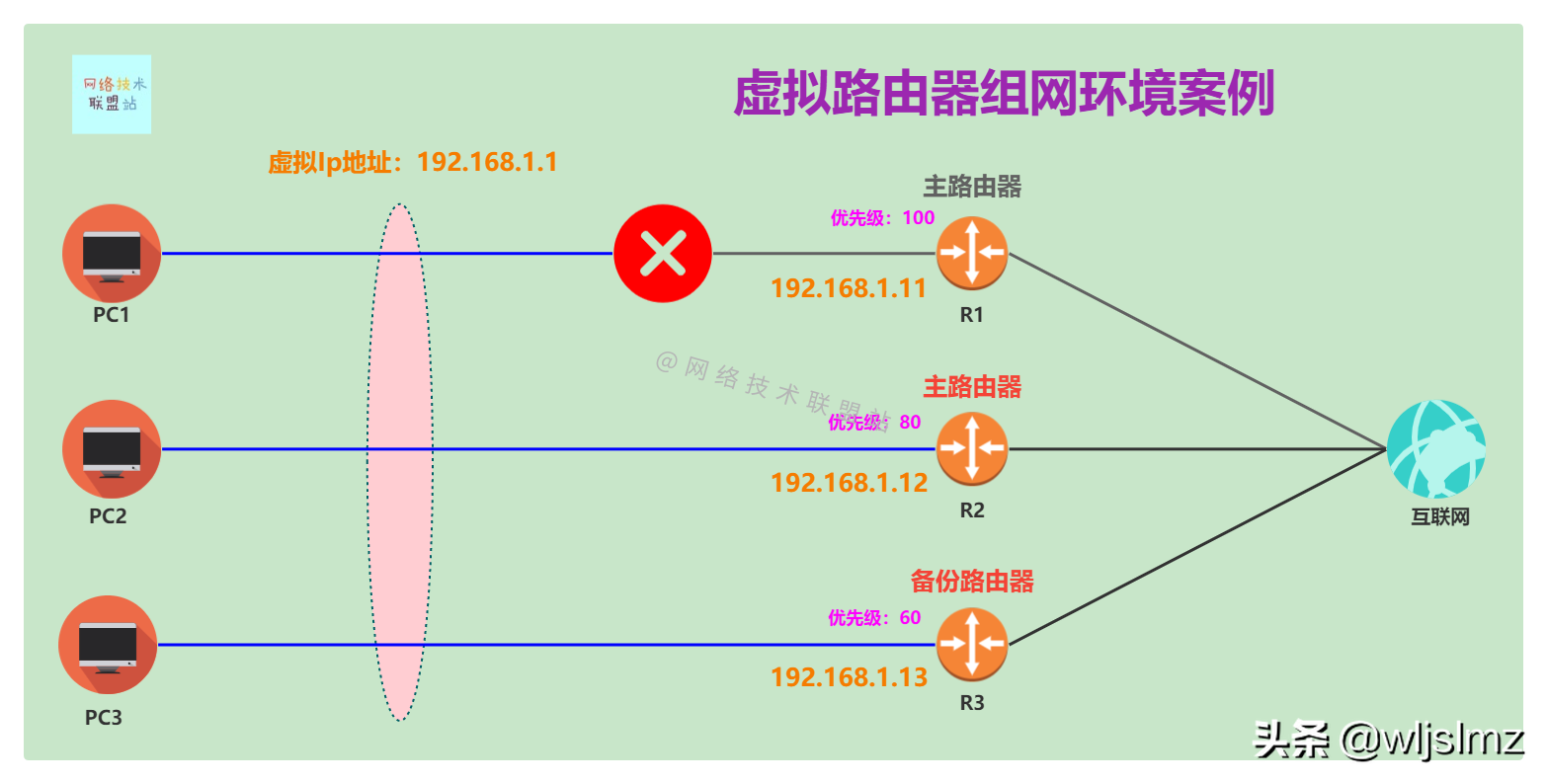
R1 fails, R2 and R3 have different priorities
As shown in the figure, due to the failure of R1, its link has been grayed out. At this time, since the priority of R2 is 80, which is higher than the 60 of R3, R2 is the primary router, and R3 is still the backup router.
R1 fails, R2 and R3 have the same priority
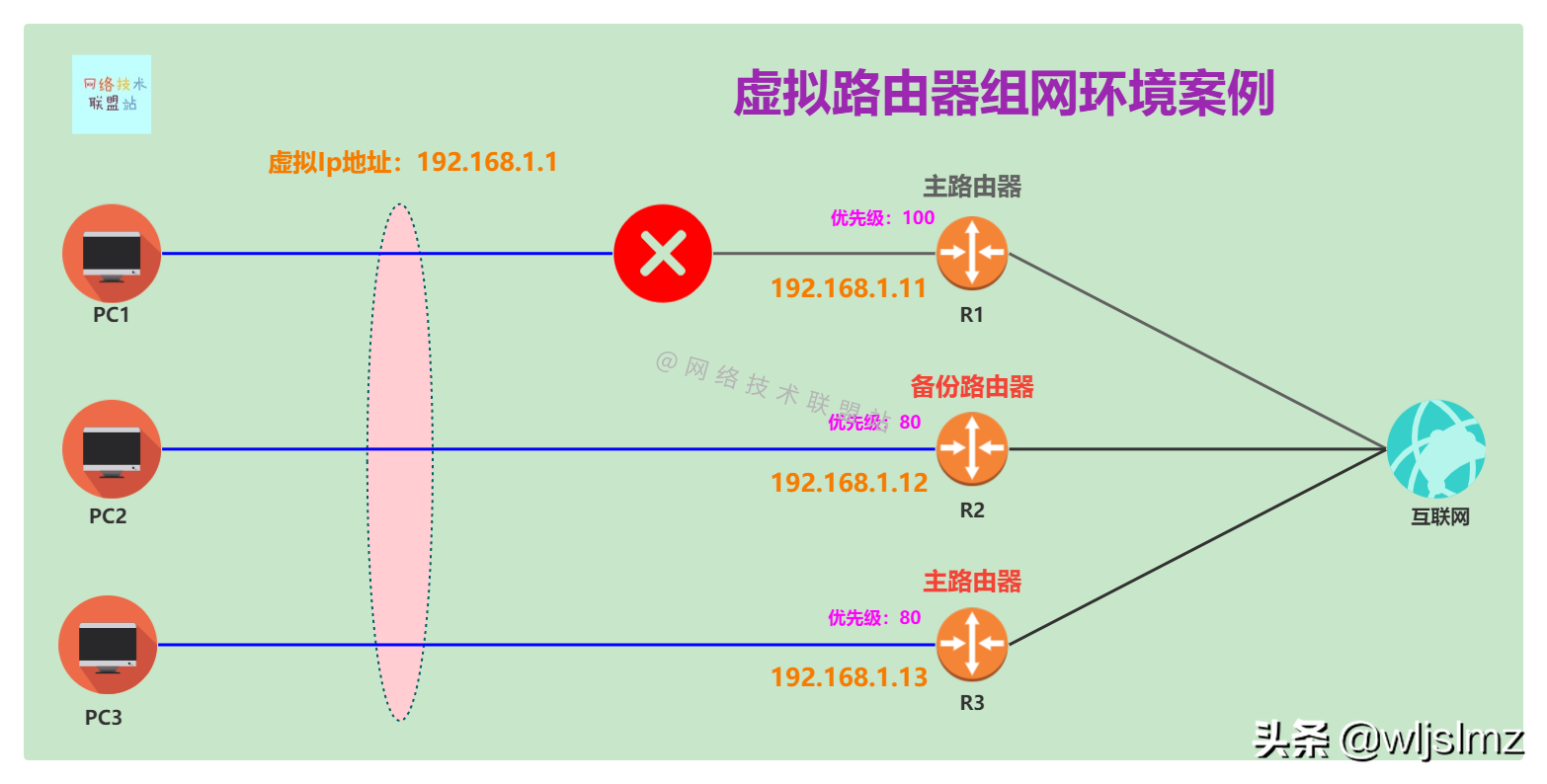
R1 fails, R2 and R3 have the same priority
As shown in the figure, the priorities of R2 and R3 are both 80. At this time, the size of the IP address is compared. Since the IP address of R3 is 192.168.1.13 higher than that of R2 with the IP address of 192.168.1.12, R3 is the main router and R2 is the main router. as a backup router.
Notice:
VRRP rejects packets in any of the following situations:
- Authentication schemes for routers and incoming packets are different.
- Routers and incoming packets have different MD5 digests.
- Authentication characters are different on routers and incoming packets.
VRRP other small points
VRRP preemption
VRRP preemption is enabled by default, which enables a higher priority virtual router backup that can take over from the virtual router backup elected as the virtual router master, or if preemption is disabled, the virtual router is elected The master virtual router backup remains the master until the original virtual router master recovers and becomes the master again.
VRRP version
There are two versions of VRRP: version 2 and version 3.
Among them version 2 is widely used.
- VRRPv2: Support IPv4
- VRRPv3: Supports IPv4 and IPv6
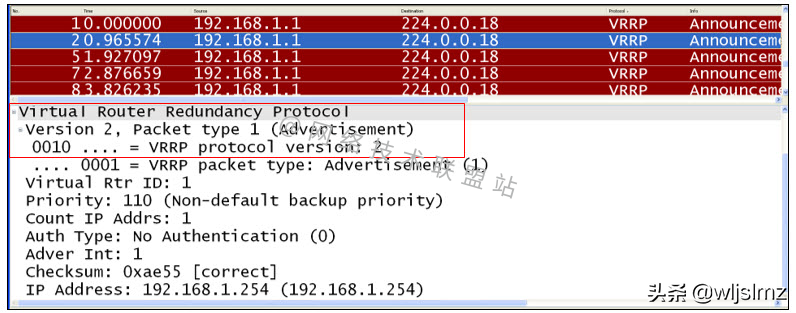
VRRP Packet Capture - Version Information
VRRP certification
VRRP provides a number of authentications to ensure that the infrastructure running VRRP is protected from malicious attacks. Generally, there are two types of authentication:

VRRP certification
Authentication is not enabled by default.
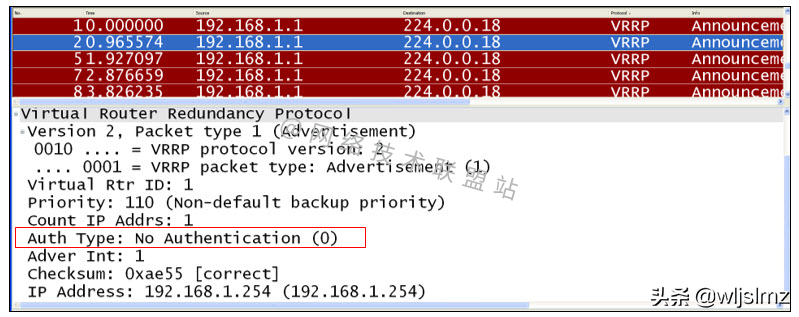
VRRP authentication packet capture
As shown in the packet capture, authentication is not enabled.
Advantages of VRRP
VRRP provides failover/redundancy at the network gateway.
There is no single point of failure because the standby unit is configured to take over if the primary unit fails.
Failover happens quickly (usually within seconds).
VRRP is used in an active-passive (primary-backup) configuration and can also be configured in an Active-Active configuration with load balancing.
VRRP is an IETF open standard protocol, so multiple vendors/multiple types of devices can be part of a VRRP group.
A primary gateway device can have multiple backup devices.
Summarize
VRRP is an open standard IEEE protocol that enables a group of routers to form a single virtual router. Using VRRP, several routers are grouped together to appear as a default gateway for the network. Provides redundancy in the network, eliminating the single point of failure inherent in a static default routing environment.
VRRP is a network layer protocol, the protocol number is 112, the number of routers in the group acts as a virtual logical router, acts as the default gateway for all local hosts, and if any router fails, other group members can take responsibility for forwarding traffic.
This article mainly introduces Ruige:
- What is VRRP?
- VRRP terminology
- How VRRP works
- VRRP three states Initialize Initialize Master Active state Backup Backup state
- VRRP election mechanism case
- VRRP Other Small Points VRRP Preemption VRRP VersionVRRP Certification
- Advantages of VRRP