What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?

What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?

Today, there is an ever-increasing demand for faster Internet and data transmission speeds in various business and industrial sectors. Whereas Cat7 cables are designed to support higher frequency signals than Cat5e and Cat6 cables.
Category 7 cable ( Cat 7 ) is a shielded twisted-pair cable used in high-speed Ethernet-based computer networks of 1 Gbps or higher between directly connected servers, switches, and computer networks. It is defined and regulated by the ISO/IEC 11801:2002 Class F specification. Cat7 cables Ethernet cable types and speeds are backward compatible with Cat 6, Cat 5/e cabling standards and Cat5/e equipment.
What is CAT 7 cable used for?
Cat7 cable is a high-end patch cord used to provide the core infrastructure of a wired Gigabit Ethernet setup. Some common examples include:
ethernet cable
Cat7 Ethernet cables ( LAN cables ) are used to connect modems, hubs, and individual computers on networks of all shapes and sizes.
commercial and industrial applications
Cat7 cables can withstand a variety of hazards including temperature extremes, UV/moisture exposure, and direct contact with different chemicals and oils.
home application
In addition to enthusiast gaming setups, Cat7 cables are gaining popularity among home users in a variety of Cat7 LAN cable networking and connection setups.
Characteristics and Specifications of Cat7 Cable
ISO/IEC 11801:2002 specifies the Cat7 Ethernet cable specification. Since Cat7 cables are sometimes referred to as ISO Class F cables, the Cat 7 cable specification is also referred to as the Class F standard.
1. The transmission rate of the seven types of wires
Cat7 cable was designed to support 10 Gbps Ethernet, but lab tests have shown it can transmit up to 40 Gbps at 50 meters and even 100 Gbps at 15 meters.
Compared to the previous version, it is theoretically six times better than Cat5e (100 MHz) and 2.4 times better than Cat6 (250 MHz) in terms of raw performance.
 What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
Classification specification
2. Category 7 network cable specifications
In 2002, the Cat7 cabling standard was approved to allow copper cabling for 10 Gigabit Ethernet Cat7 cables . Cat7 has the same maximum length as Cat5e, Cat6 and Cat6A, with a maximum distance of 328 feet (100 meters).
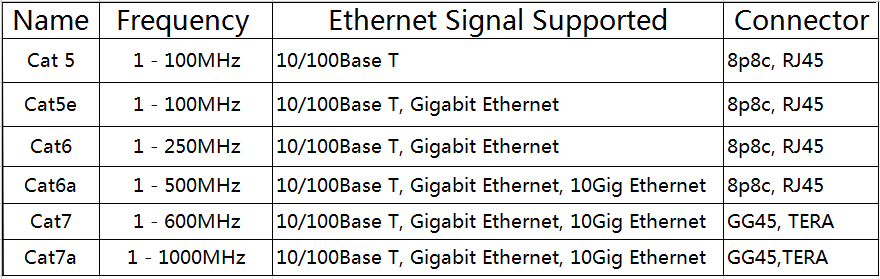
Category 7 cable has four shielded twisted copper pairs and an overall cable shield. This helps it meet stringent standards for signal loss over distance and ensures that Cat7 cables are better protected against crosstalk and possible degradation in performance caused by Electromagnetic Interference (EMI).
 What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
Category 7 network cable
What types of Cat7 cables are there?
Here are the different types of Category 7 Ethernet cables:
1. Cat7a cable
Cat7a is short for "Category 7 Plus". Frequency up to 1000 MHz is defined in Amendment 2 (2010), 2nd Edition of ISO 11801. Cat7a Ethernet cables are usually slightly thicker because of the extra shielding designed to boost speeds up to 1000 MHz.
2. RJ45 Cat7 cable
Most Cat 7 Ethernet cables are terminated with RJ45 connectors on both ends for plug and play. This is the plug you need for the cable outlet on any standard home router or LAN cable switch, and is standard in almost all Ethernet connection setups.
3. Cat7(a) UTP cable
Cat7(a) UTP cable refers to an unshielded twisted pair design. The four twisted pairs of copper wires that make up a Cat7 Ethernet cable are surrounded only by their own inner jacket and, in this configuration, the jacket of the outer cable.
4. Cat7(a) F/UTP cable
Similar to the UTP design discussed above, F/UTP cable (foiled/unshielded twisted pair) has no additional shielding around the twisted pair itself. Nonetheless, a single foil shield beneath the cable's outer jacket holds the four pairs twisted together.
5. Cat7(a) STP and FTP Cat7 cables
These acronyms stand for Shielded Twisted Pair and Foiled Twisted Pair respectively. STP and FTP indicate that the cable has an extra wrap around each twisted pair made of a protective foil shield.
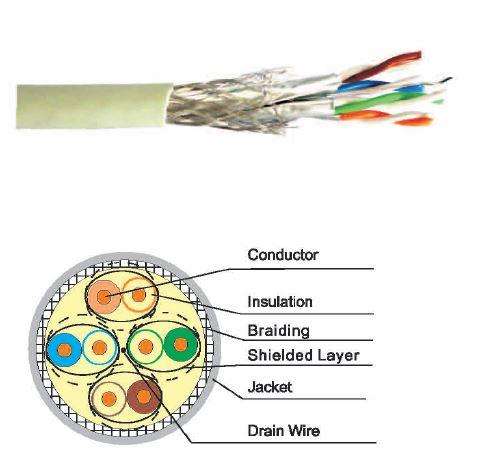
 What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
Cat7 F/STP transmission specification
6. SFTP Cat7 cable and SSTP Cat7 cable
SFTP (Shielded Foiled Twisted Pair) or SSTP (Shielded Spliced Pair) (double shielded twisted pair). Cat7(a) SFTP or SSTP means the twisted pair has a foil screen/shield between the outer cable jacket and the inner wires and is individually wrapped around each twisted pair.
 SSTP Cat7 cable
SSTP Cat7 cable
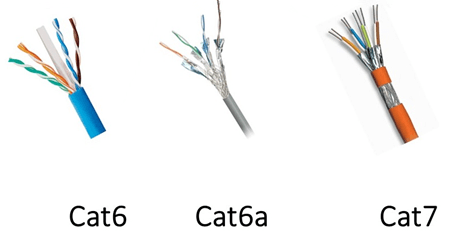
What is the difference between Cat6 and Cat7 cables?
The physical makeup of Cat7 cables is similar to the previous Cat6 cables. Both versions feature the same twisted-jacketed four-pair cable design capable of transmitting 10 Gbps Ethernet signals over distances of up to 100 m.
 What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
Cat7 has been double shielded to meet stricter specifications. They provide better shielding from EMI and crosstalk.
The main difference between Cat6 and Cat7 is speed and frequency. As you probably know, Cat7 or Cat7a has a maximum speed of 10000 Mbit/s and Cat6 cable has a maximum speed of 1000 Mbit/s.
Also, Cat 7 has a higher frequency than Cat6. Therefore, a CAT 7 shielded Ethernet cable will be able to transmit data faster than a Cat6 cable. There are also stricter performance and longevity standards for Cat 7 shielded cables .
However, as with many other products of this type, the key is to choose the product that best suits your job, depending on what is required, and at the most cost-effective price to meet those requirements. Cat 7 is primarily used in data centers.
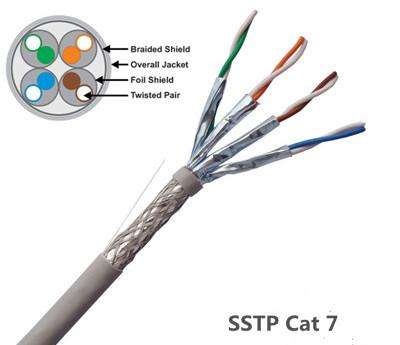
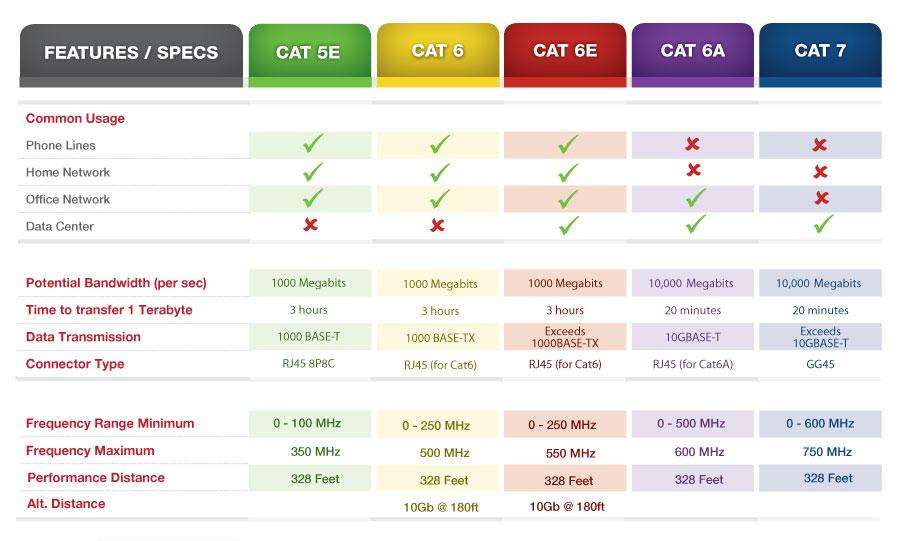 Cat5 v Cat6 v Cat7 specifications
Cat5 v Cat6 v Cat7 specifications
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is Cat7 faster than Cat6?
The main difference between Cat6 and Cat7 is the increased bandwidth and improved shielding. Cat7 has a maximum speed of 10000 Mbit/s and Cat6 cable has a maximum speed of 1000 Mbit/s. Also, Cat7 has a higher frequency than Cat6. Therefore, Cat7 cables can transfer data faster than Cat6 cables.
Say you need to increase your internet speed or connect another device. In this case, Cat7 standard cables are the best choice, while Cat6 cables provide enough speed to run most connected applications and devices in the home or office.
 What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
What are the characteristics and uses of Category Seven (Cat7) cables?
2. What does the A in Cat7a stand for?
The "A" in Cat7 stands for Enhanced and includes shielding for each twisted pair as well as overall shielding (S/FTP). Cat7a, or Enhanced Category F, is the latest recognized standard for network cables defined by IEC/ISO in 2010.
Additional jackets enable higher bandwidths up to 1000 MHz. Each pair of wires is shielded with foil to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI), which is critical in electrically noisy environments such as data centers. An overall braided shield surrounding all four pairs provides additional EMI protection. When terminated, Cat7A cables include a drain wire to ground the power.
3. What do UTP, SFTP, FTP, STP, and SSTP mean for Category 7 cables?
These prefixes refer to the various wire shielding configurations used within the cable body:
Cat7(a) UTP cable: The unshielded twisted pair design provides adequate EMI and signal attenuation protection to meet the baseline requirements of this standard.
Cat7(a) F/UTP Cable: Foil/unshielded twisted pair cable provides more protection against signal loss than the UTP version.
STP Cat7 cable and FTP Cat7 cable: Shielded twisted pair or foiled twisted pair cables are closer for maximum safety.
SFTP Cat7 Cable and SSTP Cat7 Cable: Shielded Foiled Twisted Pair or Double Shielded Twisted Pair provides the most complete additional signal protection.
4. Can Category 7 network cables be used at home?
Yes, many people were early adopters of Ethernet connections in home hubs and naturally sought out the latest version when replacing or upgrading old cables. For example, those planning to wire a smart home today may prefer Cat7 and Cat7a, as home hardware and connection speeds are expected to continue to accelerate over the next few years.
The Cat7 and Cat7a versions are significantly thicker, stiffer, and heavier than their Cat5 predecessors, which can limit your ability to route neatly in areas where space is limited or very precise bends are required.
5. Is unshielded Cat7 cable better than shielded Cat7 cable?
Cat7 UTP cable Unshielded twisted pair cable consists of four pairs of twisted copper wires surrounded only by their own inner jacket and the jacket of a Cat7 outer Ethernet cable . UTP Cat7 cables are usually the most cost-effective version of Cat7 and Cat7a Ethernet cables with adequate EMI and signal attenuation protection.
Cat7 STP cable and FTP cable. Shielded twisted-pair and foiled twisted-pair cables have a protective foil wrapped inside each twisted pair. Again, this is closer to optimal protection than previous versions.
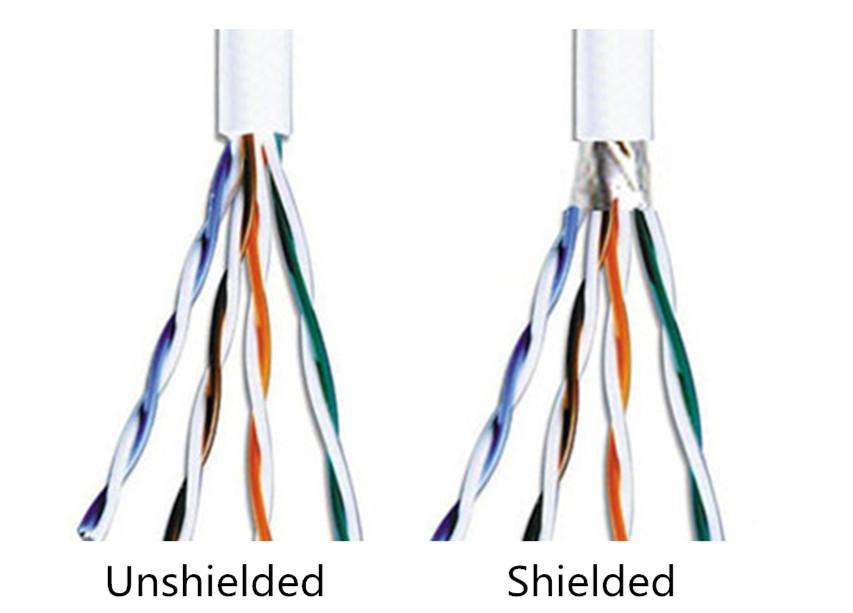 Unshielded and shielded Cat7 cables
Unshielded and shielded Cat7 cables
6. Are there Category 8 cables?
Category 8 or Cat8 cable is a different type of Ethernet cable than the others. It operates at frequencies up to 2 GHz (2000 MHz). This is the main difference between Cat7 and Cat8 . Cat 8 Ethernet cables are limited to 30m2 connector lanes. Also, it requires shielded wiring.
 Cat 8 cable compared to previous models
Cat 8 cable compared to previous models
The most important consideration is that it can carry speeds up to 35 or 40 Gbps. Overall, the physical appearance is similar to low-grade cables and can be terminated with RJ45 or non-RJ45 connections. And backwards compatible with all previous versions. It is compatible with previous versions of standard connectors such as Cat-7 .
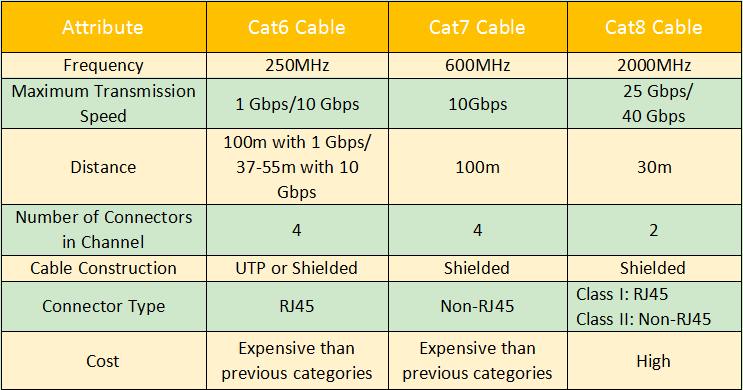 Cat 8 cable compared to previous models
Cat 8 cable compared to previous models