What changes will 6G bring to 2030?

We are in the midst of a great digital wave.
Innovation like a tide brings people a variety of choices and new opportunities.
In many countries, this change profoundly affects every person, every family, every vehicle and every industry, redefining how we work, learn, live and be healthy.
Today, the accelerated deployment of 5G around the world brings unprecedented possibilities. We are witnessing an era in which 5G will comprehensively change life, innovate industries, and reshape society.
Looking ahead to 2030 and beyond, what do we want the next generation of mobile communications to bring us?
1.1 Evolution of Mobile Communication
Since the 1980s, mobile communication systems have changed dramatically, with a new generation of technology produced roughly every decade. The popularization of mainstream services in mobile networks and the mature application of new frequency bands usually take two generations (that is, 20 years) to mature.
As shown in Figure 1-1, each generation of radio access network and core network adopts new technologies, new design principles, and new architectures, and the capabilities are significantly improved compared to the previous generation.
The main driving force for 2G and 3G networks comes from mobile users who are mainly voice communication. As the penetration rate of mobile phones and the usage rate of voice services tend to be saturated, this business model that depends on the number of users begins to grow weakly.
From 3G to 4G, data services have developed rapidly, and mobile broadband has become the dominant service of 4G. The major advances in mobile communications over the past 10 years have had a profound impact on the way people live. For example, smartphones carrying various applications have penetrated into every aspect of life. At this time, the revenue of 4G network operators mainly depends on traffic rather than the number of users, and the growth of per capita traffic consumption drives business growth.
Thanks to the advancement of 4G technology capabilities, a large number of mobile-oriented application innovations have emerged, completely changing our daily life. In China, the shift from cash to online payments is a strong example. Today, online payment methods such as Alipay, WeChat Pay and Huawei Pay have long become popular payment methods. Whether it’s shopping for groceries or paying for parking, people can easily pay without having to carry cash. Another example is the rise of social media. Anyone can share pictures and videos with others anytime, anywhere from their smartphone. Social media has become a news vehicle, accelerating the dissemination of information.
This innovative trend will continue in 5G as more and more high-speed, high-bandwidth applications continue to emerge. These applications involve high-definition video, as well as immersive media such as Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR). Currently, there are approximately 3.8 billion smartphones in use worldwide. By 2025, this number is expected to reach 8 billion. By then, the number of mobile Internet users will exceed 6.5 billion, of which 80% use mobile broadband. In addition, the number of AR/VR users will reach 440 million, and 40% of vehicles will be connected to the network.
With the standardization of Narrowband Internet of Things, Industrial Internet of Things, and Internet of Vehicles, mobile networks have shifted from human-connectivity based on enhanced Mobile BroadBand (eMBB) to Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency communications (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency). Communication, URLLC) and Massive Machine Type of Communication (mMTC). This shift, in turn, facilitates the digital transformation of businesses and prepares them for the next wave of economic growth.
5G commercialization initially focused on consumer business, but the evolution goal of subsequent versions of the 3GPP 5G standard (such as R16, R17, etc.) is to mature vertical applications such as the Internet of Vehicles and the Industrial Internet of Things. In order to achieve different levels of autonomous driving and Industry 4.0 in many enterprises and industries, the mobile communication field is working closely with major vertical industry alliances such as 5G-ACIA and 5GAA to accelerate the application of mobile technology. It is estimated that Level 4 autonomous driving will be achieved after 2025, and the popularity of the Internet of Vehicles will also greatly improve transportation efficiency. Optimized business processes and higher production efficiency will be key drivers of future GDP growth.
5G opens the door to the interconnection of everything, and 6G is expected to evolve into a platform for the connection of everything. Through this platform, the mobile network can connect a large number of smart devices to realize intelligent interconnection. We have reason to believe that the next wave of digitalization will bring more innovations to meet our needs in all aspects. Through artificial intelligence and machine learning, the physical world and the digital world can be connected in real time, and people can capture, retrieve and access more information and knowledge in real time, and enter an intelligent and fully connected world. At the same time, technologies such as perception, distributed computing, advanced integrated non-terrestrial networks, and short-range wireless communications will also lay the foundation for future intelligent mobile communication networks.
1.2 Key Drivers
The three key drivers in Figure 1-2 will enable a new generation of intelligent interconnected networks. Below we explain one by one.
Driving Force 1: New Applications and New Businesses
Currently, operators' business revenue depends on the growth of traffic consumption per user. As shown in Figure 1-3, from 2020 to 2030, the average monthly mobile traffic consumption per user (indicated by solid lines) and number of users (indicated by square bars) of IoT and non-IoT devices worldwide is expected to continue to grow. The data in the figure is from Report ITU-R M.2370.
As can be seen from the figure, the growth of smartphone users has been saturated in 2020, and the compound annual growth rate from 2020 to 2030 is about 6%.
In addition, according to the Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA) forecast, from 2019 to 2025, the penetration rate of individual mobile users will increase by only 3 percentage points, from 67% to 70%. Nonetheless, mobile data traffic per Mobile BroadBand (MBB) subscriber is expected to grow 50-fold within 10 years, from 5.3 GB/month in 2020 to 257 GB/month in 2030.
The 5G platform has widely supported high-speed and large-bandwidth applications, driving traffic consumption and stimulating the demand for network capacity. In the 6G era, more applications will emerge. Extended Reality (XR) cloud services, haptic feedback, and holographic displays are likely to become mainstream applications, covering 360-degree VR movies, AR-assisted remote services, virtual 3D educational travel, Application scenarios such as haptic telemedicine and teleoperation.
According to Huawei's Global Industry Vision Report, by 2025, there will be more than 337 million users of head-mounted VR/AR devices, and more than 10% of enterprises will use AR/VR technology to conduct business, and these numbers will definitely increase by 2030. With the increase in the number and popularity of cloud XR applications, as well as the increase in display size, resolution and refresh rate, the evolution of 5G capabilities may be difficult to meet the speed and latency requirements. The exponential growth in traffic demand per user, stringent requirements for latency and reliability, and the dramatic increase in the number of such users will become major challenges for 6G network design. Moreover, many operators have launched unlimited data packages, which has become a mainstream business model and will also bring about an increase in data traffic.
As can also be seen from Figures 1-3, by 2030, the number of IoT devices will be 13 times higher than in 2020, and both enterprise and consumer IoT connections will continue to grow.
In its 2020 Mobile Economy report, the GSMA predicts that by 2024, enterprise IoT will overtake consumer IoT. Therefore, artificial intelligence will be the engine of various automations, sensing the real-time environment and making real-time decisions using massive amounts of data. In scenarios such as smart homes, smart medical care, smart cars, smart cities, smart buildings, and smart factories, broadband sensors will be deployed on a large scale to acquire massive amounts of data required for artificial intelligence.
Big data is the basis for the success of machine learning, and it is also an important driving force for the order of magnitude improvement in 6G network throughput.
In addition, new capabilities such as network perception and non-terrestrial communication will become an integral part of the 6G mobile system, using wireless communication signals and the perception capabilities of massive network nodes and terminal devices to realize real-time environmental monitoring and imaging of large areas.
High-performance industrial IoT applications also place higher demands on wireless performance in terms of deterministic latency and jitter, and availability and reliability must be guaranteed. For example, time-sensitive command and control, multi-robot motion coordination and collaboration, all require high performance. These application scenarios are also the driving force for the extreme and diversified performance of 6G.
Driving force 2: Pratt & Whitney Intelligence
In the coming decades, the digital economy will continue to be the main driver of global economic growth, at a rate much faster than global economic growth itself. Taking the statistics of 2019 as an example, the growth rate of the digital economy is 3.5 times that of the global economy, reaching US$15.6 trillion, accounting for 19.7% of the global economy. This proportion is expected to reach 24.3% by 2025. In terms of investment leverage, in the past 30 years, every $1 increase in digital economy investment has leveraged $20 in GDP growth, while the average leverage ratio of non-digital economy investment is only 1:3.
Mobile communication is one of the most dynamic fields in the information and communication technology (Information and Communications Technology, ICT) industry. increase. With mobile technologies and services expected to contribute 4.9% of global GDP (nearly $5 trillion) by 2024, the growing popularity of mobile services will benefit more industries while increasing productivity and efficiency.
It is believed that this development trend will continue into 2030 and beyond. As inclusive intelligence becomes an important foundation for future business and economic models, the four key factors shown in Figures 1-4 will drive a paradigm shift in wireless technology and network architecture.
Native AI support: Although 5G introduces a new network function (ie, network data analysis) into the core network design to achieve intelligence, the current application scope of AI in network operation and maintenance management is still limited. In fact, 5G only regards AI as an OTT (Over-The-Top) business. 6G is different. The best support for AI and machine learning is considered in the design of the end-to-end mobile communication system. AI is not only a basic function, but also achieves optimal efficiency. From an architectural point of view, running distributed AI at the edge can achieve extreme performance, and at the same time, it can solve the problem of data ownership of individuals and enterprises, and meet the regulatory requirements of different countries and regions. 6G's "native" AI support aims to provide AI services anytime, anywhere, and continuously improve system performance and user experience through continuous optimization. Therefore, intelligence has reached a truly ubiquitous level, and combined with the deeply integrated ICT system, it provides abundant connection, computing and storage resources on the edge side, which has become the native attribute of 6G. The corresponding algorithms, neural networks, databases, Application Programming Interface (API) and other capabilities must also be integrated into the 6G system as part of the network implementation. The 6G network architecture with native AI support will realize the networking of AI, transforming from the current centralized "cloud AI" to the future distributed "interconnected AI".
Native data privacy protection: Building on the network security capabilities of 5G and previous generations, 6G incorporates privacy protection into key design requirements and principles. It has become crucial to provide comprehensive privacy protection for 6G networking and data. On the one hand, two key factors, data ownership and access rights, pose challenges to the privacy-preserving implementation of network architectures. On the other hand, the network architecture of native AI also puts forward privacy protection requirements for distributed data processing and access capabilities. Although data is protected by network and application service providers, the authorization is exercised by the user of the data subject, and the user as the data subject should exercise the right to control and operate the data. Next-generation systems should be designed with privacy protection a top priority, not an added feature. At the same time, it should also ensure the data ownership of the data subject, enable the control, operation and processing of the data under the authorization of the data subject, and adapt to data privacy/protection regulations or laws (such as the EU's General Data Protection Regulation) , establishing basic guiding principles for future technology design and application.
Native trust: To support various application scenarios and diverse markets, a verifiable and measurable trust system must be customized for 6G. The operation and authorization in 5G and previous generations of communication networks all adopt a centralized model. In the future, 6G will likely evolve into a multi-party participation and win-win model. This business model requires a trusted architecture that must take into account many factors. An open and inclusive multi-mode trust model will be more suitable for 6G networks and services than the previous single trust model. Therefore, in addition to adapting to future network and service requirements, a trustworthy 6G architecture should also consider network security, privacy, resilience, functional safety, reliability, etc. Multiple factors of credibility.
Diversified ecology: The three elements of AI are data, algorithms and computing power. However, a single enterprise may not have all the capabilities of these three elements, and cannot independently complete the digital transformation characterized by intelligent and rapid technological innovation. In this way, building an open, sustainable and collaborative ecosystem is an indispensable prerequisite for business success.
And, with the gradual expansion of 5G capabilities, the vertical wireless market is expected to continue to heat up in the 2020s. Players in the ICT and Operational Technology (OT) industries are already exploring how to collaborate to create new revenue streams. At this prelude to the 6G era, building a common ICT framework is of great benefit. This framework can provide a global perspective for all industries, thereby accelerating cooperation and convergence in the ICT and OT fields. The first wave of 6G commercialization is expected to inject strong momentum into both the consumer and vertical industries.
Driver 3: Social Responsibility and Sustainable Development
Mobile networks have the potential to revolutionize business, education, government, healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing and the environment, and the way we interact with others. Mobile networks continue to promote social progress and have the potential to redefine the human world.
According to the GSMA report, in 2015, the United Nations proposed sustainable development goals aimed at changing the world, and mobile communication is the core cornerstone and an important means to achieve these goals. Around all 17 of these goals, the mobile industry plays an important and interrelated role, and this growing influence provides a solid foundation for the digital economy and acts as a catalyst for diverse and innovative businesses.
Huawei and the United Nations analyzed quantitative benchmarks for the relevance of ICT to the SDGs to measure the extent to which the development of ICT technology contributes to the achievement of the SDGs. According to the 2019 assessment, the maturity of ICT technology and the advancement of the SDGs showed a strong correlation (the correlation was 0.86). As shown in Figures 1-5, Goal 3 (health care) and Goal 4 (quality education) have the highest correlation with ICT technology, indicating that digital technology can maximize national governance capabilities in these two areas.
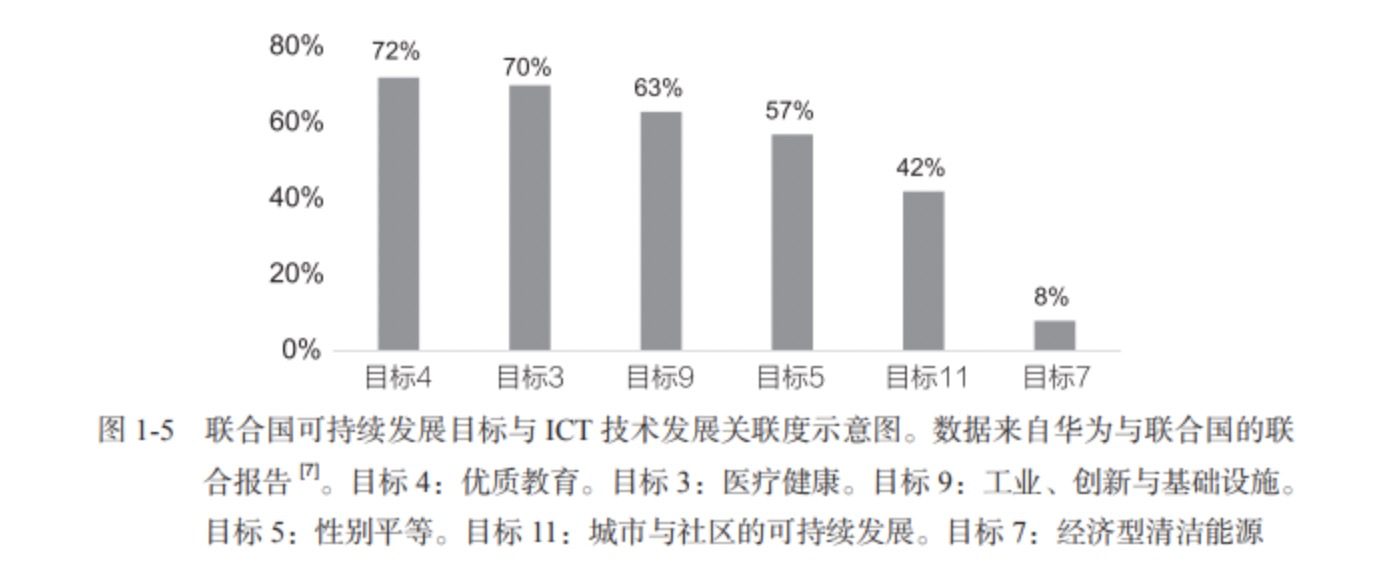
In terms of sustainable development of the environment, the evolution of ICT technology has a profound impact on the achievement of Goal 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and Goal 11 (Sustainable Development of Cities and Communities). The world is becoming increasingly urbanized, and forecasts show that by 2030, the urban population will reach 5 billion, occupying only 3% of habitable land, but consuming as much as 60% to 80% of global energy. With the continuous improvement of energy efficiency per bit, ICT technology will become more and more carbon neutral, and rich solutions based on ICT technology, such as smart grid, smart logistics, and smart industry, will make the future world more energy-efficient and enhance the world sustainability of development.
As of 2020, about 60% of the world's population has access to mobile networks. The other 40% is expected to be connected in 5G and 6G networks by integrating technologies such as satellite communications. For example, 5G networks have attempted to incorporate non-terrestrial access technologies into 5G NR. The ambitious constellation satellite plan will gather thousands of ultra-low-orbit satellites to enhance ground-air communication, and may bear fruit in the 6G era. The services, applications and content provided through the mobile network help to expand economic integration and enhance social cohesion. Emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things, big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are increasingly integrated into network infrastructure, bringing great potential for in-depth changes in society and the environment. Due to the high correlation between ICT technology and the SDGs, we must comprehensively consider how the design of 6G communication systems and networks can support the achievement of the SDGs.
1.3 Overall vision
Mobile communications have revolutionized the world in just four decades. Today, not only is the work and life of individuals highly dependent on wireless networks, but the digital transformation of enterprises is also inseparable from it. With the gradual implementation of the latest generation of 5G technology, wireless networks will expand from connecting everyone to connecting everything. This hyperconnectivity enables the full automation of society. At the same time, the momentum of wireless innovation has continued unabated. As the book Science, the endless frontier points out, there is no end to the exploration of wireless technology.
In the next decade, wireless technology will continue to innovate, artificial intelligence based on machine learning will rise, and digital twins that replicate the physical world into the digital world will also be born. Artificial intelligence and digital twins will form a two-wheel drive, further boosting technological breakthroughs. The resulting 6G network will reshape society and the economy, laying a solid foundation for the future intelligence of everything.
As the next-generation wireless communication technology, 6G will transition from the Internet of People and the Internet of Things to the Internet of Everything. As society moves towards the intelligence of everything, 6G will be a key factor in the popularization of artificial intelligence, bringing intelligence to everyone, every home, every vehicle and every business.
6G is like a distributed neural network spread across communication links, merging the physical and digital worlds. It is no longer a simple bit transmission pipeline. While connecting all things, it can also perceive all things, so as to realize the intelligence of all things. Therefore, 6G will be the network that enables perception and machine learning, its data center will become the nerve center, and machine learning will be spread all over the network through communication nodes. This is the picture of the future intelligent digital world of all things.
6G will drive comprehensive digital transformation across all verticals. It offers extreme performance such as multi-terabit bit rates, sub-millisecond latency, and "seven nines" (99.999 99%) reliability. Compared with 5G, 6G will make a major leap in key performance indicators, and some indicators will be improved by more than an order of magnitude. 6G will provide high-performance universal connectivity with speeds and reliability comparable to optical fiber, but all wirelessly. Since it gets rid of the limitations of functions and performance, 6G will become a universal platform, supporting the creation of any business and application, and finally achieving "extreme connectivity"!
The disruptive technologies and major innovations of 6G will open a significant gap with previous generations.