No more worries! Teach you how to quickly locate Eth-Trunk faults and easily solve network problems!

1. How to locate the Eth-Trunk that cannot be Up in manual load balancing mode?
When encountering this kind of problem, the editor summarized the following positioning ideas for everyone, and they have proven successful over time:
- Check whether the physical status of the manual Eth-Trunk member port is UP;
- Check whether the lower threshold for the number of active interfaces is configured on the Eth-Trunk interface.
For the specific positioning steps, please take a look below:
Step 1: Check whether the physical status of the member port is UP
The physical status of member ports is UP, which is a prerequisite for the normal operation of Eth-Trunk.
Run the display eth-trunk command to check the member interface information of the Eth-Trunk interface. If the status of the member port under Eth-Trunk is Down, please refer to this article " Ethernet Interface Physical DOWN Fault Special Topic ".
Step 2: Check the configuration under the Eth-Trunk interface
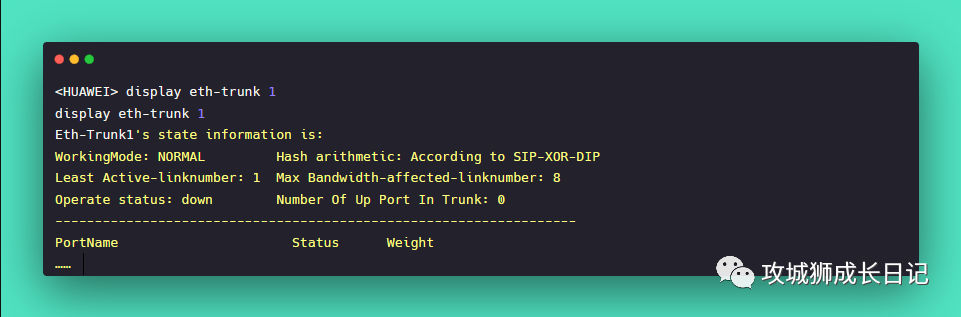
Run the display eth-trunk command to check whether the lower threshold for the number of active interfaces is configured on the Eth-Trunk interface. If the number of Up member interfaces on an Eth-Trunk interface is less than the configured lower threshold for the number of active interfaces, the Eth-Trunk status will change to Down.
In the following echo, the Least Active-linknumber represents the lower threshold of the member link in the Up state, which is 3. The number of UP member ports on the Eth-Trunk interface is 1. The number of UP members is less than the lower threshold of the number of active interfaces. Therefore, the Eth-Trunk status Operate status is Down.
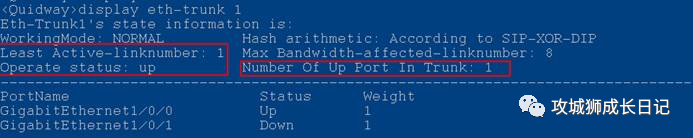
In addition, friends, please note that by default, the lower threshold for the number of active interfaces in an Eth-Trunk is 1. You can use the command least active-linknumber link-number to configure the lower threshold for the number of active interfaces in a link aggregation group.
2. How to locate the failure of Eth-Trunk negotiation in LACP mode?
Similarly, the editor also summarized the positioning ideas for this type of fault:
- Check whether the physical status of the Eth-Trunk member port is Up;
- Check whether the upper threshold for the number of link aggregation bandwidth interfaces is configured under the Eth-Trunk interface;
- Check whether the Eth-Trunk member interface can send and receive LACP packets normally.
Step 1: Check whether the physical status of the member port is UP
The physical status of a member port is UP, which is a prerequisite for being selected by the Eth-Trunk. Run the display eth-trunk command to check the member interface information of the Eth-Trunk interface. If the status of the member port under Eth-Trunk is Down, it is the same as above. Please troubleshoot the cause of the interface failure first.
Step 2: Check the configuration under the Eth-Trunk interface
Check whether the configurations on both ends of the Eth-Trunk are equal. Because it involves the negotiation of device LACP messages, both ends need to be configured in LACP mode. Run the display eth-trunk command line to check whether the upper and lower thresholds for the number of active interfaces are configured under the Eth-Trunk. If the number of Up member interfaces on an Eth-Trunk interface is less than the configured lower threshold for the number of active interfaces, the Eth-Trunk status will change to Down.
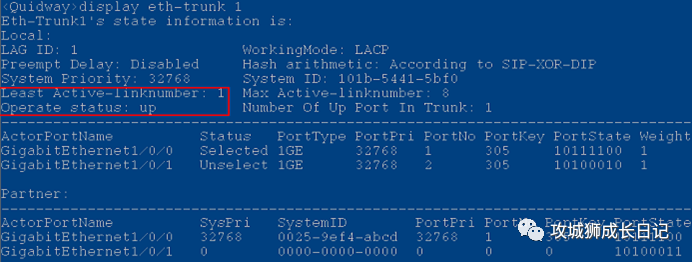
By default, the lower threshold for the number of active interfaces on an Eth-Trunk is 1, which can be configured with the least active-linknumber _link-number_ command; the upper threshold for the number of active interfaces is 8, which can be configured with the max active-linknumber _link-number_ command.
If the least active-linknumber command has been configured before configuring this command, you need to ensure that the upper threshold configured in this command is greater than or equal to the lower threshold set in the least active-linknumber command.
Step 3: Check whether the Eth-Trunk member interface is sending and receiving LACP messages normally.
Run the display lacp statistics eth-trunk command line to check whether the LACP negotiation packets on the Eth-Trunk member interface are being sent and received normally.
The number of increased packets is related to the packet timeout configured on the Eth-Trunk interface:
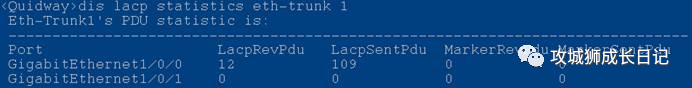
The number of packet growth is related to the packet timeout configured on the Eth-Trunk interface. You can execute the lacp timeout { fast | slow } command in the Eth-Trunk interface view to configure the timeout for the Eth-Trunk interface to receive LACP protocol packets in LACP mode. time.
- After configuring the fast timeout, the peer sends LACP packets at a cycle of 1 second. The response performance is good, but the occupied system resources are larger than the slow parameter.
- After configuring the slow timeout, the peer sends LACP messages every 30 seconds. The responsiveness is lower than that of fast, but it also takes up less system resources. The timeout time configured on both ends can be different, but to facilitate maintenance, it is recommended that users configure a consistent LACP protocol packet timeout time.
- If the count of received LACP protocol packets increases incorrectly, check whether the peer device did not send them or the local device received them and then discarded them. If the count of LACP packets received by the local device is incorrect, check why the port is not functioning properly. Receive LACP protocol messages.
3. How to locate uneven traffic load sharing on the Eth-Trunk interface?
Similarly, the editor also summarized the positioning ideas for this type of fault:
- Confirm whether the packet characteristics match the load sharing method;
- Check whether the number of selected member interfaces is an exponential multiple of 2;
- Check whether there is a stack/cluster cross-chassis Eth-Trunk.
Step 1: Confirm whether the packet characteristics match the load sharing method
Check whether the characteristics of the packets forwarded through the Eth-Trunk interface match the configured load balancing mode. If they do not match, for example, the MAC address of forwarded packets changes and the load balancing mode is set to src-ip, load balancing cannot be performed.
You can check and modify it through the following steps:
(1) Confirm message characteristics
- Determine the packet forwarding method: The forwarding processes of known unicast and non-known unicast are different, and the default load balancing algorithms are also different, so you need to first confirm whether the forwarded packet is known unicast or non-known unicast.
- Determine the change factor of the message: What determines the change of the message is the MAC address, IP address or Label of the message, etc.
- Determine the type of packet: Determine whether the packet is an IP packet, MPLS packet, or Layer 2 packet.
Note: If the destination MAC address of the packet is not in the MAC table, the packet is an unknown unicast packet.
(2) Check the load balancing mode of the Eth-Trunk interface.
Check the load sharing mode of the Eth-Trunk interface based on the packet forwarding mode confirmed in the previous step (known unicast or non-known unicast).
Check the load sharing method of known unicast:
Run the display eth-trunk command to view the Hash arithmetic field to confirm the configured load balancing method. You can also run the display this command in the Eth-Trunk interface view to view it.
Load sharing mode parameter description:
- SIP represents the source IP address, DIP represents the destination IP address, SA represents the source MAC address, and DA represents the destination MAC address.
- SIP-XOR-DIP means to select the outgoing interface based on the XOR operation of the source IP address and the destination IP address.
- SA-XOR-DA indicates that the outgoing interface is selected based on the XOR operation of the source MAC address and the destination MAC address. ENHANCED indicates that the enhanced load sharing template is applied, and the outgoing interface is selected based on the load sharing method specified by various types of packets in the enhanced template.
- If the load sharing mode is ENHANCED, you need to further check the load sharing mode of the enhanced template.
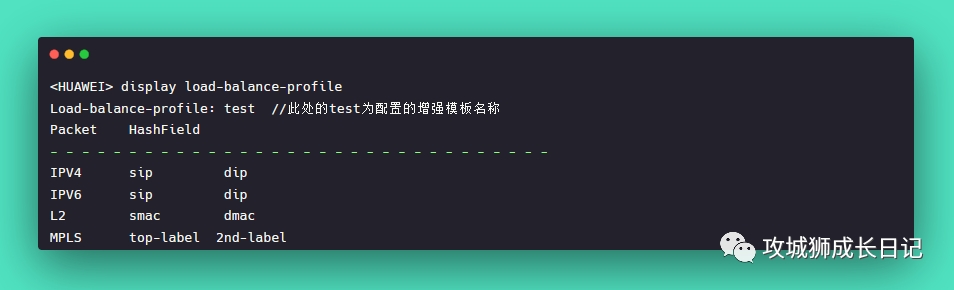
The enhanced load sharing mode has only one global template, which is also effective for known unicast and non-known unicast. Different fields are selected for HASH calculation for different packet types.
You can run the display load-balance-profile command to view the load balancing mode for each characteristic packet, where the HashField represents the configured load balancing mode.
For unknown unicast, run the display current-configuration | include unknown-unicast load-balance command to check the load balancing method of unknown unicast. By default, the device performs load balancing on unknown unicast based on the source MAC address and destination MAC address of the packet.
(3) Confirm whether the forwarded packet characteristics match the load sharing method
If the packet characteristics do not match the current load-sharing method, you can modify the load-sharing method based on the live network traffic model. The more frequently this parameter changes in the traffic, the more balanced the traffic selected in this load sharing mode will be. For example: When testing only a single PC, since the source IP address and source MAC address remain unchanged, only the destination IP address and destination MAC address change, and the load sharing method selected at this time is based on the source IP address or source MAC address, the traffic cannot Load sharing needs to be modified to a load sharing method based on the destination IP address or destination MAC address. If the packet is known unicast, modify the command as follows:
<HUAWEI> system-view
[HUAWEI] interface Eth-Trunk 1
[HUAWEI-Eth-Trunk1] load-balance dst-mac
[HUAWEI-Eth-Trunk1] quit- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
If the packet is a non-known unicast, modify the command as follows:
<HUAWEI> system-view
[HUAWEI] unknown-unicast load-balance dmac- 1.
- 2.
If the load balancing mode adopted is enhanced mode, you need to check and modify the load sharing mode of the corresponding packet type in the enhanced template based on the packet type (such as IPv4, IPv6, MPLS, L2). For example: Modify the IPv4 packet load sharing mode in the enhanced template "test" to dip.
<HUAWEI> system-view
[HUAWEI] load-balance-profile test
[HUAWEI-load-balance-profile-test] ipv4 field dip
[HUAWEI-load-balance-profile-test] quit- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Step 2: Check whether the number of selected member interfaces is an exponential multiple of 2
When the number of member interfaces selected under the Eth-Trunk interface is an exponential multiple of 2, traffic load sharing is more balanced. Run the display eth-trunk command to view the selected member interfaces. The identification method of the selected member ports under the Eth-Trunk interface is as follows:
- In LACP mode (V100R006C03/V100R006C05/V200R001 versions, WorkingMode is STATIC, V200R002 and later versions, WorkingMode is LACP), Status is the Selected interface.
- In manual mode (WorkingMode is NORMAL), the Status is Up interface.
Step 3: Check whether there is a stack/cluster cross-chassis Eth-Trunk
If the packet is a non-known unicast packet, this step does not need to be performed.
The local priority forwarding function is enabled on the Eth-Trunk interface by default. That is, in a stack/cluster scenario, packets entering from a stack/cluster member device port, if the outgoing port is an Eth-Trunk, there is a member interface of the Eth-Trunk in this frame, and if the member interface is not faulty, it will only be sent from the Eth-Trunk. The packets are forwarded through the Eth-Trunk member interfaces on the chassis and will not be forwarded from the Eth-Trunk member interfaces of other stack/cluster members.
In this case, you can use the following command to disable the local priority forwarding function.
<HUAWEI> system-view
[HUAWEI] interface Eth-Trunk 1
[HUAWEI-Eth-Trunk1] undo local-preference enable
[HUAWEI-Eth-Trunk1] quit- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
The traffic local priority forwarding function is only effective for known unicasts, but not for broadcasts, multicasts, and unknown unicasts.
The fault location tips in this issue have been shared with you. I believe that friends can easily deal with Eth-Trunk faults when they encounter them again. If there are any fault cases in the future, I will share them with you, bye. ~~