Industrial Internet communication protocol types, functions and connection methods

Industrial Internet communication protocol types, functions and connection methods
With the arrival of Industry 4.0, the Industrial Internet has become an important support for the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry. The Industrial Internet connects various devices, systems and services together to achieve real-time collection, analysis and optimization of data, thereby improving production efficiency, reducing costs, and improving product quality and innovation capabilities. In this process, communication protocols, as the cornerstone of the industrial Internet, play a vital role. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the types, functions and connection methods of industrial Internet communication protocols.
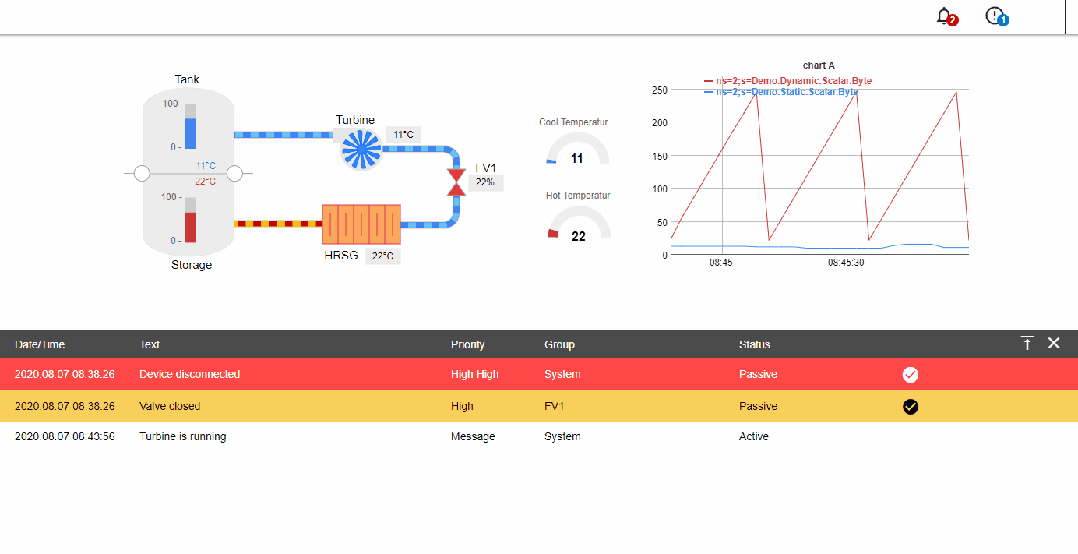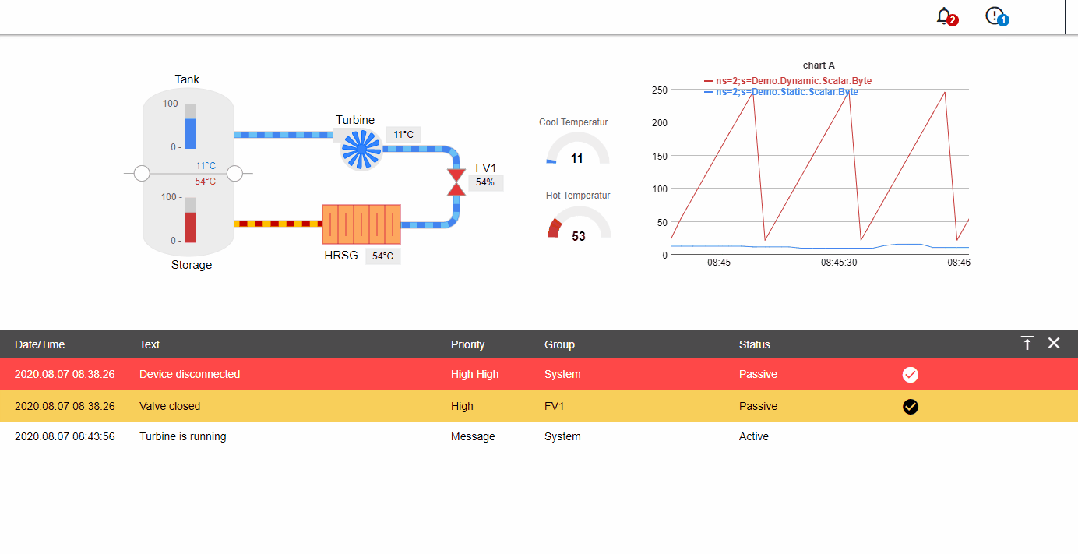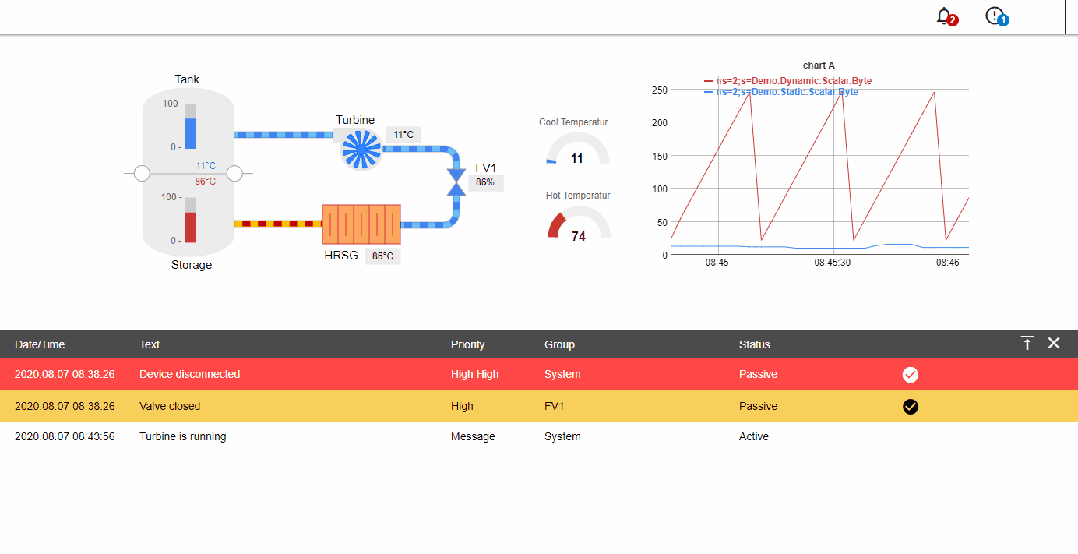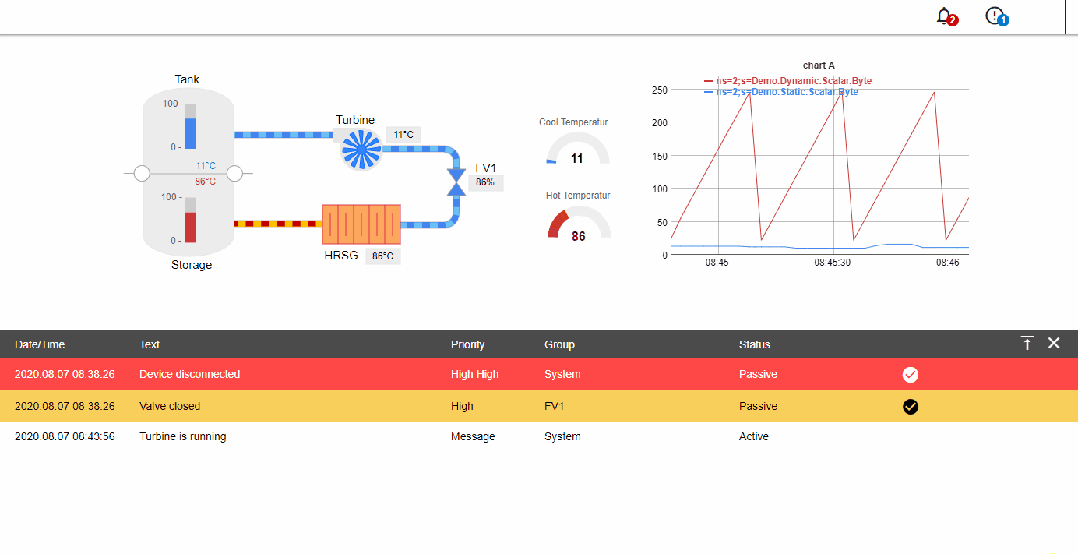
1. Industrial Internet communication protocol types
Wired communication protocol
Wired communication protocols mainly include Ethernet, industrial Ethernet, fieldbus, etc. These protocols have advantages in data transfer rate, stability and anti-interference capabilities, and are suitable for scenarios that require high immediacy and reliability.
- Ethernet: Ethernet is a widely used computer LAN technology, and its communication protocols include TCP/IP, UDP, etc. In the industrial Internet, Ethernet is mainly used for high-speed data transmission between devices.
- Industrial Ethernet: Industrial Ethernet is a communication protocol developed on the basis of Ethernet and suitable for industrial environments. Its main features are high immediacy, reliability and security. Industrial Ethernet communication protocols include PROFINET, EtherCAT, etc.
- Fieldbus: Fieldbus is a digital communication system used to connect industrial field devices. Fieldbus communication protocols include CAN, Modbus, etc. Fieldbus is mainly used to realize data exchange and control between devices.
Wireless communication protocol
Wireless communication protocols mainly include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, LoRa, etc. These protocols have advantages in connection flexibility and installation convenience, and are suitable for scenarios that are sensitive to wiring costs and space constraints.
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi is a wireless LAN technology based on radio waves, and its communication protocols include 802.11a/b/g/n/ac, etc. Wi-Fi is mainly used in the industrial Internet for remote monitoring and management of equipment.
- Bluetooth: Bluetooth is a short-range wireless communication technology, and its communication protocols include Bluetooth 5.0 and so on. Bluetooth is mainly used in the industrial Internet for low-rate data transmission of devices and short-distance communication between devices.
- ZigBee: ZigBee is a low-power, low-cost wireless communication technology, and its communication protocols include ZigBee PRO and so on. ZigBee is mainly used in the industrial Internet for connection and data collection of IoT devices.
- LoRa: LoRa is a long-distance, low-power wireless communication technology, and its communication protocols include LoRaWAN and so on. LoRa is mainly used in the industrial Internet for device connection and data transmission within a wide area.
2. Industrial Internet communication protocol functions
- Data exchange: The communication protocol realizes the instant transmission and exchange of data between devices, providing a data foundation for the industrial Internet.
- Equipment control: The communication protocol enables remote monitoring and control of equipment, improving the automation level of the production process.
- System integration: Communication protocols realize the integration between different devices, systems and services, providing a unified platform for the industrial Internet.
- Data analysis: Communication protocols enable the collection and analysis of large amounts of data, providing decision-making support for the Industrial Internet.
3. Industrial Internet communication protocol connection method
- Point-to-point connection: Point-to-point connection refers to the direct establishment of a communication link between two devices, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, etc. This connection method is suitable for scenarios with a small number of devices and simple communication requirements.
- Many-to-one connection: Many-to-one connection means that multiple devices communicate through a central node, such as fieldbus, ZigBee, etc. This connection method is suitable for scenarios with a large number of devices and complex communication requirements.
4. Development Trends of Industrial Internet Communication Protocols
With the continuous development of the industrial Internet, communication protocols are also constantly evolving and innovating. The following are some development trends of industrial Internet communication protocols:
- High speed: As industrial equipment requires higher and higher data transmission rates, communication protocols need to provide higher transmission rates and lower delays. For example, Ethernet has evolved from 10Mbps to 1Gbps, 10Gbps and even 100Gbps, while 5G technology provides higher transmission rates and lower latency.
- Enhanced reliability: In an industrial environment, the stable operation of equipment is crucial. Therefore, communication protocols need to have higher reliability and fault tolerance. For example, the PROFINET and EtherCAT protocols of Industrial Ethernet improve system reliability through redundancy mechanisms and real-time optimization.
- Improved security: The industrial Internet involves a large amount of sensitive data and key equipment, so the security of communication protocols is very important. Future communication protocols will pay more attention to security measures such as data encryption, identity authentication and access control.
- Energy efficiency optimization: In industrial production processes, energy consumption is an important consideration. Future communication protocols will pay more attention to the optimization of energy efficiency and achieve energy conservation and emission reduction goals by reducing power consumption and optimizing data transmission methods.
- Multi-protocol integration: There are many different devices and systems in the industrial Internet, and they may use different communication protocols. In order to achieve interconnection and interoperability between devices, future communication protocols will pay more attention to the integration and compatibility of multiple protocols.