Enlightenment on using Smallcell to solve deep network coverage in the post-5G era

Enlightenment on using Smallcell to solve deep network coverage in the post-5G era
1. Current status of network coverage in the post-5G era
2019 is the first year of 5G commercial use in China. 5G has brought great convenience to people’s lives. The latest data from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology shows that as of the end of September 2023, my country has built and opened a total of 3.189 million 5G base stations, covering all prefecture-level cities and counties. The number of 5G base stations per 10,000 people has reached 22.6, and the total number of base stations accounts for 60% of the world. above. In the more than four years since 5G has been commercialized, 5G applications have covered many areas of life such as transportation and medical care. 5G communications play a huge role in the live broadcast of the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympics, COVID-19 prevention and control, telemedicine, connected car autonomous driving, and smart venues for the Hangzhou 2023 Asian Games.
In the early stages of 5G network construction, network coverage focuses on breadth. As the number of users increases, traffic in hotspot areas will surge during peak periods, resulting in a decline in user experience. Entering the post-5G communications era, people have put forward higher requirements for the transmission speed of wireless communications. With the deployment of 5G high-frequency bands, 5G macro station signal transmission has experienced greater path loss, coupled with the obstruction of buildings, making Indoor 5G signal coverage is seriously insufficient. So the current dilemma arises: first, the high frequency band of 5G makes it difficult for outdoor macro station signals to reach indoors; second, more and more business and traffic demands in the 5G tob and toc era occur indoors. However, the cost of building a website by simply increasing macro site coverage is too high. In response to the above dilemma, small base stations have become a "sharp tool" to solve the pain points of 5G networks, providing new solutions for achieving deep 5G coverage. The networking mode of "macro base stations as the main base and small base stations as the supplement" is the main network deployment method in the post-5G era.
2. Introduction and application prospects of Smallell
Smallcell originated from Femtocell. International standards organizations such as Smallcell Forum and 3GPP have conducted long-term research on femtocell and carried out a lot of work on technical standards. As Femtocell has moved from home base station applications to various application scenarios such as enterprises and indoor hotspots, its name has been changed to Smallcell. Smallcell inherited the basic standards of Femtocell, and expanded various application scenarios and new requirements, forming a complete Smallcell technical standard. There are two main definitions of Smallcell: First, it is defined in the 3GPP standard as a low-power device node with lower transmit power than macro base stations, aiming to improve capacity in indoor and outdoor hotspot scenarios and cope with the blowout growth of data traffic. Second, the Smallcell Forum defines smallcell as a variety of low-transmission power, small-range coverage wireless access equipment that works in authorized frequency bands and is deployed by operators to help improve the coverage and capacity of macro cellular networks and become an efficient use of wireless spectrum for operators. A useful addition to resource and data offloading. Smallcell device form and application scenarios are shown in Figure 1.
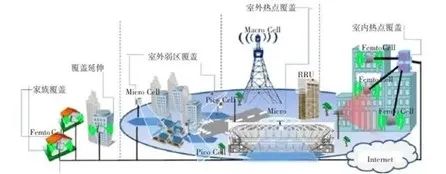 Figure 1 Smallcell device form and application scenario diagram
Figure 1 Smallcell device form and application scenario diagram
As shown in Figure 1, large-scale deployment of Smallcell (including femtocell\microcell\picocell) can solve the indoor coverage, hotspot coverage, deep coverage and other problems of mobile communication networks, make up for the shortcomings of macro cells, improve spectrum efficiency, increase network capacity, and more It can well meet the development needs of future mobile communication services and improve user experience. In general, Smallcell technology has broad application prospects and can provide better solutions for wireless communications in various fields and promote the process of digitalization and intelligence.
In 2022, professional research organization ABI Research predicts that when Massive MIMO macro stations cannot meet 5G capacity needs, outdoor small station Smallcell deployment will begin to increase around 2025. Fei Liu, ABI Research and 5G mobile network infrastructure industry analyst, pointed out: 5G small cells and macro cells complement each other to increase network capacity and expand coverage in densely populated areas where signals are weak or unavailable. As an effective supplement to 5G macro stations, 5G small station Smallcell applications are becoming more and more common. According to the prediction in the "SCF market status report July 2020" by the Smallcell Forum (SCF), the number of small base stations will maintain an average annual growth of 13% from 2019 to 2026, from 2.7 million to 6.3 million. A total of 38.3 million units have been deployed. Among them, the deployment of small base stations by telecom operators in urban environments has grown at an average annual rate of 24%, with 80% concentrated indoors in enterprises, industries and schools. The number of small base stations deployed by enterprises will grow at an average annual rate of 9%, accounting for 68% of the total; the small base stations deployed in rural and remote areas will maintain an average annual growth of 19%, mainly in service industries and Internet of Things enterprises. By 2026, they will 957,000 installed.
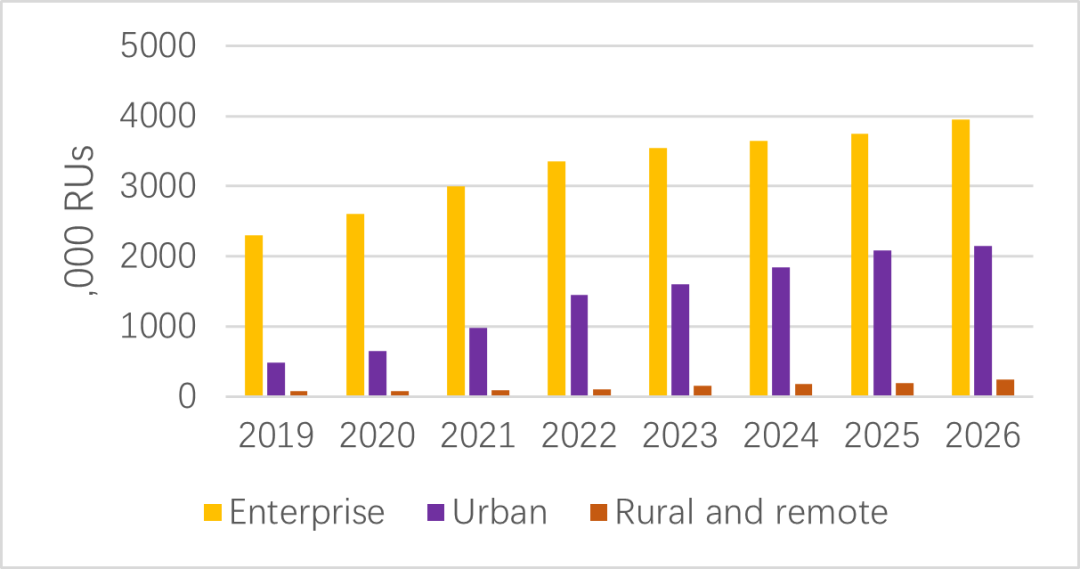 Figure 2 Smallcell station growth trend chart
Figure 2 Smallcell station growth trend chart
3. Smallcell deployment scenario
Smallcell deployment scenarios are very diverse, helping operators meet users' high-speed communication needs anytime and anywhere. Some typical application scenarios are as follows:
a) Indoor coverage
Smallcell can provide better wireless coverage and capacity in indoor places such as large shopping malls, hotels, and office buildings, improving user experience.
b) city streets
Smallcell can provide better wireless coverage and capacity in dense areas such as urban streets and squares to meet users' communication needs.
c) Rural and remote areas
Smallcell can provide better wireless coverage and capacity in rural and remote areas, make up for the coverage blind spots of traditional base stations, and improve the quality of communication services.
d) Internet of Things (IoT)
Smallcell can be used to connect IoT devices to provide more stable and efficient communication support for smart cities and smart homes.
e) Transportation field
Smallcell can provide better wireless coverage and capacity in transportation hubs such as subways, train stations, and airports, and improve user experience.
f) Industrial sector
Smallcell can provide better wireless coverage and capacity in industrial parks, factories and other places, and support applications such as the Industrial Internet of Things.
g) Medical field
Smallcell can provide better wireless coverage and capacity in hospitals, clinics and other places, and support applications such as the medical Internet of Things.
4. Smallcell security risks
a) Physical security hazards
Smallcell stations are usually installed outdoors or indoors in exposed locations that are susceptible to vandalism, theft or vandalism. Unauthorized personnel may interfere with or damage equipment, causing interruption of communication services.
b) Data security risks
Smallcell stations may store some sensitive communication data. If it is not properly protected, it may be attacked by hackers or illegally obtained, causing the risk of user privacy or communication information being leaked.
c) Spectrum security risks
Unauthorized spectrum use may cause spectrum interference and affect the normal operation of surrounding communication equipment.
d) Network security risks
Smallcell stations connected to the network may be subject to network attacks, including DDoS attacks, malware attacks, etc., resulting in interruption of communication services or data leakage.
In order to solve these security risks, measures such as the following need to be taken to ensure the safe and compliant operation of small stations:
a) Equipment authentication and authorization: Authentication and authorization for Smallcell stations to ensure that only authorized personnel can access and operate the equipment, and implement regular password resets and permission upgrades to prevent unauthorized access and operations.
b) Adopt frequency supervision and other technical means to supervise.
c) Regularly conduct compliance reviews of Smallcell stations to ensure that the deployment and use of small stations comply with local laws and regulations.
d) Access control and rights management: Implement strict access control and rights management, and classify and restrict the access rights of different personnel.
e) Data transmission security: Protect the security of data transmission between Smallcell station equipment, and use encryption technology to encrypt data to prevent data leakage and tampering.
5. Summary and suggestions
Small base stations were born in the 3G era, but as the development of 5G networks is playing its role, Smallell technology solves the problem of deep network coverage in the post-5G era and provides better wireless communication support and user experience for different industries and fields. Becoming an important addition to cellular network infrastructure. However, with the large-scale deployment and application of Smallcell, security risks have become increasingly prominent. For example, criminals use Smallcell stations to steal sensitive user information, providing new means for network attacks. In order to deal with the security risks caused by small base stations, the regulations and standards for the small base station industry should be strengthened, including regulations on location selection, power control, spectrum management, etc. of small base stations to ensure the compliance and security of small base stations.
 references
references
[1] Gao, Z., Zhang, S. (2022). Encrypted 5G Smallcell Backhaul Traffic Classification Using Deep Learning. In: Su, C., Sakurai, K. (eds) Science of Cyber Security - SciSec 2022 Workshops. SciSec 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1680. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7769-5_2.
[2] Guo Honggang. Analysis and research on 5G indoor coverage of radio and television [J]. Wireless Internet Technology, 2022, 19(19):1-4.
[3] Sun Zhaoxi, Liu Chao. Research on 5G network indoor coverage [J]. Information Recording Materials, 2020, 21(9):2.
[4] Feng Wanrong. Research on Small Cell self-healing technology in cellular heterogeneous networks [D]. Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications.
[5] Huawei Smallcell White Paper "Five Major Trends towards Smallcell 2020"