Bluetooth vs. WiFi: Choosing the Great Options for Your IoT Devices

Bluetooth vs. WiFi: Choosing the Great Options for Your IoT Devices

Both Bluetooth and WiFi are commonly used in IoT devices, but both options have advantages and disadvantages because they operate differently. In this article, we will compare the differences between Bluetooth and WiFi for IoT.
Bluetooth IoT device
Bluetooth is a wireless technology protocol that relies on physical proximity to establish a connection between devices without the need for a password. Bluetooth technology operates on radio frequencies in the 2.4 GHz spectrum. Although the Bluetooth SIG reports that the technology's range can vary from 1 meter to 1 kilometer (3 feet to about 0.6 miles) depending on device class and environment, Bluetooth is generally considered best suited for short-range situations.
Examples of Bluetooth technology include Apple's wireless headphones, AirPods, and many wireless devices such as speakers, computer mice, and keyboards.
Bluetooth IoT Compatibility Requirements
For an IoT device to be Bluetooth-compatible, it must have a microprocessor capable of handling Bluetooth technology, as well as a second device to pair with it. Bluetooth provides two versions commonly used by IoT devices: Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). These two versions are designed for devices that require low power consumption.
Developers often choose Bluetooth over WiFi for IoT devices for a number of reasons. First, Bluetooth typically requires physical proximity to initiate a signal broadcast, which reduces potential attack vectors that can arise from improperly secured networks. Second, Bluetooth requires much less energy than WiFi, making it more suitable for low-power IoT devices such as basic sensors.
WiFi IoT devices
WiFi is a wireless network technology that uses radio waves in various frequency bands to transmit information between devices. All modern computers and smartphones have built-in WiFi capabilities.
WiFi IoT Compatibility Requirements
WiFi usage on IoT devices requires microchips, which are easily available and cost-effective. However, actual implementation also involves firmware management of the device's WiFi credentials, as WiFi can be vulnerable to attacks by malicious actors.
WiFi is typically used in large fixed IoT centers, but can also be used in smaller devices. To connect to WiFi, IoT devices need to be close to the WiFi access point (i.e. not located too far away).
IoT Bluetooth vs. WiFi: Features Comparison
Now that we've discussed the basics of Bluetooth and WiFi, let's take a look at how these two technologies stack up in terms of different capabilities.
1. Speed
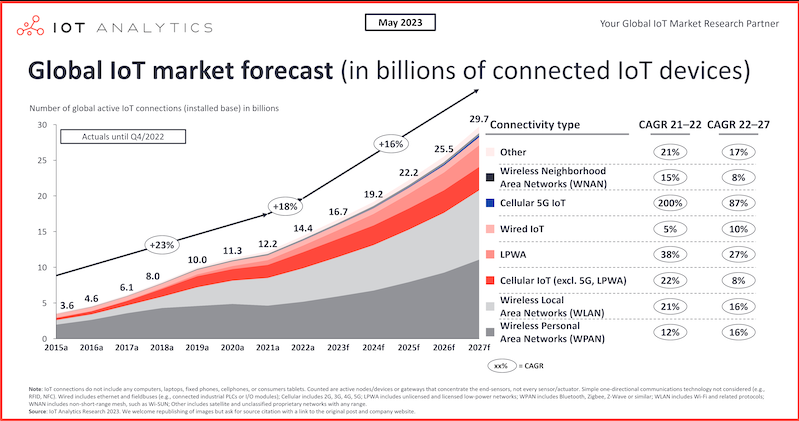
WiFi's maximum theoretical speed is much faster than Bluetooth: WiFi is close to 10 Gbps, while Bluetooth is only 3 Mbps. Therefore, Bluetooth is better suited for transmitting small pieces of data, such as values from IoT sensors, while WiFi excels at transmitting larger data files, such as videos and photos.
2. Security and privacy
Bluetooth provides adequate security for most purposes, although it is not a completely secure protocol. However, if you are concerned about sensitive data transmission, using WiFi can help. WiFi can add an extra layer of security by using security protocols such as WEP, WPA, WPA2 and WPA3 (the latest and preferred version of WPA).
3. Location detection
The correct answer here depends on the accuracy and precision required for your use case. Both WiFi and Bluetooth can provide accurate location information, although Bluetooth may be more reliable in some situations.
4. Proximity detection
BLE provides much more accurate proximity data than WiFi, but it's still not very accurate. (We're talking estimates not within inches, but within tens of feet.)
5. Scope
Bluetooth generally has a smaller range than WiFi. The maximum range of a Class 1 Bluetooth device is expected to be 100 meters (328 feet), but most consumer Bluetooth devices have a range of less than this—usually only 10 meters (33 feet). Additionally, the range of Bluetooth will depend on the density of obstacles and walls between the two devices. WiFi range also varies based on factors such as frequency, transmission power, antenna type, and environment; WiFi routers located outdoors generally have greater range.
6. Power usage
If you use WiFi, you may need to add additional direct-connect power to your device. Bluetooth consumes less power than WiFi, especially when using the BLE protocol.
7. Easy to log in
Bluetooth offers the potential for a consistent self-registration process for all devices and situations. However, due to network configuration requirements, WiFi self-registration may require additional steps or customer support to ensure successful integration.
8. Mobility
Although Bluetooth has a shorter range than WiFi, it is a more mobile technology because devices can be moved remotely and easily reconnected to a hub or gateway when possible. Gateways can also be moved remotely, such as where a cell phone provides service at a remote location. WiFi networks are typically limited to the location where the network is created, and have excellent mobility within that range, but very limited ability to expand further.
Bluetooth vs. WiFi for the Internet of Things: Which is better?
When considering Bluetooth vs. WiFi for IoT, there is no definite answer. The choice depends on your specific business needs, priorities, and how you will use the device.
Note that it is technically not possible for an IoT device to only use Bluetooth, as it still requires an intermediary device that will broadcast the data it receives using some networking technology (such as WiFi or cellular).
Generally speaking, Bluetooth is more suitable for mobile devices with limited power requirements. Meanwhile, WiFi is better suited for larger, more stationary devices that need to connect directly to the Internet.
Best choice for IoT devices
When it comes to the question of Bluetooth vs. WiFi for IoT, the right answer will depend on your specific situation. Consulting a knowledgeable IoT development company can help you make the best connectivity decisions for your product.