How much do you know about the development history of Wi-Fi?

How much do you know about the development history of Wi-Fi?
You who use Wi-Fi every day, have you ever thought about how Wi-Fi develops?
Today, Mr. Doc will take you to revisit the development of Wi-Fi~
Wi-Fi standard development
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) refers to high-quality wireless local area networks. It is a brand name created by the Wi-Fi Alliance to popularize various standards of IEEE 802.11. Wi-Fi is essentially a commercial certification. A product with this certification means that it complies with the IEEE 802.11 series of wireless network protocols and has passed the interoperability test certification. The IEEE 802.11 series protocol belongs to the short-distance wireless transmission technology, which uses the frequency band around 2.4GHz or 5GHz, which allows computers, smart phones and other devices to connect and communicate with each other through wireless networks.
The development history of Wi-Fi can be traced back to the 1990s, when the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) released restrictions on the use of the 2.4GHz frequency band, enabling the rapid development of wireless local area network (WLAN) technology.
Doc Jun uses a simple axis chart to summarize the development milestones:
Year 1999
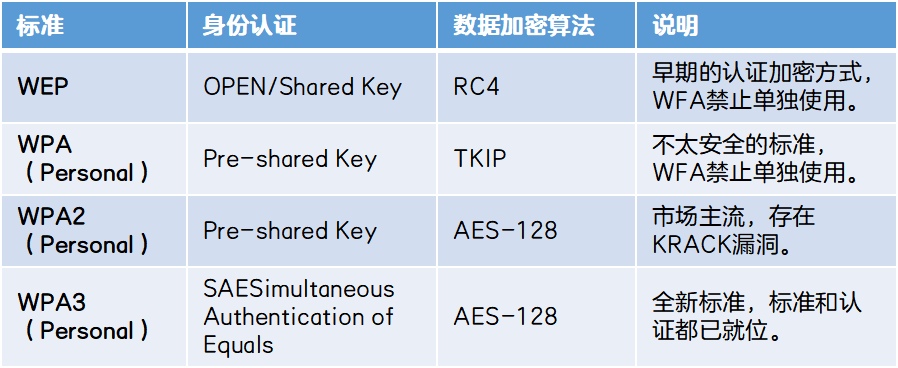
The IEEE 802.11b standard was released to support higher data transfer rates up to 11Mbps.
year 2006
The IEEE 802.11n standard was released to support higher data transmission rates and longer coverage, up to 600Mbps.
2019
The release of the IEEE 802.11ax standard, also known as Wi-Fi 6, enables more devices to connect simultaneously and provides higher data transfer rates and better network performance.
2021
The IEEE 802.11be standard is released, also known as Wi-Fi 7. The introduction of CMU-MIMO technology can support up to 16 data streams. In addition to the traditional 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands, WiFi 7 will also support the 6GHz frequency band, and three The frequency bands can work at the same time.
1997
The IEEE 802.11 standard is released, which provides technical support for the development of WLAN technology.
Year 2003
The IEEE 802.11g standard was released, with a maximum data transmission rate of 54Mbps, becoming the most mainstream Wi-Fi standard at that time.
year 2013
The IEEE 802.11ac standard was released, using more efficient technology to support higher data transmission rates and greater network capacity, up to 6.9Gbps.
2019
The release of the IEEE 802.11ax standard, also known as Wi-Fi 6, enables more devices to connect simultaneously and provides higher data transfer rates and better network performance.
Next, use a table to summarize the characteristics of each IEEE 802.11 standard.
Wi-Fi authentication and encryption
Wi-Fi network security mechanisms include authentication and encryption mechanisms.
Let's take a look at the evolution of Wi-Fi authentication and encryption methods:
- WEP security encryption method
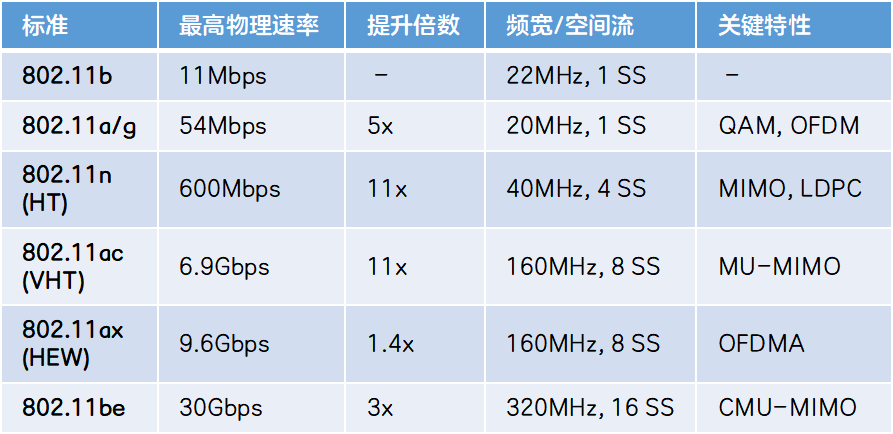
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), a data encryption algorithm, is used to provide protection equivalent to that of a wired LAN. Its security technology is derived from the RSA data encryption technology named RC4, which is a necessary security protection layer for wireless local area network WLAN.
With the application of technology, some test results show that only a few hours of listening in the network can crack the RC4 key, thereby cracking the WEP encryption method. After the publication of this research result, automatic cracking tools for the WEP protocol also came into being, officially declaring that the WEP protocol is no longer safe.
- WPA security encryption method
After WEP, WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) appeared. Unlike the static key of WEP before, WPA needs to constantly change the key. WPA adopts an effective key distribution mechanism, which can be applied across wireless network cards of different manufacturers. As an upgraded version of WEP, it is more thorough in terms of security protection than WEP, mainly reflected in identity authentication, encryption mechanism and data packet inspection, and it also improves the management ability of wireless networks.
- A higher level of WAP2
WPA2 is the authentication form of the IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA2 implements the mandatory elements of 802.11i and uses the CCMP (Counter CBC-MAC Protocol, Counter CBC-MAC Protocol, Counter Mode Cipher Block Chain Message Integrity Code Protocol) message authentic ation code , which is recognized as completely safe, instead of the Michael algorithm. The RC4 encryption algorithm has also been replaced by AES, and the security protection capability of the current WPA2 encryption method is better than that of WPA.
- More comprehensive protection: WAP3
WPA3 is a new generation of Wi-Fi encryption protocol released by the Wi-Fi Alliance in 2018. WPA3 has improved WPA2 and added many new features to provide stronger encryption protection for data transmission between users and Wi-Fi networks, making it diffic ult for Hackers to spy on users' traffic and obtain private information.
Finally, use a table to compare these authentication and encryption methods: