Improve CKA certification success rate: Kubernetes Ingress seven-layer proxy guide!

1. Introduction to Ingress
Ingress is the mechanism in Kubernetes that is responsible for directing external requests to services within the cluster. By mapping services to URLs outside the cluster, external accessibility of services is achieved. Ingress supports configuring services in the cluster so that they can be accessed through external URLs, and also provides functions such as traffic load balancing and domain name-based virtual hosting.
A simple understanding of Ingress is to abstract the cumbersome steps that originally required manual modification of Nginx configuration and configuration of domain name and service mapping into an Ingress object. By using YAML files to create and update Ingress objects, we no longer need to manually operate Nginx configuration files, but manage the relationship between domain names and services in a more convenient way.

However, this raises a question: "How should Nginx handle these changes?" At this time, the Ingress Controller appears to specifically solve the problem of Nginx's processing method. The Ingress Controller interacts with the Kubernetes API and senses changes in Ingress rules in the cluster in real time. Once there are changes, the Ingress Controller will read these rules and generate the corresponding Nginx configuration based on its own template. Then, it writes this configuration to the Nginx Pod, and finally triggers the reload operation of Nginx to ensure that the configuration takes effect.
Through the cooperation of Ingress and Ingress Controller, we have become more flexible and convenient in managing external access. We have got rid of the trouble of manually modifying Nginx configuration, allowing us to focus more on the mapping relationship between services and domain names, and improving the maintainability of Kubernetes clusters. sex.
1.Ingress Controller Introduction
Ingress Controller is a seven-layer load balancing scheduler that serves as the first stop for client requests, receiving and processing all external requests. Under the action of this seven-layer load balancing scheduler, the request will pass through the reverse proxy and finally be routed to the backend Pod. Common seven-layer load balancers include nginx, traefik, etc. Taking the familiar nginx as an example, when a request reaches nginx, nginx will configure a reverse proxy to the backend Pod application through upstream.
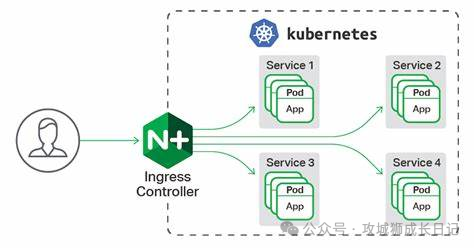
Ingress Controller
However, the IP address of the backend Pod changes dynamically. To solve this problem, we introduced Service. This Service is not an actual service, but serves to group the backend Pods. Therefore, when configuring upstream, we only need to fill in the address of the Service and do not need to care about the specific IP address of the backend Pod.
Through this design, the Ingress Controller can flexibly handle changes in the backend Pod and ensure that requests can be correctly routed to services in the cluster. This model makes it easier for us to manage changes in backend services without having to worry about the problems caused by the constant changes in the Pod's IP address.
2.Ingress resources
A minimal Ingress resource example:
apiVersion:networking.k8s.io/v1
kind:Ingress
metadata:
name:minimal-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target:/
spec:
ingressClassName:nginx-example
rules:
-http:
paths:
-path:/testpath
pathType:Prefix
backend:
service:
name:test
port:
number:80- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
Ingress needs to specify the apiVersion, kind, metadata and spec fields. The name of the Ingress object must be a legal DNS subdomain name[1].
3.Ingress Controller agent k8s internal application process
- Deploy the Ingress controller. Our ingress controller uses nginx.
- Create a Pod application, you can create a pod through the controller
- Create Service to group pods
- Create Ingress http and test accessing the application through http
- Create Ingress https and test accessing the application through https
You must have an ingress controller to meet the requirements of Ingress. Simply creating an Ingress resource is invalid.
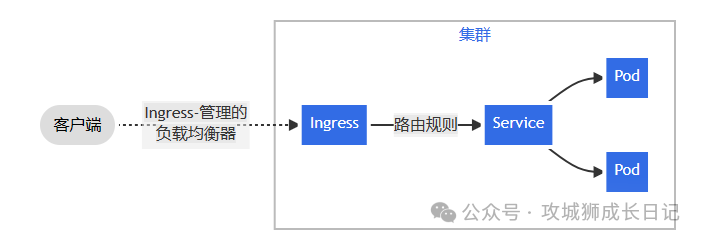
Ingress
(1) Deploy ingress-nginx
Here we also use the killercoda platform for testing, which deploys the latest version V1.29.0 of the K8S environment.
Because Ingress is not deployed in this environment. The following is an example of deploying ingress-nginx[2]. By checking the official ingress-nginx, we know that V1.29.0 corresponds to V1.10.0 or v1.9.6 of Ingress-NGINX. as follows:
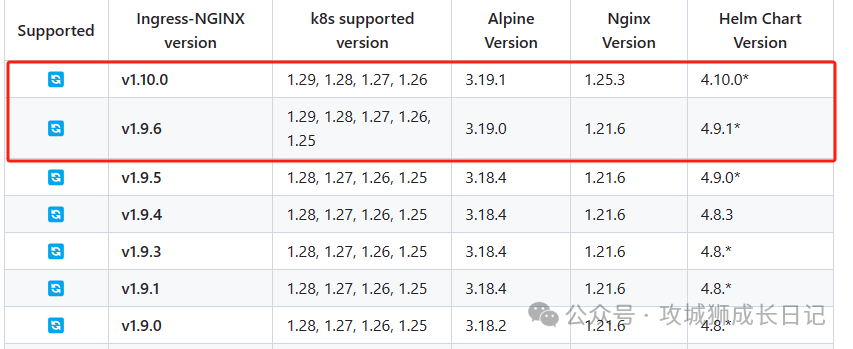
Ingress-NGINX version list
Deploy V1.10.0 of Ingress-NGINX by executing the following command.
kubectl apply -f \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.10.0/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml- 1.
- 2.
After executing the above command, the following results will be output:
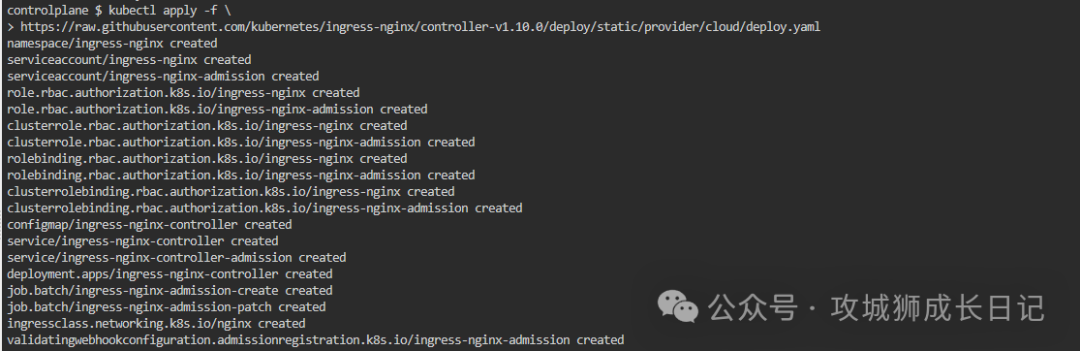
Check the deployment status through the following command:
controlplane $ kubectl get pod -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ingress-nginx-admission-create-d69wp 0/1 Completed 0 102s
ingress-nginx-admission-patch-hkv66 0/1 Completed 0 102s
ingress-nginx-controller-7dcdbcff84-gfqcs 1/1 Running 0 102s
controlplane $ kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.98.23.38 <pending> 80:30770/TCP,443:31444/TCP 3m57s
ingress-nginx-controller-admission ClusterIP 10.102.219.183 <none> 443/TCP 3m57s- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
(2) Deploy the backend tomcat service
Test the Ingress HTTP proxy k8s internal site by deploying the tomcat service and write the following resource list:
apiVersion:v1
kind:Service
metadata:
name:tomcat
namespace:default
spec:
selector:
app:tomcat
release:canary
ports:
-name:scport
targetPort:8080
port:8009
---
apiVersion:apps/v1
kind:Deployment
metadata:
name:tomcat-deploy
namespace:default
spec:
replicas:2
selector:
matchLabels:
app:tomcat
release:canary
template:
metadata:
labels:
app:tomcat
release:canary
spec:
containers:
-name:tomcat
image:tomcat:8.5.34-jre8-alpine
imagePullPolicy:IfNotPresent
ports:
-name:containerport
containerPort:8080
name:ajp
containerPort:8009- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- twenty one.
- twenty two.
- twenty three.
- twenty four.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
Check whether the pod is deployed successfully:
controlplane $ kubectl apply -f ingress-demo.yaml
service/tomcat created
deployment.apps/tomcat-deploy created
controlplane $ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
tomcat-deploy-7c67c4d459-5s859 1/1 Running 0 11m
tomcat-deploy-7c67c4d459-bvp2k 1/1 Running 0 11m- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
(3) Write Ingress rules
apiVersion:networking.k8s.io/v1
kind:Ingress
metadata:
name:ingress-myapp
namespace:default
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target:/
spec:
ingressClassName:nginx
rules:# 定义后端的转发规则
-host:tomcat.test.com# 通过域名进行转发
http:
paths:
-path:/#配置访问路径,如果通过url进行转发。需要修改,空的默认访问路径是"/"
pathType:Prefix
backend:# 配置后端服务
service:
name:tomcat# 配置关联的serverce
port:
number:8080# service暴露的端口- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
ingressClassName: This value can be obtained through kubectl get ingressclasses.
View the details of ingress-myapp:
controlplane $ kubectl apply -f ingress-myapp.yaml
ingress.networking.k8s.io/ingress-myapp created
controlplane $ kubectl get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress-myapp nginx tomcat.test.com 80 8s
controlplane $ kubectl describe ingress ingress-myapp
Name: ingress-myapp
Labels: <none>
Namespace: default
Address:
Ingress Class: nginx
Default backend: <default>
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
tomcat.test.com
/ tomcat:8080 ()
Annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Sync 62s nginx-ingress-controller Scheduled for sync- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- twenty one.
- twenty two.
Check which node ingress-nginx is deployed on, as shown below:
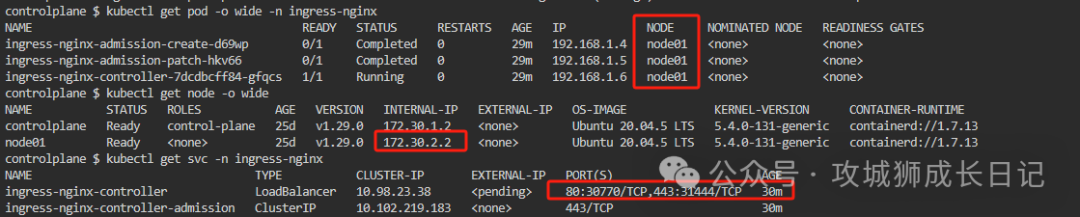
From the above figure, we can see that ingress-nginx is deployed on node1, and the SVC method is deployed through LoadBalancer. If you want to access this backend tomcat service, you need to do domain name resolution. as follows:
...省略..
172.30.2.2 tomcat.test.com- 1.
- 2.
Normal access is as follows:
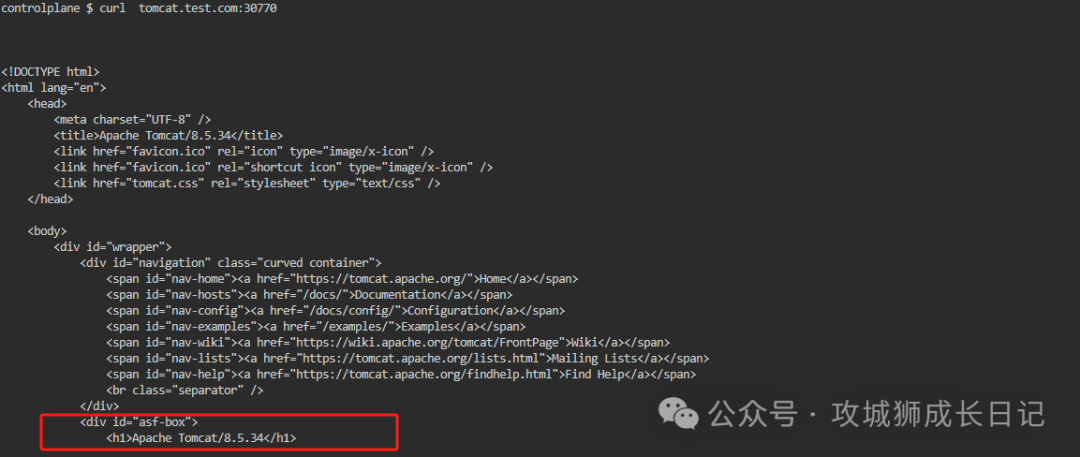
4.CKA real questions
(1) Screenshots of real questions

(2) Chinese analysis
Switch k8s cluster environment: kubectl config use-context k8s
Task:
Create a new nginx lngress resource as follows:
Name: pong Namespace: ing-internal
Expose service hi on path /hi using service port 5678
The availability of service hi can be checked using the following command, which should return hi, curl -kL/hi
(3) Official reference documents
Ingress[3]
(4) Solving problems and answering questions
Switch k8s cluster environment:
kubectl config use-context k8s- 1.
Create a file called pong.yaml. The resource content is as follows:
apiVersion:networking.k8s.io/v1
kind:Ingress
metadata:
name:pong
namespace:ing-internal
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target:/
spec:
ingressClassName:nginx-example
rules:
-http:
paths:
-path:/hi
pathType:Prefix
backend:
service:
name:hi
port:
number:5678- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- The value of ingressClassName is recommended to be passed kubectl get ingressclasses during the exam.
- The value of service.name is not told in the question. It is recommended to check it through kubectl get svc during the exam.
Submit resource list:
kubectl apply -f pong.yaml- 1.
Verify with curl -kL<INTERNAL_IP>/hi to see if hi is returned.
References:
- [1]DNS subdomain name: https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/names#dns-subdomain-names
- [2]ingress-nginx: https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx
- [3]Ingress: https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/concepts/services-networking/ingress/