Introduction to each category of network cables, what are Category 5 lines and Category 6 lines?

1. Overview of network cables
The commonly referred network cable is an Ethernet network cable, that is, a twisted pair. It is a data transmission line formed by twisting two mutually insulated metal wires into stranded pairs according to a certain winding density, and then combining multiple pairs of wires. This article mainly introduces the classification and difference of twisted pairs.

2. Classified by electrical properties
According to the classification of electrical properties, twisted pair can be divided into: type one (CAT1), type two (CAT2), type three (CAT3), type four (CAT4), type five (CAT5), super five type (CAT5e), six type (CAT6), super six type (CAT6A), seven type (CAT7). Among them, the common and applied to Ethernet transmission are Category 3 wires, Category 5 cables, Category 5 cables, Category 6 wires and the latest Category 7 lines, the former has a thin wire diameter and the latter has a thick wire diameter. The following are the introductions of each of them:
(1) Class 1 line:
The maximum frequency bandwidth of the cable is 750kHZ and is used for alarm systems, or only for voice transmission (a type of standard is mainly used for telephone cables before the early eighties) and is not used for data transmission.
(2) Class II line:
The maximum frequency bandwidth of the cable is 1MHZ, which is used for voice transmission and data transmission at a maximum transmission rate of 4Mbps, which is common in older token networks that use the 4Mbps specification token passing protocol.
(3) Three types of lines:
Refers to the cable specified in the ANSI and EIA/TIA568 standards, the transmission frequency of the cable is 16MHz, the maximum transmission rate is 10Mbps (10Mbit/s), mainly used in voice, 10Mbit/s Ethernet (10BASE-T) and 4Mbit/s Token Ring, the maximum network segment length is 100m, and the connector in the form of RJ has been faded out of the market.

(4) Four types of lines:
This type of cable has a transmission frequency of 20MHz and is used for voice transmission and data transmission at a maximum transmission rate of 16Mbps (referring to 16Mbit/s Token Ring), mainly used for token-based LANs and 10BASE-T/100BASE-T. The maximum network segment length is 100 m, and the connector in the form of RJ is not widely used.
(5) Category 5 lines:
This type of cable increases the winding density, the jacket is a high-quality insulating material, the maximum frequency bandwidth of the cable is 100MHz, the maximum transmission rate is 100Mbps, for voice transmission and the maximum transmission rate of 100Mbps data transmission, mainly used for 100BASE-T and 1000BASE-T networks, the maximum network segment length is 100m, and the connector in the form of RJ is adopted. This is the most commonly used Ethernet cable. Within a twisted pair cable, different pairs have different lay lengths. Normally, the 4 pairs of twisted pair twist period are within 38.1mm in length, twisted in a counterclockwise direction, and the twist length of a pair is within 12.7mm. As shown below:

Category 5 unshielded twisted pair with 4 wound pairs, but no wire resistance.
(6) CAT5e line:
Category 5 has reduced attenuation, less crosstalk, and has a higher attenuation-to-crosstalk ratio (ACR) and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), smaller time delay difference, and the performance is greatly improved. Category 5 cables are mainly used for Gigabit Ethernet (1000Mbps).
The CAT5e wire uses 4 winding pairs and 1 anti-string wire. The color of the pair is exactly the same as that of the five types of lines.

(7) Six types of lines:
The transmission frequency of this type of cable is 1MHz~250MHz, and the comprehensive attenuation crosstalk ratio (PS-ACR) of the Category 6 cabling system should have a large margin at 200MHz, which provides 2 times the bandwidth of Category 5e. The transmission performance of Category 6 cabling is much higher than that of Category 5e standards, and it is most suitable for applications with transmission rates higher than 1Gbps.
An important difference between Category 6 and Category 5e is the improved performance in terms of crosstalk and return loss, which is extremely important for the next generation of full-duplex high-speed network applications. The basic link model is cancelled in the six types of standards, and the cabling standard adopts a star-shaped topology, and the required wiring distance is: the length of the permanent link cannot exceed 90m, and the channel length cannot exceed 100m. As shown below:
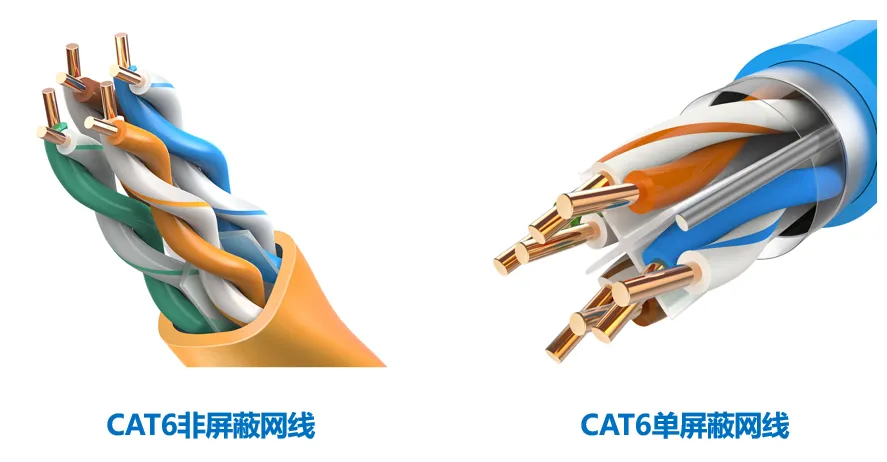
Category 6 wire has certain differences from Category 5 or Category 5 in terms of shape and structure, not only the insulated cross skeleton is added, the four pairs of twisted pair wires are placed in the four grooves of the cross skeleton, and the diameter of the cable is also thicker. The cross skeleton in the center of the cable rotates with the change of length, and the four pairs of wires are stuck in the groove of the skeleton to maintain the position of the four pairs of twisted pairs, improving the balance characteristics and crosstalk attenuation of the cable.
(8) Cat6e or 6A:
The transmission frequency is 500MHz, which is twice that of Category 6 cables, and the maximum transmission speed can reach 10Gbps, which is mainly used in 10 Gigabit networks. CAT6e is an improved version of CAT6, which is also an unshielded twisted pair cable specified in ANSI/EIA/TIA-568B.2 and ISO CAT6/E standards, which has greatly improved crosstalk, attenuation and signal-to-noise ratio. As shown below:

(9) Seven types of lines:
Category 7 wire is an 8-core shielded wire, each pair has a shielding layer (generally metal foil shielding DINTEK), and then there is a shielding layer outside the 8 cores (generally metal braided mesh shielding DINTEK), and the interface is the same as the current RJ-45. As shown below:

The transmission frequency can reach at least 600 MHz and the transmission rate can reach 10 Gbps, which is mainly to adapt to the application and development of 10 Gigabit Ethernet technology. This wire is the newest type of shielded twisted pair in the ISO Class 7/Class F standard. In addition, the connector type of Category 7 cable is also different from other types of network cables, which is GigaGate45 (CG45).
The larger the number of types, the newer the version, the more advanced the technology, the wider the bandwidth, and of course, the more expensive the price.
3. Classification according to whether there is shielding or not
Depending on whether there is a shielding layer, twisted pair is divided into shielded twisted pair (STP) and unshielded twisted pair (UTP).
(1) Shielded twisted pair
Shielded twisted pair has a metal shield between the twisted pair and the outer insulating envelope. Shielded twisted pair cables are divided into STP and FTP (Foil Twisted-Pair), STP means that each wire has its own shielding layer, while FTP only works when the entire cable is shielded and both ends are properly grounded. Therefore, the whole system is required to be shielded devices, including cables, information points, crystal heads and distribution frames, etc., and the building needs to have a good grounding system. The shielding reduces radiation, prevents information from being eavesdropped, and also prevents the ingress of external electromagnetic interference, making the shielded twisted pair have a higher transmission rate than comparable unshielded twisted pairs.
(2) Unshielded twisted pair
An Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) is a data transmission line consisting of four pairs of transmission lines of different colors, which are widely used in Ethernet and telephone lines.
Unshielded twisted-pair cables offer the following advantages:
- No shielding jacket, small diameter, saving occupied space and low cost;
- Light weight, easy to bend, easy to install;
- minimizing or eliminating crosstalk;
- Flame retardant;
- Independence and flexibility for structured cabling.
Therefore, unshielded twisted pair cables are widely used in integrated wiring systems.
4. The transmission distance of the network cable
The transmission rate of a network cable is strongly correlated with various conditions such as network topology and network equipment. In actual use, in the case of short distance, low-specification network cables can also be used for high speed, such as the use of CAT5e can indeed reach 10Gbps in short distance and short time, but this cannot be guaranteed. The following table is the transmission distance and rate of various network cables summarized by reference to the IEEE802.3 standard.
The type of network cable | Usage scenarios | Transmission frequency | Maximum transfer rate | Transmission distance |
CAT5 | 100Base-T and 10Base-T networks | 1~100MHz | 100Mbps | 100m |
CAT5e | 1000Bsae-T network | 1~100MHz | 1000Mbps | 100m |
CAT6 | 1000Bsae-T network | 1~250MHz | 1000Mbps/10Gbps | 100m/37~55m |
CAT6A | 10GBase-T network | 1~500MHz | 10Gbps | 100m |
CAT7 | 10GBase-T network | 1~600MHz | 10Gbps | 100m |