How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?

How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?

Fiber optic and cable connection arrangements are the background technology behind the high speed, wide coverage and increased bandwidth of modern communication systems. Individual components such as optical fibers, cables, connectors, and end-to-end optical fibers have evolved over decades to support current and emerging applications. Today, the need for data has reached new heights, especially during and after the pandemic. In order to meet this demand, existing traditional cable deployment methods are no longer sufficient, and 10X fiber needs to be deployed at 3X speed. This article will discuss the following topics and bring out the best solutions for denser and faster fiber deployments.
- Network Evolution and Bandwidth Growth
- Advantages of cable technology and microcables
- Example
Major technology and capex changes
Ever-increasing data demands put a lot of pressure on fiber optic factories. Upgrades to fiber optic equipment are inevitable, and designing smarter methods of cable deployment is a current need. The main reasons for such data needs are:
- The arrival of 5G
- Large data centers installed by cloud computing companies
- Connect everything with IoT
- Virtualization (Software Interrupt Networking)
- Technological Changes Affecting Fiber Optic Cables
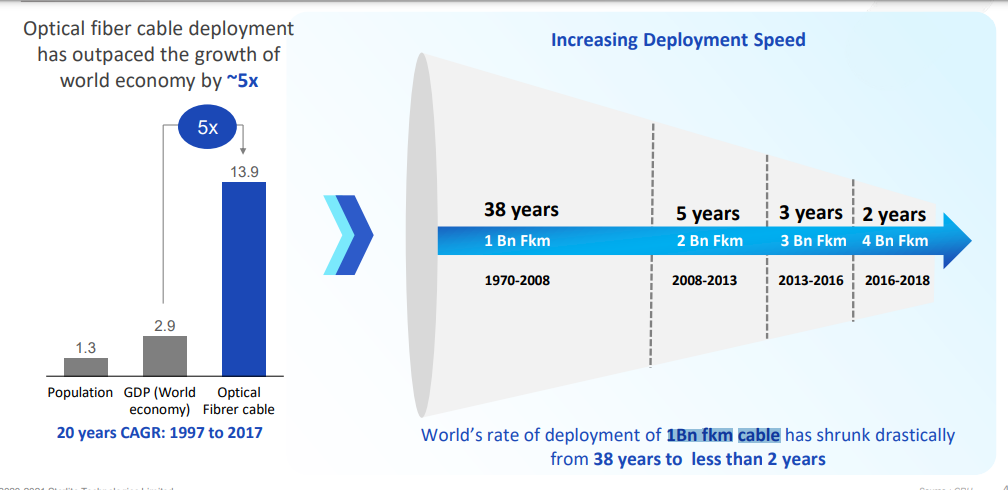
Optical Fiber Demand Growth Unabated
Judging from the 20-year CAGR (compound annual growth rate) from 1997 to 2017, the deployment speed of optical fiber has exceeded the growth rate of the world economy by 5 times. From 1970 to 2008, the deployment speed of 1 billion feet of cable decreased dramatically from 38 years to 2 years. From 2016 to 2018, 4 billion kilometers of cable have been deployed, which is quite remarkable. But the pandemic accelerated the process even further, as lockdowns shifted education and work to home and doubled the number of people watching visual content online. Although the rate of wire deployment has increased, it is still not enough to meet current data demands. The need to deploy 10x fiber at 3x speeds is reportedly forcing network operators to develop new cable technologies.
 How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?
How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?
Fiber Optic Cable Deployment Growth
micro cable
Micro cables are the best solution for faster, denser fiber deployments to meet current and future bandwidth requirements. The technology will allow network operators to install fiber optic cable systems faster than before, while reducing labor and equipment costs. These micro-cables provide the right balance between deployment speed and fiber density.
A micro cable is a fiber optic cable that has a smaller outer diameter (OD) and cable weight than conventional cables. For example: the outer diameter of the traditional Unitube Drop cable is about 4-8 mm, while the outer diameter of the micro cable is about 2.5 mm or even 1.6 mm.
Miniature cable designs include stranded loose tube, center tube, and single tube designs. What all these designs have in common is light weight, large outer diameter and reduced gum. Typically, miniature cables have no metallic or dielectric covering and therefore cannot be buried directly in the ground. The miniature cable design is suitable for outdoor and indoor environments. The features and advantages of microcable technology are:
Features:
- thin appearance
- tube small
- Holds more fibers per tube
- 200um optical fiber
- IBR functional area
advantage:
- optimize maximization
- Cable diameter reduction
- light weight
- easy to operate
- Efficient logistics with smaller drums
- Reduced risk of cable damage
The different types of micro cables used are as follows:
 How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?
How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?
Types of Micro Cables
How can we build denser networks faster?
Combining micro-cable technology and blown equipment allows for denser networks to be built at a faster rate. Its advantages and challenges are:
- Dense Urban Deployment
- Micro trench green space installation
- Expand existing pipeline space
- service isolation
- multiple pipes
- Reduce the risk of service continuity
- challenge
- MLT design – longer splicing time
- Professional setting
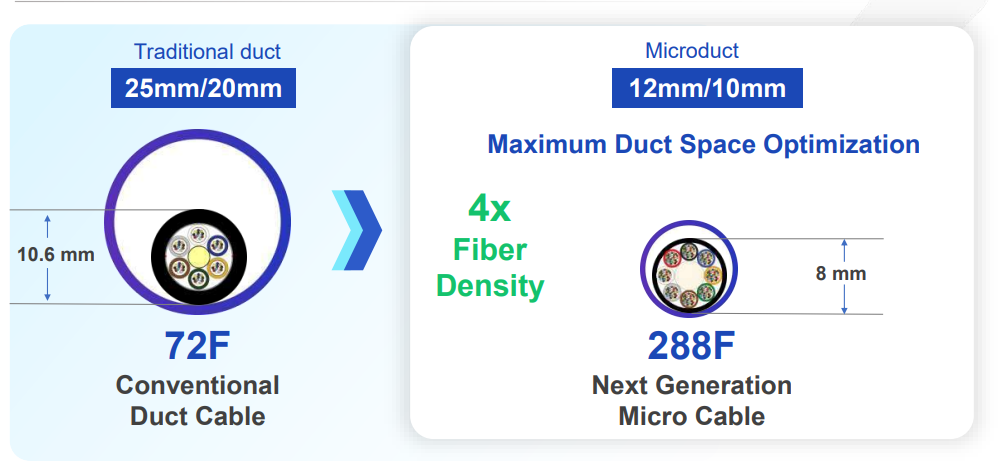
Denser – 4x the number of fibers
Typically, full-size underground cables are installed inside polyethylene conduits, known as inner conduits. These 25-51mm diameter inner pipes are located inside the telecommunications piping system. When installing the micro-cable, it is necessary to place the matching micro-tube first, and then insert the micro-cable by blowing. These micro-ducts allow the installation of denser micro-cables according to current needs and provide enough surplus space for future installations according to future needs.
 How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?
How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?
Micro Cable Thickness
Faster – Blow-In vs Pull-In
Pull installation is a method of laying down pipes and cables for short distances. It is often used to place large diameter conventional cables and pipes. Blow-fitting, on the other hand, is a device-driven installation method for placing micro-ducts and micro-cables. When comparing the two methods, the blow install seems to be far superior to the pull install method and is much faster.
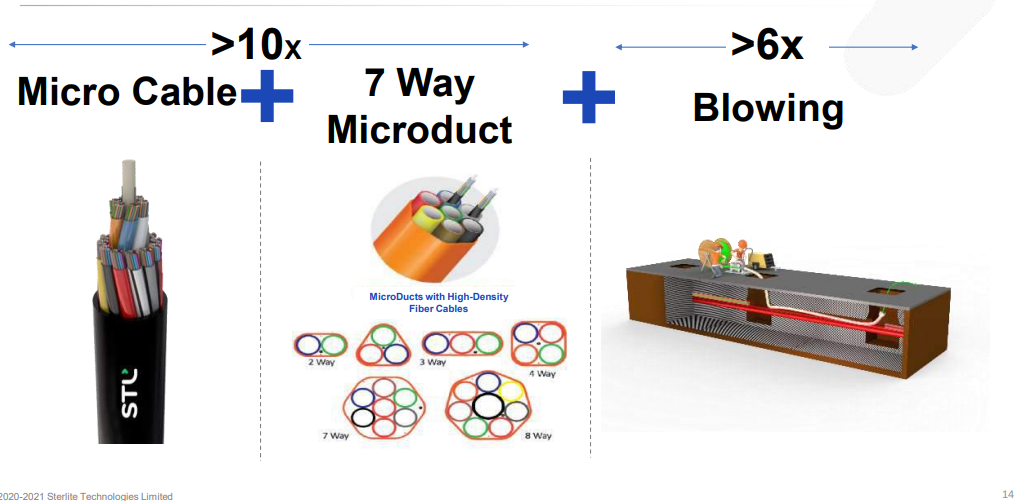
And, the combination of microcables, 7-way microducts, and blow-and-fill methods will help network operators place denser fibers 16 times faster than traditional cable deployments.
 How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?
How do fiber optic cables meet today's connectivity needs?
Blow-In vs. Pull-In
Summarize
With the development of 5G and other next-generation technologies and changes in capital expenditures, the demand for data will explode, requiring faster and denser fiber deployment. If you continue to use traditional cable and pull methods without adapting to changing needs, you have no chance of meeting future needs. Therefore, microcable technology is the single best solution with all the necessary attributes to meet current and future data and bandwidth requirements.