A brief talk about link aggregation, have you learned it?

Speaking of the Airport Expressway, everyone often uses it to go to and from the airport, and often encounters traffic jams. In fact, some cities will build a second airport expressway. At this time, the expressway to the airport is widened, and the traffic jam is alleviated. Even if one of the expressways is blocked, drivers who are informed in advance can take another expressway. . The network also has a method similar to multiple airport highways - link aggregation. Today I will talk about link aggregation.
1. What is link aggregation?
Link aggregation refers to "bundling" physical link segments with the same transmission medium type and the same transmission rate together so that they appear to be one link logically. Link aggregation, also known as trunking, allows peer-to-peer physical links between switches or between switches and servers to simultaneously increase bandwidth exponentially.
Link aggregation modes are divided into static aggregation and dynamic aggregation.
1. Static aggregation
Static aggregation is also called static Trunk (On mode). Users need to manually configure the aggregation group number and port members, and directly add multiple physical ports to the aggregation group to form a logical port.
Static aggregation does not run the LACP protocol. Since the status of the peer port of the link cannot be detected, if the peer port is down but as long as the local port is up, traffic will still be forwarded to the peer port, which may cause some service interruptions.
 picture
picture
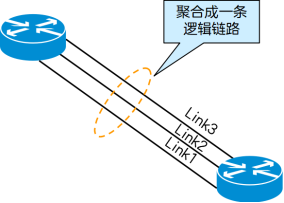
2. Dynamic aggregation
Dynamic aggregation runs the LACP protocol based on IEEE802.3 ad. LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is a standard protocol described by IEEE 802.3ad.
LACP is a protocol that implements dynamic link aggregation. Simply put, it is a protocol that dynamically aggregates multiple physical ports into a Trunk group to improve bandwidth and redundancy.
LACP allows switches to negotiate through messages to determine which physical links can be bundled together and set corresponding parameters, such as priority, activity status, etc. When multiple physical links are bundled into a logical link, they will share the same IP address and MAC address, thus forming a logical high-speed channel.
 picture
picture
2. How does LACP work?
1. LACP dynamic mode aggregation group establishment process
LACP exchanges information with the peer through LACPDU (Link Aggregation Control Protocol Data Unit). After the LACP protocol is enabled on a certain port, the LACPDU message contains information such as the device's system priority, MAC address, interface priority, interface number, and operation key. After the peer receives this information, it combines this information with the information saved by other ports. The information is compared to select a port that can be aggregated. Both parties reach an agreement on whether the port joins or exits a dynamic aggregation group, and determines the link responsible for business traffic.
- Both ends send LACPDU messages to each other to create a link aggregation group on the devices at both ends, configure the LACP mode, and configure member interfaces. At this time, the LACP protocol is enabled on the member interface, and both ends send LACPDU messages to each other. The LACPDU message contains information such as the device's system priority, MAC address, interface priority, interface number, and operation key.
- When a member interface joins a link aggregation group, devices at both ends will receive LACPDU packets from the opposite end. Both ends view and record the peer information, compare this information with the information saved by other member interfaces of the aggregation group, and select a link aggregation group to join.
- Determine the active interfaces of the aggregation group. Select active interfaces in the link aggregation group based on the interface priority, and forward data from these active links in a load-sharing manner.
2.LACP working mode
LACP working modes can be divided into active mode and passive mode.
- In active mode, the network device actively sends LACPDU and waits for a response from the peer device. If the peer device also supports LACP and is configured in passive mode, it will respond with LACPDU to establish link aggregation.
- In passive mode, the network device only receives LACPDU and responds accordingly according to the request. Devices in passive mode are usually not active.
If the LACP working mode of the dynamic aggregation group member port is passive mode and the peer end is also the same, neither end will send LACPDU. If the working mode of LACP on either end is active mode, LACPDUs can be exchanged between member ports.
3.LACP timeout mode
LACP timeout modes include long timeout and short timeout.
- The long timeout mode is to send LACPDU slowly (30 second cycle), and the long timeout is a 90 second timeout.
- The short timeout mode is to send LACPDU quickly (1 second period), and the short timeout is 3 seconds timeout.
The default LACP timeout mode is long timeout, that is, the sending cycle is 30 seconds to send a LACP protocol message, and if no LACP protocol message from the peer is received for more than 90 seconds, the negotiation fails.
3. What benefits does link aggregation bring?
- Increase link bandwidth Link aggregation can increase network bandwidth. Link aggregation forms a logical interface by aggregating multiple physical ports together. The maximum bandwidth of the link aggregation interface can reach the sum of the bandwidths of all member interfaces; thereby achieving a peer-to-peer physical link and doubling the bandwidth at the same time.
- Improve network reliability and link aggregation to achieve link redundancy backup. When link aggregation is configured, when an active link fails, traffic can be switched to other available member links, thereby improving the reliability of the link aggregation interface and achieving link redundancy. For example, in the case of cross-slot link aggregation, service interruption caused by a single slot failure can be well avoided.
- To achieve traffic load sharing within a link aggregation group, traffic can be shared to all member links based on certain rules, such as a five-tuple including source IP, destination IP, etc., thereby achieving inbound/outbound load balancing on each member link. Load sharing on the network reduces the pressure on a single link.
4. What are the usage scenarios of link aggregation?
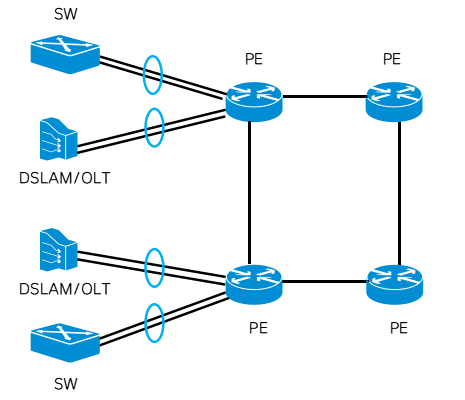
1.Fixed home broadband & campus network access scenario
With the increase in fixed network services including home broadband, IPTV and other traffic, the access bandwidth pressure of OLT is gradually increasing. Fast and convenient broadband can be doubled through link aggregation. In addition, the increase in campus network access traffic is also experiencing rapid growth, and link aggregation is also widely used in campus network switch connections.
 picture
picture
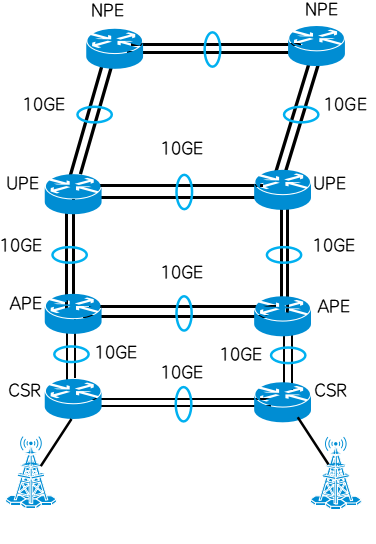
2. Mobile bearer access scenario
With the rapid growth of 5G services such as data and high-definition video services, the requirements for large bandwidth and high reliability of mobile bearer networks have also increased significantly. In fact, link aggregation technology is widely deployed in mobile backhaul IPRAN networks, both to achieve 10GE/ The 100GE link bandwidth is expanded and link redundancy is ensured to achieve high reliability business guarantee.
 picture
picture
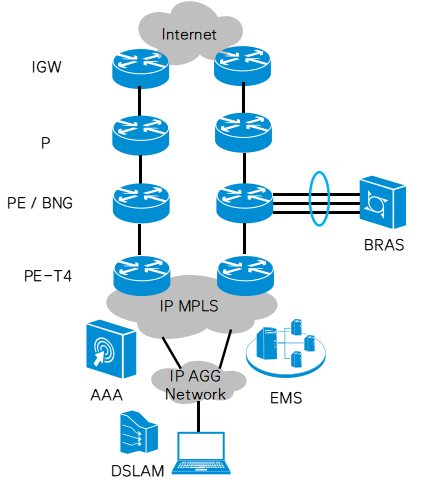
3.BRAS network scenario
BRAS is the core equipment for fixed network business authentication and authentication. Whether it is the increase in access user traffic or link security and reliability, it has very high requirements. The deployment of link aggregation in the BRAS network has the flexibility of bandwidth expansion. As access user traffic increases, link aggregation group members can be added to dynamically adjust the bandwidth of the link aggregation link; at the same time, link aggregation cross-board Bundling ensures the reliability of each board for tens of thousands of users.
 picture
picture
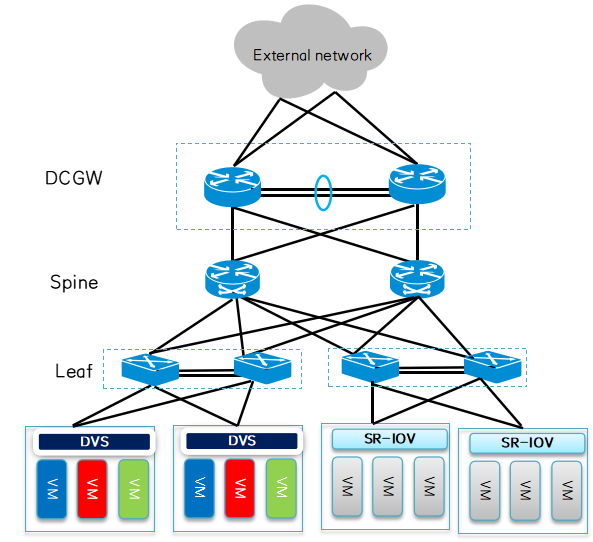
4. Data center scenario
Data centers such as 5G telecom cloud networks are the most core and critical networks for mobile services. The large number of applications of link aggregation ensures the bandwidth expansion of mobile services in the data center, link reliability, and the load of link aggregation. Balancing can effectively utilize each member link of the link group to ensure efficiency.
 picture
picture