Development Trend of International 5G Private Network Application

Development Trend of International 5G Private Network Application
As an important driving force for the digital transformation of the industry, 5G technology promotes the integration of information technology and operation technology through the three application scenarios of eMBB, URLLC and mMTC, and improves industry productivity and operational efficiency . The 5G private network can not only use 5G technology to meet the performance requirements of the industrial field, but also ensure security and control data through self-built networks, so it has become an important area of concern for all countries. Recently, some countries and regions are t aking Various measures to accelerate the introduction of 5G private networks, cultivate the 5G private network industry ecology, and enhance the competitiveness of industries and services. This article analyzes the development trend of 5G private networks around the world, summarizes the promotion policies of 5G private networks in major countries, and the status quo of industrial ecological development, and puts forward thoughts and suggestions on the development of 5G private networks.

5G Private Network Development
5G private network is still in the development stage of extensive exploration
Since 2018, the number of private networks using 5G technology has continued to grow. According to GSA data, there will be 181 new 5G private networks in 2022, accounting for 56% of the number of new private networks. Enterprises in various fields such as manufacturing, mining, ports, logistics, healthcare, and public utilities have begun to deploy 5G private network applications. Although the number is growing rapidly, it is still in the stage of extensive exploration. Among many cases, the test bed and laboratory as a service (Device Testing&Lab as a service) cases accounted for 11%, which is to test, verify and accelerate 5G private network equipment. , The technology is mature and the test infrastructure is provided. The manufacturing industry is the most active private network application industry, with application cases accounting for 26% (122), of which 96 are discrete manufacturing application cases. Details are shown in Figure 1. From the perspective of terminal equipment, the ecological development of 5G private network terminal equipment is relatively slow, and industrial-grade 5G terminals are still lacking, especially 5G terminal equipment for specific industries, such as AGV, robots, embedded devices, etc.
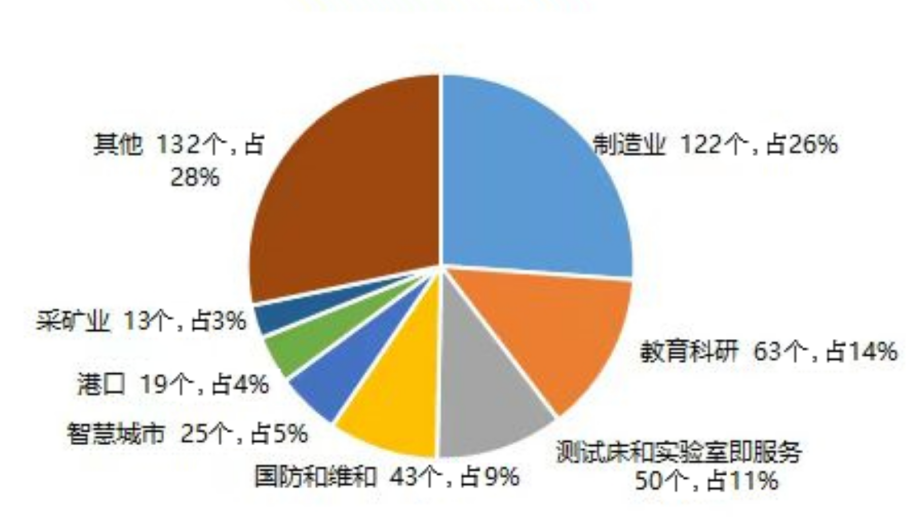
Figure 1 Industry distribution of 5G private network applications
5G Private Network Suppliers Show Diversification
The construction and operation and maintenance of 5G private network requires a deep professional technical background. In this case, a small number of capable large-scale industrial enterprise users among end users build and operate 5G private network by themselves, and the vast majority of industrial enterprise users adopt the hosting method. Private network planning, deployment and operation and maintenance are carried out by private network providers. In the initial stage of 5G private network development, mobile operators rely on network deployment and operation experience, as well as bargaining power with equipment vendors, to a certain extent dominate the private network market. Mobile operators in major countries around the world have launched 5G private network for industry users. Network solutions, flexible customization for enterprises of different sizes; the professional capabilities of equipment manufacturers are trusted by industry enterprises, and their integrated solutions have attracted a large number of users. With the development of technology and market, the development prospect of 5G private network has attracted various market entities to enter. System integrators, cloud providers, cable TV companies, emerging equipment manufacturers, etc. have entered the 5G private network market and launched 5G private network solutions. Solutions and products, from demand determination, supplier and equipment selection, license application, deployment to operation and maintenance, provide full-process service support. Emerging 5G equipment suppliers are also gradually increasing. There are more than 50 manufacturers worldwide providing equipment for 5G private networks, and the 5G private network ecology is gradually taking shape.
Many countries and regions have launched 5G private network spectrum policies
In order to meet the individual needs of industry users for 5G network technology, construction, and management, some countries and regions have formulated spectrum policies related to 5G private networks. So far, 32 countries and regions around the world have issued or plan to introduce local 5G spectrum policies (17 of which have opened applications for licenses). Under industry appeals and policy guidance, Europe is the region with the most countries that have issued dedicated spectrum policies, accounting for 63%. Germany and the United Kingdom took the lead in opening up licenses for dedicated frequencies in 2019, and France allocated spectrum for mid-band and high-band private networks to test For companies in need. Japan and South Korea in the Asia-Pacific region also followed up quickly. In the Americas, the shared spectrum in the 3.5GHz CBRS frequency band in the United States has been used for 4G private networks before, and will be expanded to 5G in 2020; Brazil approved the technical requirements for low-power ground stations in the 3.7-3.8GHz private network frequency band in mid-2022, and issued the first in November. A 5G private network license. From the perspective of specific frequency bands, 56.3% of countries and regions adopt a combination of mid-band (FR1, <6GHz) and high-band (FR2, millimeter wave) to provide private network spectrum. Generally speaking, mid-band spectrum is slightly more than high-band .
The industry circles in various countries are actively applying for 5G private network frequency licenses, and the characteristics of diversification are obvious, covering telecom operators and other industry enterprises, IT service providers/integrators, scientific research institutions, universities, government agencies, etc. , OT field advantages, explore private network service model and application innovation.
5G private network progress in major countries
01 Germany
1. 5G private network promotion policy
With the development of Industry 4.0 in Germany, 5G, as a key network technology of the Industrial Internet, has attracted the attention of many large industrial enterprises. In 2019, the German automobile, machinery and equipment manufacturing and electrical equipment industry associations asked the German competent authority, the Federal Network Administration (BNetzA), to plan 5G private network spectrum for the construction of enterprise private networks. BNetzA believes that with the development of 5G technology, some new business models will emerge in the future, triggering the demand for self-built wireless networks in local areas. Based on the above requirements, BNetzA reserved the local 5G network spectrum before auctioning the 5G frequency, and opened the mid-band (3.7-3.8GHz) and millimeter wave band 5G private network license applications in stages. As of March 2023, German regulators have issued 304 mid-band spectrum licenses and 17 high-band spectrum licenses. Most of the licensees are IT service/consulting/system integrators, scientific research institutes, and industrial enterprises. Automakers have been particularly active, with major German automakers applying for local 5G licenses. From September 2022 to the present, among the applicants for new private network spectrum, IT system integrators have increased significantly, accounting for nearly 30%.
Take multiple measures to promote the development of 5G private network. The German Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs has issued a 5G park network guide for small and medium-sized enterprises (covering the procedures, application areas, and business operation models for establishing and operating a 5G park network), and the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure funds the European 5G industrial park project to accelerate 5G technology is popularized to small and medium-sized enterprises. In 2022, Germany launched a 3-year 5G campus network project to realize modular components and toolkits for the industrial, medical and logistics industries, and cooperated with France to fund the 5G private network project to create 5G private network technologies and technologies with open interfaces. application ecosystem.
2. Progress of 5G private network industry
After four years of advancement, the German 5G private network market has formed a "three pillars" situation of mobile operators, system integrators, and traditional equipment suppliers. Mobile operators can provide a variety of networking services by using public network spectrum resources; equipment suppliers provide one-stop services for end users through complete core networks, wireless access devices and cloud-based management platforms; system integration Manufacturers give priority to the use of small and medium-sized core network and base station equipment, and launch "turnkey" solutions for manufacturers' products to reduce the difficulty and cost of private network deployment. The details are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Private network solutions for 5G private network providers
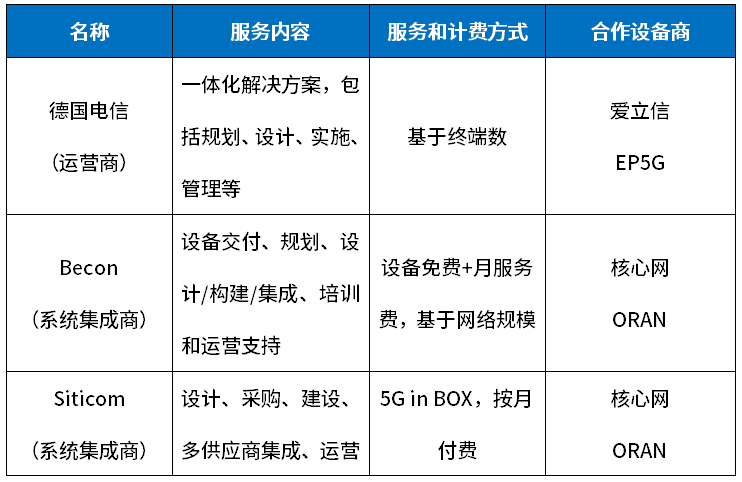
Some large industrial enterprises choose to cooperate with equipment manufacturers to build their own 5G private network, and use the specific frequency of the private network to achieve physical isolation from the operator's network. For example, the 5G private network of Bosch's semiconductor factory in Retlingen is built and operated by Bosch itself, and the 5G private network of Bosch's factory in Stuttgart is jointly built and operated by Bosch and equipment manufacturers. The production center is supported by equipment manufacturers to build a 5G private network. From the perspective of application, large German industrial companies are actively developing new 5G products. Industrial giants such as Siemens, Bosch, Schneider, and Mercedes-Benz have launched various applications such as AGV, remote access of industrial machinery, and real-time positioning of assembly line products. Each link.
02 Japan
1. 5G private network promotion policy
The wireless communication requirements represented by the Internet of Things are becoming more and more diverse. In some industry application scenarios, most services are concentrated in local areas. Considering that the national 5G services of mobile communication operators cannot fully meet the needs of fragmented and individualized industry applications in local areas, Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC) introduced a local network based on 5G technology, and relevant entities can be in railways, factories, airports, Hospitals, ports, agriculture, construction, logistics and other fields can flexibly deploy and use local 5G systems. From the end of 2019, MIC began to officially accept applications for 5G private network service spectrum license (local 5G), allowing local governments and enterprises to build their own networks. As of November 2022, a total of 126 institutions in Japan have obtained 149 licenses, including 108 in the mid-band and 31 in the high-frequency band. Applicants include manufacturing companies, cable TV companies, government agencies, educational and scientific research institutions, system integrators, and equipment Merchant etc. As of March 2023, MIC has approved 1,072 mid-band local 5G radio station licenses and 134 millimeter-wave licenses.
The Japanese government supports the development of replicable local 5G application demonstration models through project selection and funding to reduce the cost of use in other regions and accelerate the application of 5G in various industries. From 2020 to 2022, MIC has selected more than 70 private network application demonstration projects. In order to solve social problems such as population decline and aging, the demonstration projects led by MIC will focus on supporting agriculture, forestry, factories, power stations, transportation and other fields, including emergency medical treatment , Disaster prevention, remote control of agricultural machinery, telemedicine, factory machine vision, automatic driving and other scenarios.
2. Progress of 5G private network industry
From the supply side, there are many local equipment manufacturers in Japan, who can independently develop local 5G equipment and supply the Japanese market at low prices; from the demand side, in order to solve the problem of manpower shortage and improve productivity, most Japanese companies, especially manufacturing companies, In the process of production automation and digital transformation.
The promotion and popularization of 5G private network faces problems such as high deployment and operation costs and high technical difficulty. Many Japanese system integrators and local equipment manufacturers have entered the 5G private network market, launched integrated local 5G solutions, innovated operation service models, and opened up SME market. Equipment suppliers such as NEC, Fujitsu, and Mitsubishi provide end-to-end services from planning to design and deployment, carry out lightweight packaging and low-cost promotions for access network and core network equipment, and introduce ways to purchase equipment or order services. Reduce the cost of private network construction and operation and maintenance; Ehime CATV, Akita CATV and other cable TV companies cooperate to purchase local 5G equipment in a unified manner, reduce the unit price, build a shared 5G core network, and launch subscription-based local 5G services.
The Japanese government has made great efforts to promote and the industry has actively responded, creating a relatively active Japanese 5G private network industry. However, overall, Japan’s 5G private network is still in the extensive exploration stage, and commercial use is limited. According to statistics from the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, by 2023 1 At the end of the month, Japan had only 565 base stations for local 5G networks.
03 Korea
1. 5G private network promotion policy
South Korea regards the 5G private network as a sharp weapon to promote the development of the "5G + industrial ecosystem". On the one hand, it can drive the innovative development of equipment, parts and other industries, and on the other hand, it can also activate various 5G integrated services. While promoting the 5G enterprise private network application based on the public network of the three operators, South Korea vigorously promotes the development of 5G private network applications using private network spectrum. In October 2021, it released the 5G private network frequency allocation announcement. In March, more than 10 applicants have been issued private network frequency licenses. Applicants have used private network spectrum to build networks and develop applications in multiple places. 307 base stations have been built, 84 of which are used for test verification.
2. Progress of 5G private network industry
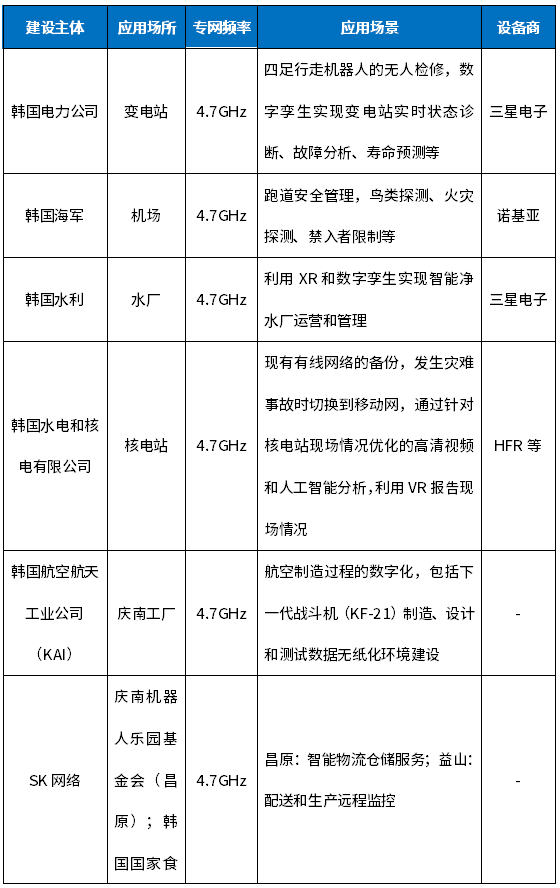
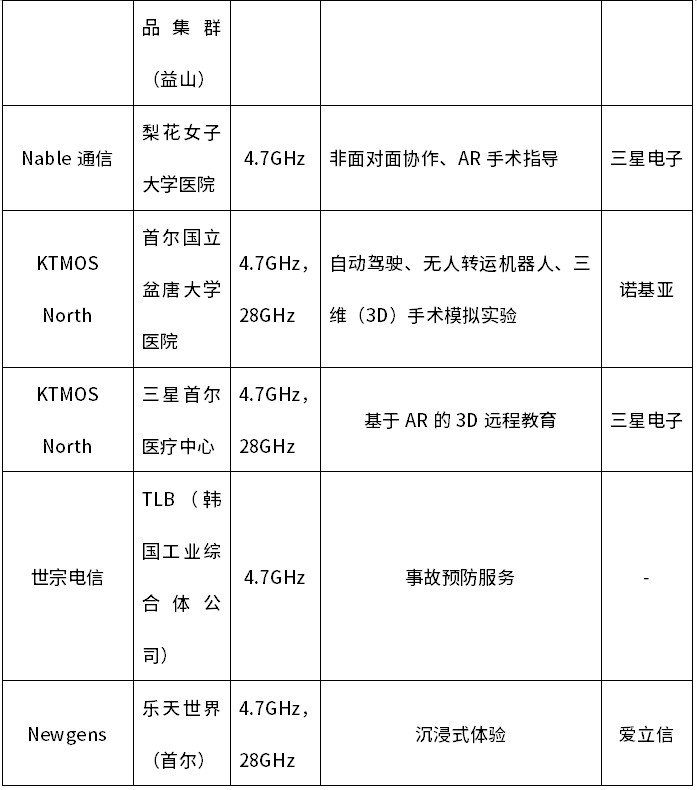
South Korea's 5G private network application using private network spectrum is still in the pilot demonstration. In order to promote the development of integrated applications, the South Korean government has launched 11 demonstration projects since June 2022. The project undertakers include both self-built and self-used enterprises. Telecom business operators and 5G equipment and solution suppliers are mostly Samsung Electronics and local system integrators, and Ericsson and Nokia have also gained some shares. In addition to promoting application demonstrations, South Korea is also vigorously promoting the R&D and production of private network equipment. In February 2023, South Korea’s first millimeter-wave 5G private network terminal equipment passed the radio wave certification. Up to now, there are 35 5G private network terminal equipment (modules) , modem) to obtain certification, most of which are Korean local enterprise products. The 5G private network demonstration projects in South Korea are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 5G Private Network Demonstration Projects in South Korea
04 America
In 2015, the FCC of the United States passed the rules for the shared commercial use of the 3550-3700MHz frequency band of the Civil Broadband Radio Service (CBRS), hoping to increase the utilization rate of this frequency band by introducing small cells and spectrum sharing technologies, and created a three-tier access and authorization framework , to adapt to the shared use of this frequency band by naval radar and commercial users. In August 2020, the priority access (PAL) license auction was completed, and 228 applicants obtained 20,625 PAL licenses. In addition to telecom operators, cable TV operators, and system integrators, the types of entities that have obtained PAL licenses include many industry and enterprise users, covering industries such as oil and gas, electric power, manufacturing, medical care, and education.
From the perspective of industrial development, the private mobile networks deployed by enterprise users in most industries in the United States using shared frequency bands are based on 4G, and 5G private networks are mostly in the testing stage. Once the 5G private network ecosystem matures, these networks can be upgraded to 5G. Mobile communication operators such as Verizon and AT&T use CBRS spectrum to provide private network services to enterprises in manufacturing, finance and other fields. For example, AT&T cooperates with Microsoft to deploy a 5G private network for Ford's electric vehicle production base based on Microsoft's Aure cloud and its 5G MEC solution, using AR to improve work efficiency such as inspections and improve the safety of automation equipment such as robots. U.S. cloud giants not only cooperate with domestic operators to provide private network services, but also launch a package of solutions, providing core network functions and application services based on the cloud, installing MEC in the enterprise, and processing some functions of the core network (user data processing, etc.) and Wireless access network function. The cloud giant's 5G private network service can quickly expand the market globally with the help of cloud infrastructure. In March 2023, AWS released the latest 5G private network solution, and cooperated with international operators such as Deutsche Telekom, KDDI, Orange, etc., based on the operator's spectrum , Utilizing cloud infrastructure and 5G network operation management tools, it can quickly and economically provide flexible private 5G networks. The target market has shifted from local small and medium-sized enterprise users to global large parks, industrial enterprises, ports and smart cities.
Thoughts and Enlightenment on the Development of 5G Private Network
Overall, the development of 5G private networks is still in the early stages, and most companies in major countries maintain a pragmatic attitude, moderately deploying, prudently advancing, and most of them are proof-of-concept and experimental projects. The reasons are analyzed from both sides of supply and demand as follows. First, it is more difficult for demanding enterprises to integrate 5G equipment into existing equipment, especially in the industrial field with a long equipment replacement cycle; and the deployment of 5G private network equipment is costly and complex in network operation and maintenance. Consideration of the cost-effectiveness of investing in 5G private networks has to a certain extent affected the willingness of enterprises to widely adopt 5G private networks. Second, from the perspective of the supply side, the needs of vertical industries are characterized by differentiation and fragmentation. On the one hand, high requirements are placed on the diversity and capabilities of terminals in the 5G industry. The terminal equipment market has not yet formed a large-scale value, so to a certain extent It affects the R & D and manufacturing of technical products, resulting in fewer types of terminal equipment and high prices; on the other hand, it is difficult for private network providers to replicate the scale of existing projects, and it is difficult to ensure profitability.
In the face of obstacles and problems in the development of private networks, consider starting from the activation of the industrial ecology: first, focus on the development of terminal equipment to facilitate the seamless integration of existing facilities, networks and 5G; second, reduce the burden of enterprise 5G network operations, including development and promotion Lightweight, low-cost equipment, and the launch of private network hosting services, etc.; the third is to establish a supply-demand docking platform, summarize best practices, and analyze the economics of private networks.