探索Gateway API 在Service Mesh 中的工作機制

探索Gateway API 在Service Mesh 中的工作機制
前幾天 Gateway API 宣佈在0.8.0 中支持服務網格[1],這意味著 GAMMA[2](Gateway API for Mesh Management and Administration)有了新進展,雖然目前還是實驗階段。去年6 月Gateway API 發布0.5.0 時,我還寫了一篇 SMI 與Gateway API 的GAMMA 倡議意味著什麼?[3]。如今,SMI 作為sandbox 項目的年度審查已經 過了幾個月仍未提交[4],唏噓。
廢話不多說,我們來看下0.8.0 下的Gateway API 如何在Service Mesh 中工作。
TL;DR
Gateway API 對服務網格的支持仍然是實驗階段,但是已經有廠商跟進(當然也都是實驗階段)。
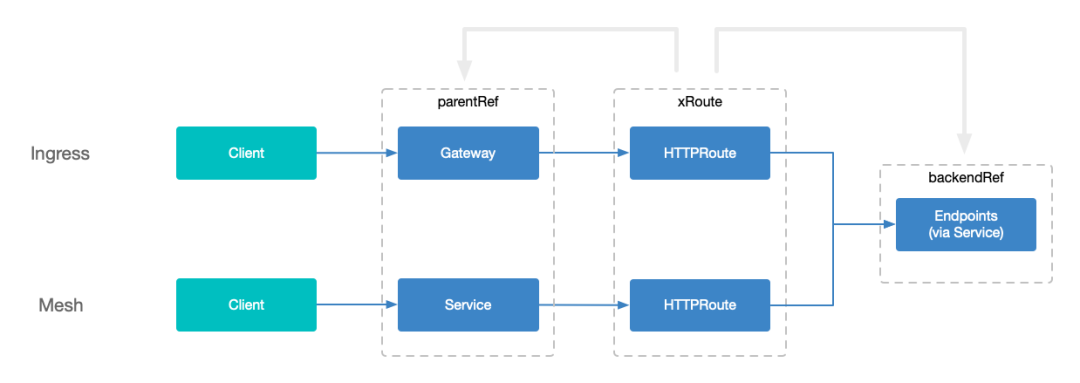
相比Gateway API 處理南北向流量將路由綁定到 Gateway 資源[5] 相比,在網格中路由則是與Service 進行綁定。簡單理解成Service 代理了Gateway 的角色,不過該Service 是目標Service。
Gateway API 中的服務網格
要說服務網格,我們先來看下服務 Service。
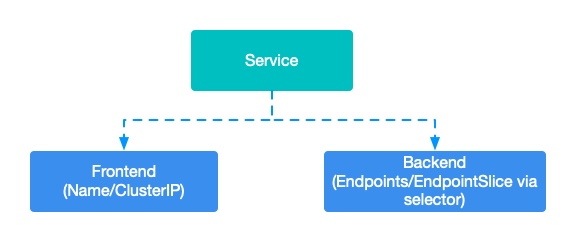
抽象 Service
Service 中Kubernetes 中是一個獨立的資源,這裡說的抽像是從邏輯上進行抽象,抽象成前端和後端兩部分。
前端(Frontend)通常就是 Service 的DNS 名字或者 ClusterIP;後端(Backend)則是通過標籤選擇器選擇的 Endpoint 或者 EndpointSlice。
 圖片
圖片
路由與服務
 圖片
圖片
把路由直接綁定到Service 上,被認為是當下最優的選擇。Service 與其他資源的耦合度太高,比如IP 分配、DNS、端點集合、負載均衡等等,但在目前的網格設計中也是唯一的最優選擇,未來會尋求更好的選擇,比如ServiceBinding(見後文)
這樣做的好處呢,就是將服務的前後端分別與現在的 xRoute API 中的 parentRef 和 backendRef 關聯,無需引入額外的API。
不同的時候,在 xRoute API 中的 backendRef 也可以是一個 Service,但是最終在路由請求時,目標還是 Endpoint 或者 EndpointSlice,只不過他們與 parentRef 中的 Service 不是強關聯的。
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: smiley-route
namespace: faces
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: smiley
kind: Service
group: core
port: 80
rules:
...- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
如果一個Service 上配置了多個路由,匹配到多條路由的請求將被拒絕。
請求流程
- 客戶端發送請求
- 網格數據面代理攔截請求
- 通過虛擬IP 地址、DNS 主機名、或者名字來確認流量是屬於哪個 Service(不會使用 xRoute 上的 hostname 字段)
- 如果 Service 沒有配置路由,將使用請求的原始目的地進行轉發
- 找到匹配的優先級最高(消費者路由高於生產者路由,見下文)的路由進行轉發
- 如果配置了路由,但都無法匹配,則拒絕請求
路由的命名空間
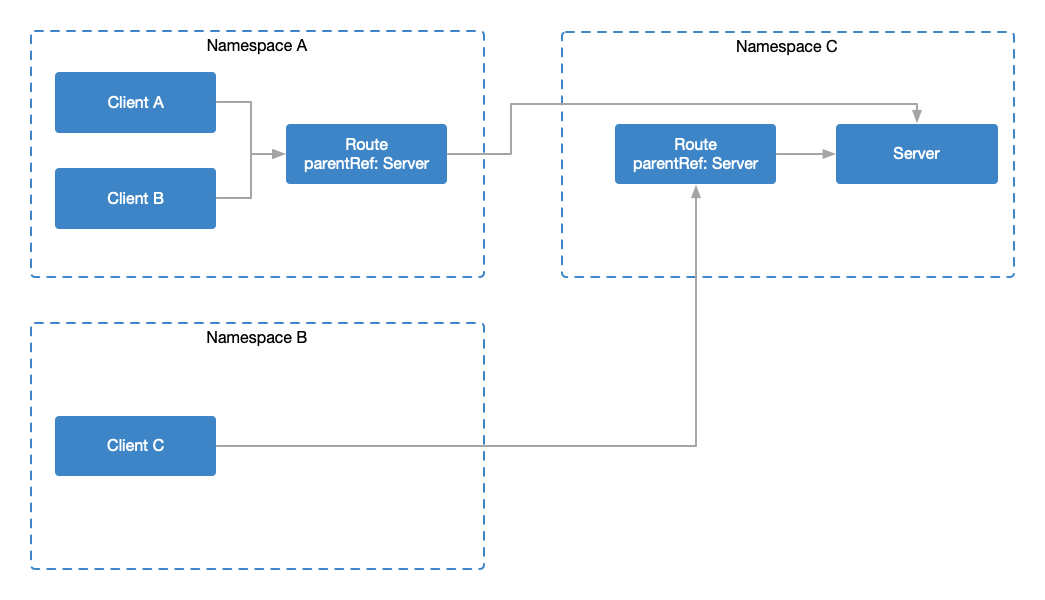
為什麼要提命名空間,是因為路由與服務在相同或者不同命名空間下所代表的含義不同。
同命名空間
路由 smiley-route 與Service smiley 位於同一個命名空間 faces,該路由上設置了請求超時時間 100ms。這意味著,所有訪問Service smiley (來自任一命名空間下的任一工作負載)並匹配 smiley-route路由規則的請求,都受該超時配置的影響。
這種路由被稱為 生產者路由(Producer Route)[6],影響目標為該服務的所有請求。
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: smiley-route
namespace: faces
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: smiley
namespace: faces
kind: Service
group: core
port: 80
rules:
...
timeouts:
request: 100ms- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
不同命名空間
路由smiley-route 與Service smiley 位於不同的命名空間,與上面不同的是,所有訪問Service smiley(來自命名空間fast-clients 下的任一工作負載)並匹配smiley-route 路由規則的請求,都受該超時配置的影響。
這種路由被稱為 消費者路由(Consumer Route)[7],影響同命名空間下訪問木雕服務的所有請求。
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: smiley-route
namespace: fast-clients
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: smiley
namespace: faces
kind: Service
group: core
port: 80
rules:
...
timeouts:
request: 100ms- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
 圖片
圖片
同一Service 上的多個路由
這裡的前提條件是這些路由都位於同一命名空間下,即同為生產者路由,或同為消費者路由。這種情況將會遵循 路由合併規則[8] 多這個路由進行合併,如果要為同一命名空間下的多個工作負載配置不同的消費者路由,目前還無法實現。唯一的
比如下面定義了兩個消費者路由 smiley-route-50 和 smiley-route-100
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: smiley-route-50
namespace: fast-clients
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: smiley
namespace: faces
kind: Service
group: core
port: 80
rules:
...
timeouts:
request: 50ms
---
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: smiley-route-100
namespace: fast-clients
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: smiley
namespace: faces
kind: Service
group: core
port: 80
rules:
...
timeouts:
request: 100ms- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
路由與策略
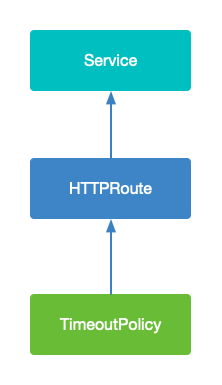
之前也寫文介紹過Gateway API 中的策略,有興趣的可以看一下 一文搞懂Kubernetes Gateway API 的Policy Attachment[9]。
在網格中策略附加可以非常簡單。策略可以應用於任何命名空間中的任何資源,但如果目標位於不同的命名空間中,則它只能應用於來自同一命名空間的請求(跟隨消費者路由的邏輯)。
 圖片
圖片
網格一致性測試
首先來看下何為 一致性配置文件[10]:
Gateway API 會提供用於一致性測試的配置文件,在運行一致性測試可以選擇這些配置文件。然後將一致性結果報告回網關API 項目並獲得認證(例如徽章)。除了測試核心的功能,也可以自主添加廠商的特定實現中的擴展功能進行測試。
這些Gateway API 的實現會將測試報告提交到 官方倉庫的一致性測試報告目錄[11] 中,可以作為大家選型時的依據之一。
目前有 HTTP、TLS、TLSPassthrough(基本上都是根據xRoute 來進行組織,因此後續也會有 GRPC、TCP、UDP)。針對服務網格,也提出了 `mesh` 配置文件[12]。
官方博客[13] 中提到Kuma 2.3+、Linkerd 2.14+、和Istio 1.16+ 中的Gateway API 實現已經全部通過 mesh一致性測試,但截止目前未看到測試報告,估計還在上傳中。
參考資料
[1] Gateway API 宣佈在0.8.0 中支持服務網格: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/blog/2023/0829-mesh-support/#service-mesh-support-in-gateway -api
[2] GAMMA: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/concepts/gamma/
[3] SMI 與Gateway API 的GAMMA 倡議意味著什麼?: https://atbug.com/why-smi-collaborating-in-gateway-api-gamma/
[4] 過了幾個月仍未提交: https://github.com/servicemeshinterface/smi-spec/issues/254
[5] Gateway 資源: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/references/spec/#gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1.Gateway
[6] 生產者路由(Producer Route): https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/concepts/glossary#producer-route
[7] 消費者路由(Consumer Route): https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/concepts/glossary#consumer-route
[8] 路由合併規則: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/api-types/httproute#merging
[9] 一文搞懂Kubernetes Gateway API 的Policy Attachment: https://atbug.com/explore-k8s-gateway-api-policy-attachment/
[10] 一致性配置文件: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/geps/gep-1709/
[11] 官方倉庫的一致性測試報告目錄: https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/tree/main/conformance/reports
[12] mesh 配置文件: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/geps/gep-1686/
[13] 官方博客: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/blog/2023/0829-mesh-support/