What is the process of DNS domain name resolution?

What is the process of DNS domain name resolution?
Interviewer: Please tell me, what is the process of DNS domain name resolution?
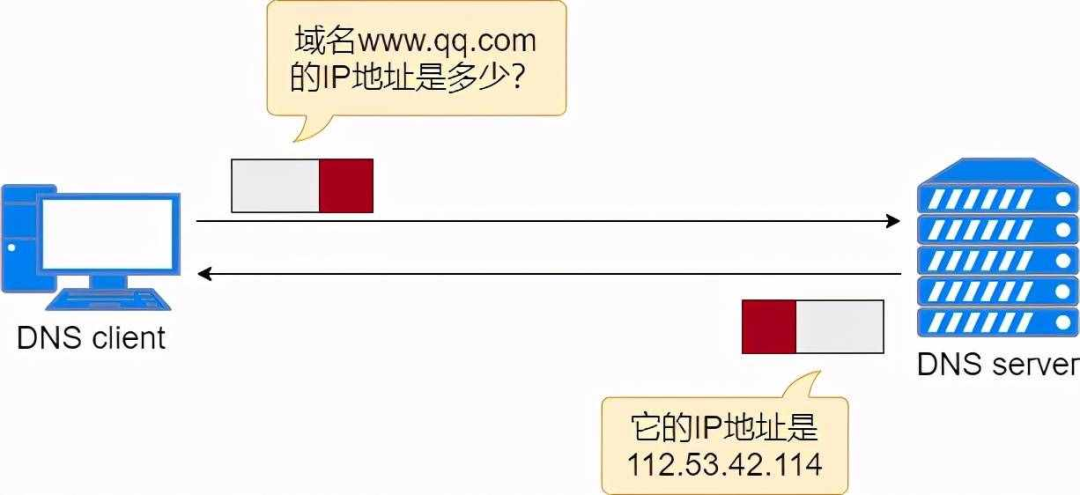
DNS protocol is an application layer protocol based on UDP. It is used to convert the website URL, also known as the domain name, into an IP address so that users can access the website.
 picture
picture
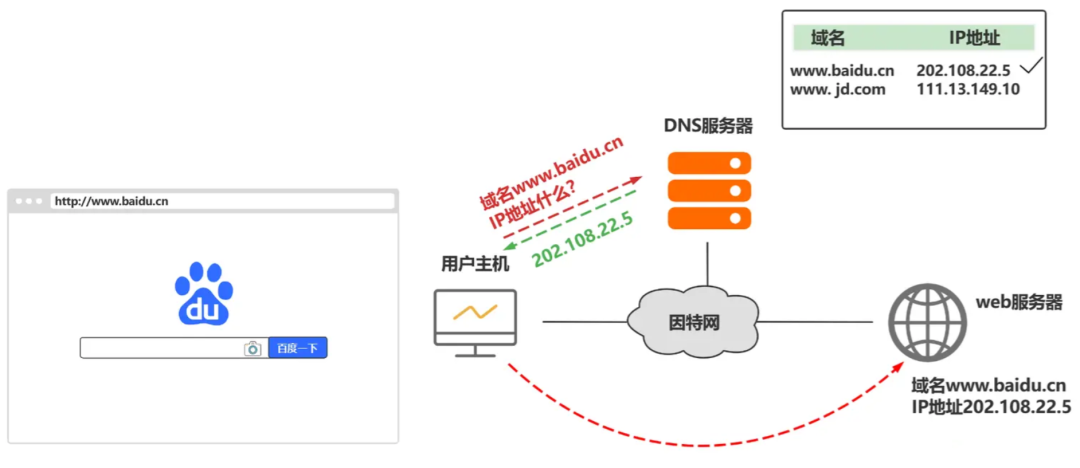
DNS links domain names and IP addresses. With a DNS server that saves the correspondence between website domain names and IP addresses, we do not need to enter the IP address to access a website. Instead, we enter the URL and then obtain the corresponding domain name by requesting the DNS server. IP to access the website.
 picture
picture
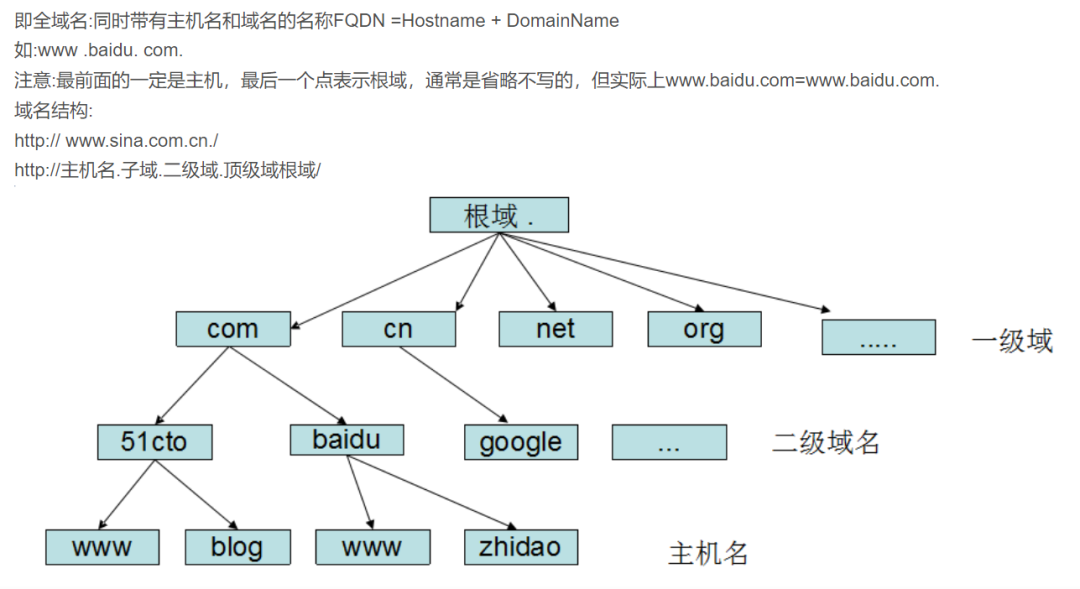
The namespace of a DNS domain is a tree-like hierarchical structure, which can generally be divided into root domain, first-level domain (also called top-level domain), second-level domain, subdomain and host name.
 picture
picture
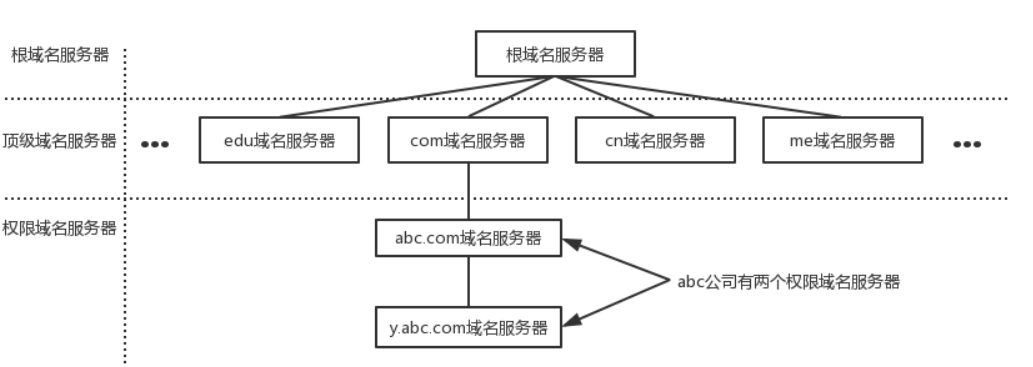
Correspondingly, there will be a domain name server at each layer of the domain name to provide domain name resolution services at the corresponding level.
 picture
picture
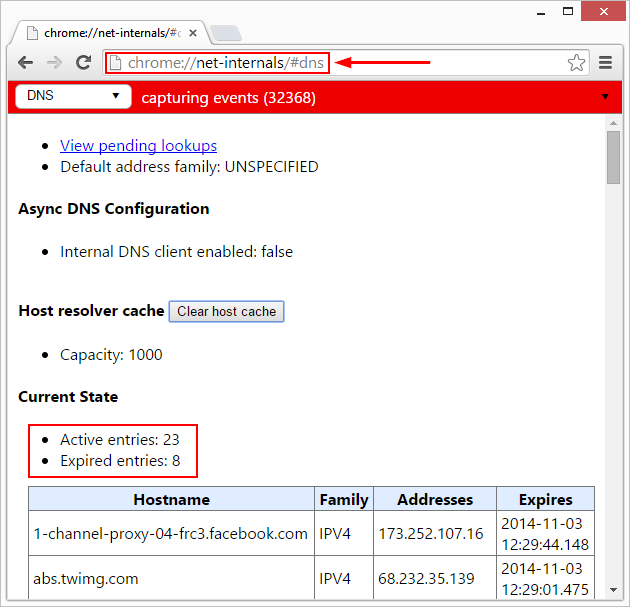
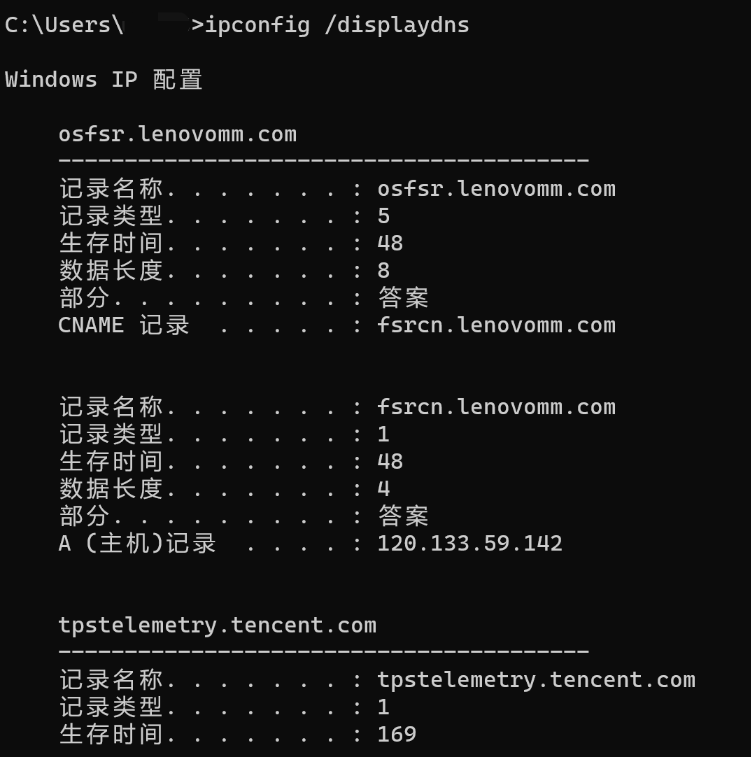
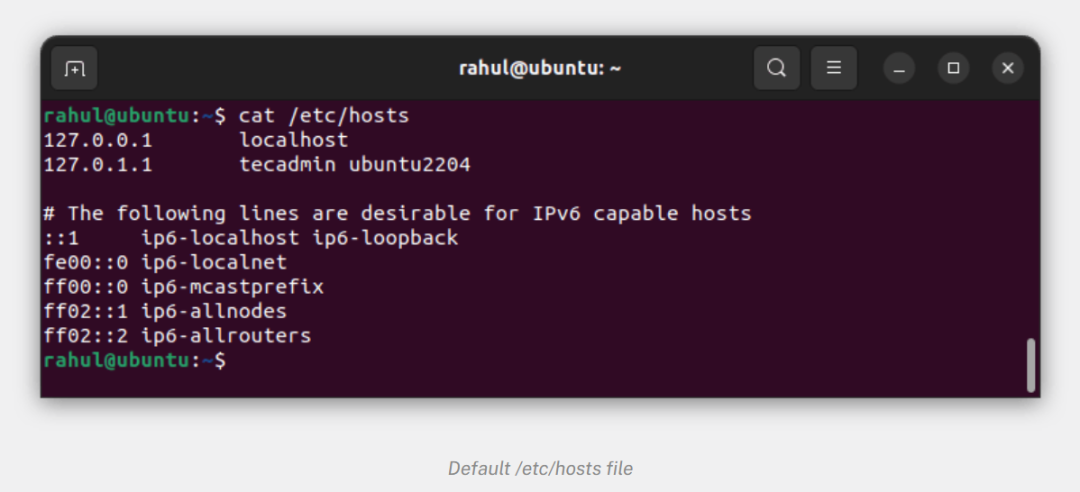
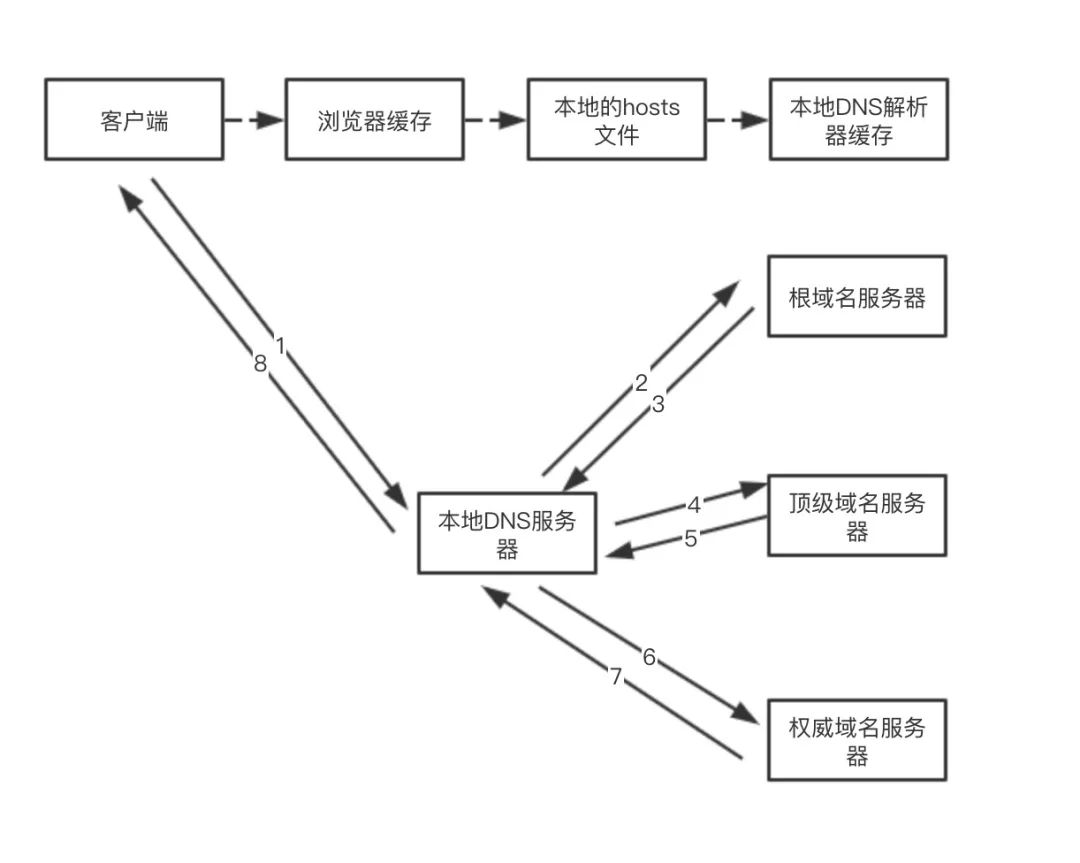
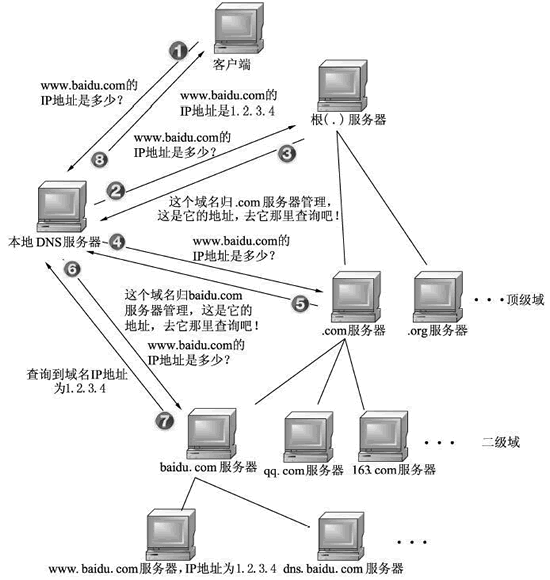
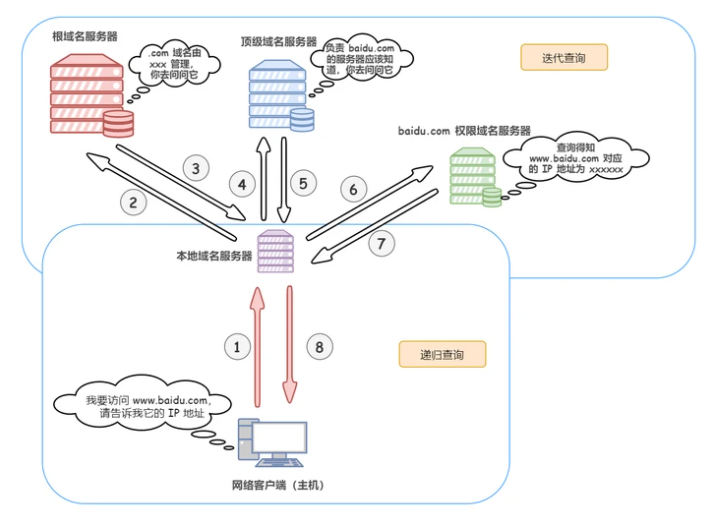
The process of DNS domain name resolution is that the host first checks the DNS cache on the local browser, and then checks the DNS cache and hosts file in the local operating system. If there are none, it will initiate a DNS domain name resolution request to the local DNS server. The local If the DNS server has the IP address corresponding to the requested domain name, it will directly return it to the host. If not, send a request to the root domain name server. The root domain name server is the highest level. It is not directly used for domain name resolution, but it will tell the local DNS server to find the corresponding top-level domain name server. Then, the local DNS server will find the corresponding top-level domain name server. When requesting a top-level domain name server, the top-level domain name server will tell the local DNS server to find the corresponding authoritative DNS server. The local DNS will then turn to the authoritative DNS server. After querying, the authoritative DNS server will tell the local DNS the corresponding IP address, and the local DNS will then query the top-level domain name server. The IP address is returned to the host.
At this time, in order to avoid going through the above parsing process again the next time DNS resolution is initiated for this domain name, both the host and the local DNS will cache the domain name resolution results just now. When parsing next time, if there is a cache, you can directly retrieve it from the cache. Get the analysis results.
 picture
picture
 picture
picture
 picture
picture
 picture
picture
 picture
picture
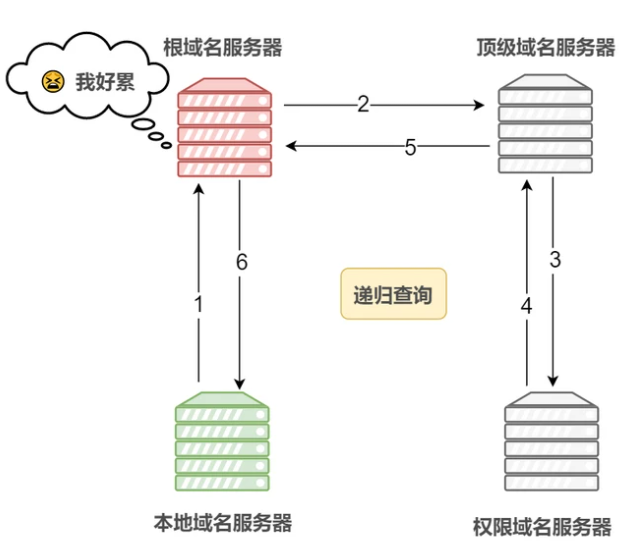
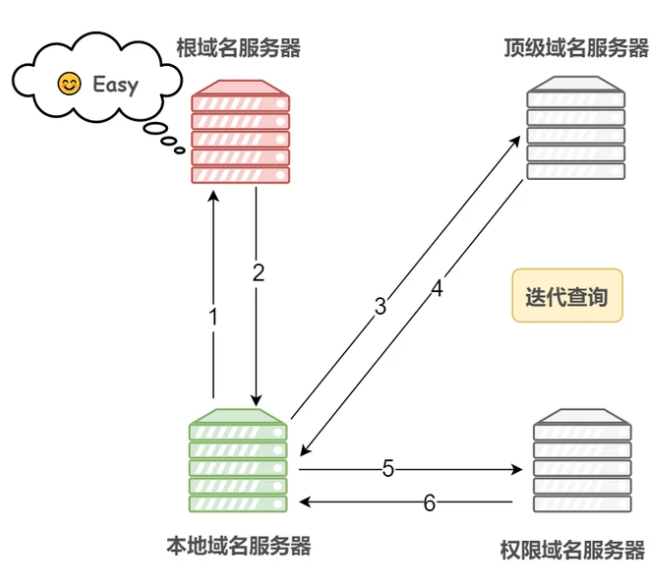
As can be seen from the above process, there are two ways to query DNS, one is recursive and the other is iterative.
Recursive query means that if A requests B, then B, as the recipient of the request, must give A the answer he wants.
 picture
picture
Iterative query means that if receiver B does not have the exact content requested by requester A, receiver B will tell requester A how to obtain the content, but will not make the request itself.
 picture
picture
In practical applications, recursive queries are usually used for queries from the requesting host to the local DNS server, while iterative queries are used for the local DNS server to issue query requests to the root domain name server or top-level domain name server.
 picture
picture