Graphical Networking: What is the DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol?

DHCP is a particularly great technology in the world of network technology, which solves the cumbersome process of statically configuring IP, and its characteristics of dynamically assigning IP addresses make the network flexible and scalable.
It's hard to imagine how we'd be connected to the Internet or our local network without DHCP, an essential part of how our devices on IP networks communicate with each other and the world around us.
So what is the rationale behind DHCP? Why is DHCP a revolutionary technology? What should I pay attention to when configuring DHCP?
In this article, Rui Ge will take you to uncover the mystery of DHCP in the form of diagrams, let us start directly!
What is DHCP?
English full name: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Chinese name: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
is a network management protocol
DHCP terminology
- DHCP has many technical terms, let's take a brief look at it:
- DHCP Discover: When a client (PC) starts up, it broadcasts a DHCP Discover message over Ethernet to locate all available DHCP servers in the same subnet, reaching all DHCP servers in the same subnet.
- DHCP Offer: When the DHCP server receives a DHCP Discover message from a client, it also broadcasts a DHCP Offer message over Ethernet to inform the client that it is available.
- DHCP Request: The client that receives the DHCP Offer message recognizes that there is an available DHCP server on the same subnet, and then it broadcasts a DHCP Request message to the server via Ethernet, requesting network configuration data, including its own IP address.
- DHCP Reservation: Predefined IP address range for the network
- DHCP ACK: DHCP acknowledgment
- DHCP Server: DHCP server, a device that runs and manages DHCP information
- DHCP Client: DHCP client, responsible for requesting an IP address and establishing a DHCP connection with a DHCP server
- DHCP Relay Agent: DHCP relay agent is a host or router that sends requests and replies between local DHCP clients and remote DHCP servers. When there is only one DHCP server in multiple LANs, the relay agent will handle all network requests .
- Lease Time: Lease time, the time the client can use the IP address assigned to it
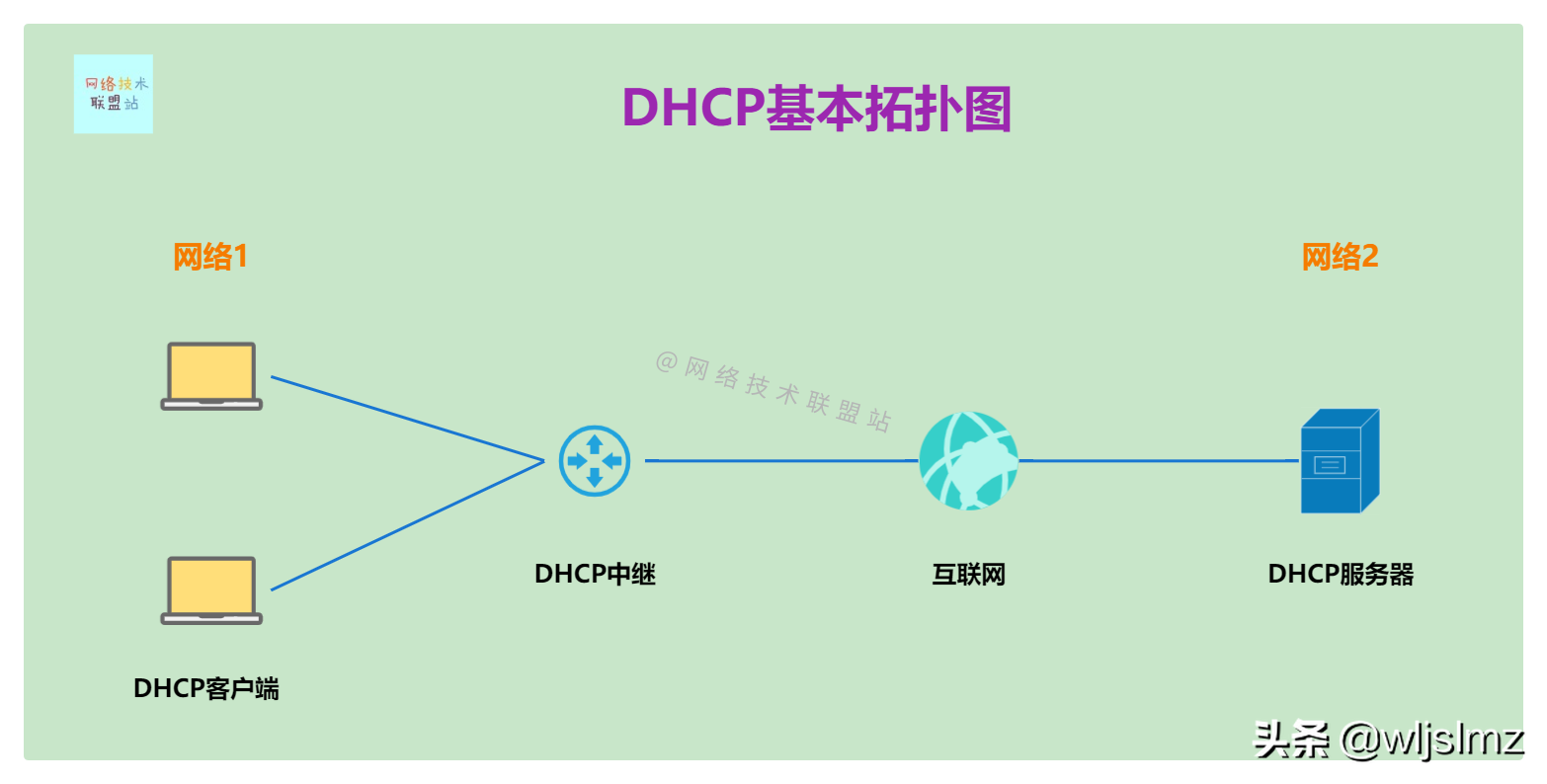
DHCP Basic Topology
DHCP components
We have introduced the terminology of DHCP above. Generally, DHCP will include the following parts:
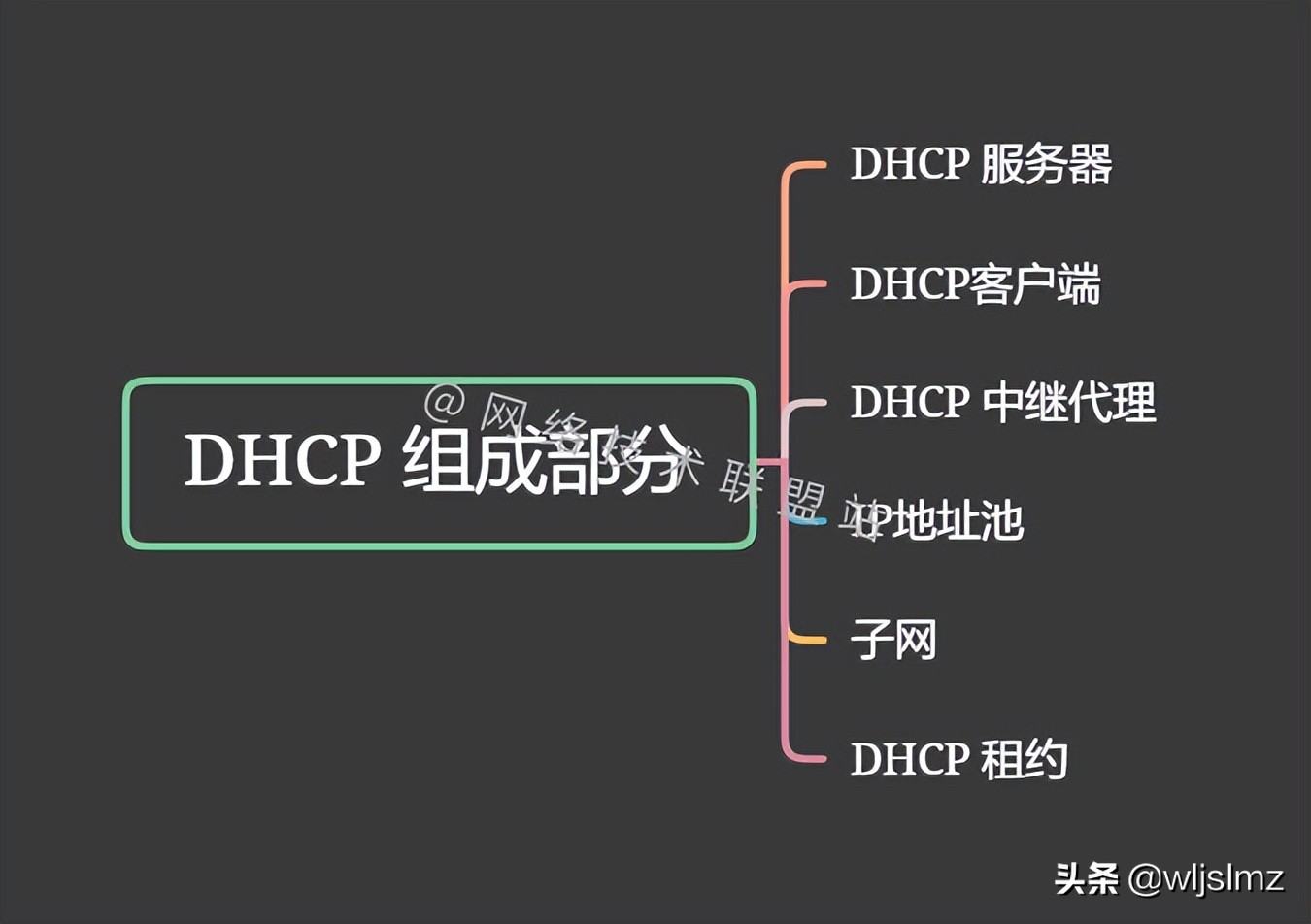
DHCP components
This confirms the basic DHCP topology above. We will introduce the IP address pool, subnet, and DHCP lease in the DHCP principle.
DHCP principle
DHCP operates at the application layer to dynamically assign IP addresses to clients by sharing DHCP transactions or DHCP sessions:
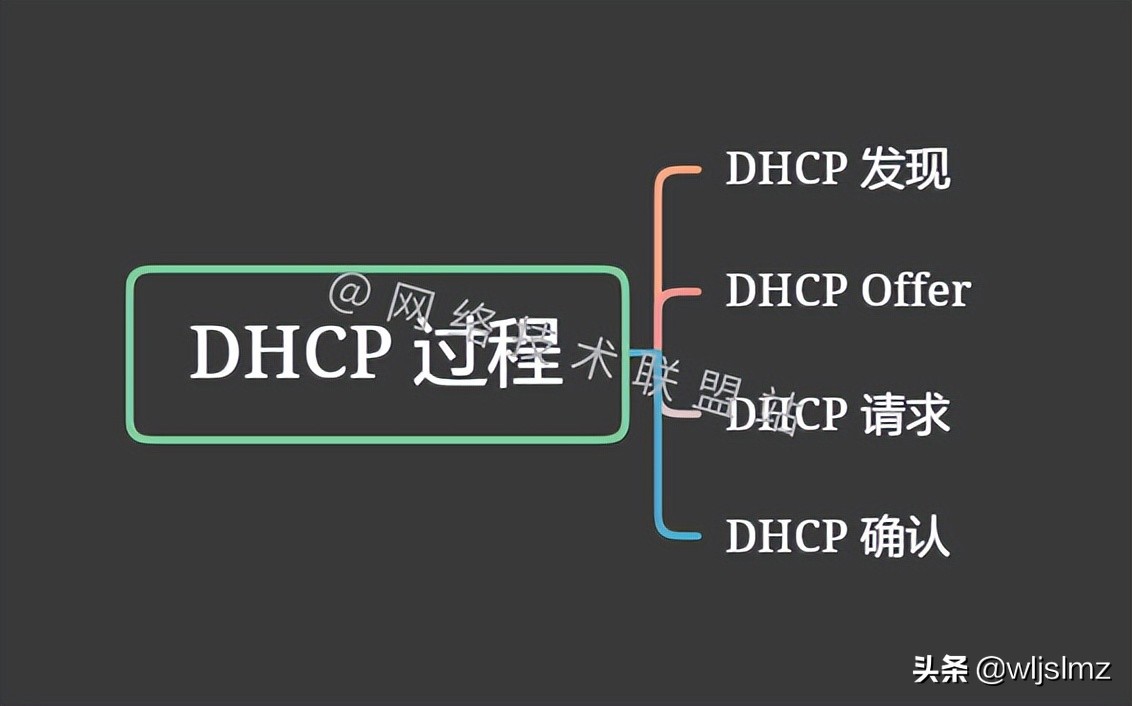
DHCP process
Let's use a diagram to briefly explain the following DHCP handshake process:
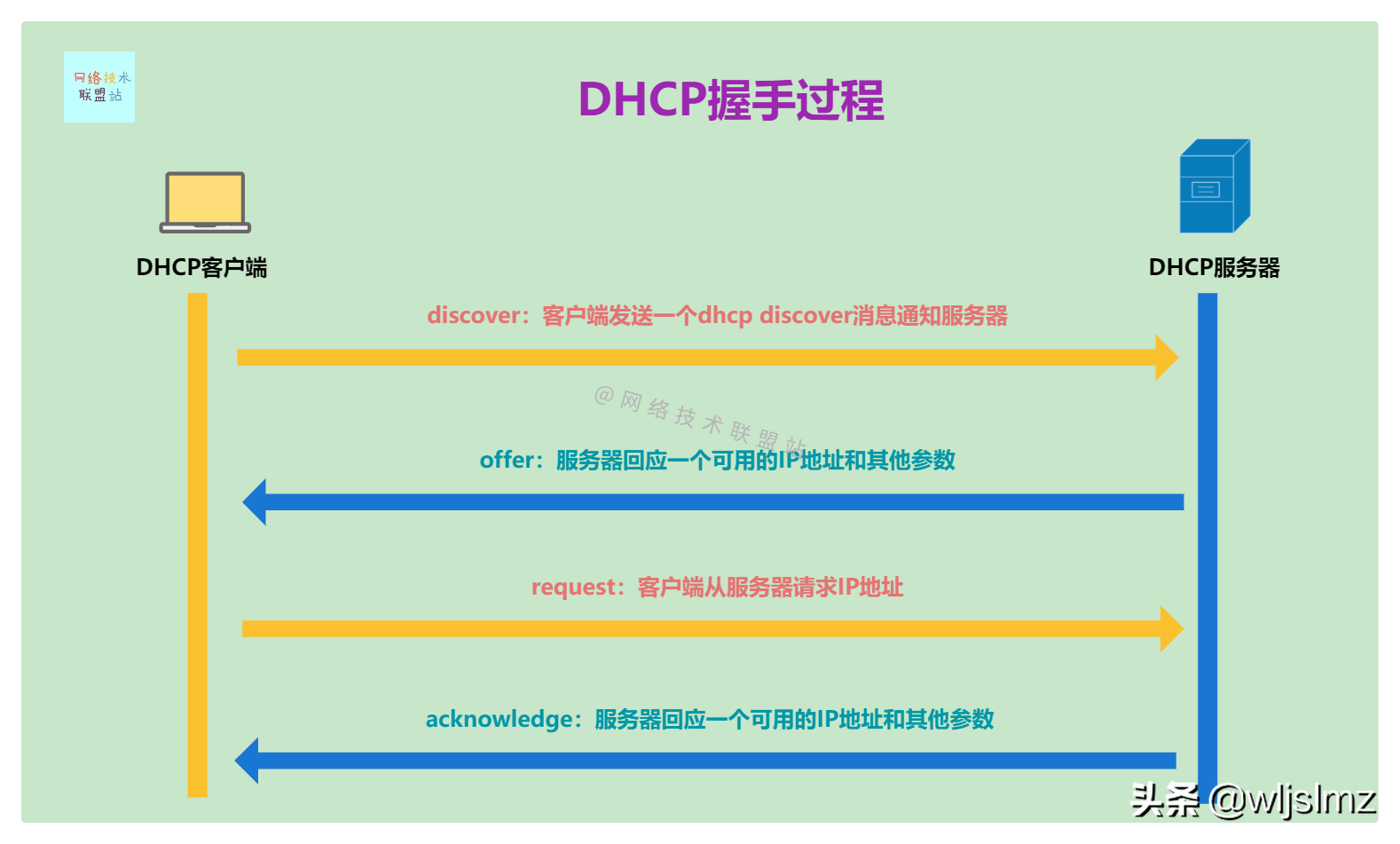
DHCP handshake process
- The first step: discover: the client sends a dhcp discover message to notify the server
- Step 2: offer: The server responds with an available IP address and other parameters
- Step 3: request: The client requests the IP address from the server
- Step 4: acknowledge: the server responds with an available IP address and other parameters
In order to facilitate your memory, we simplify the diagram:
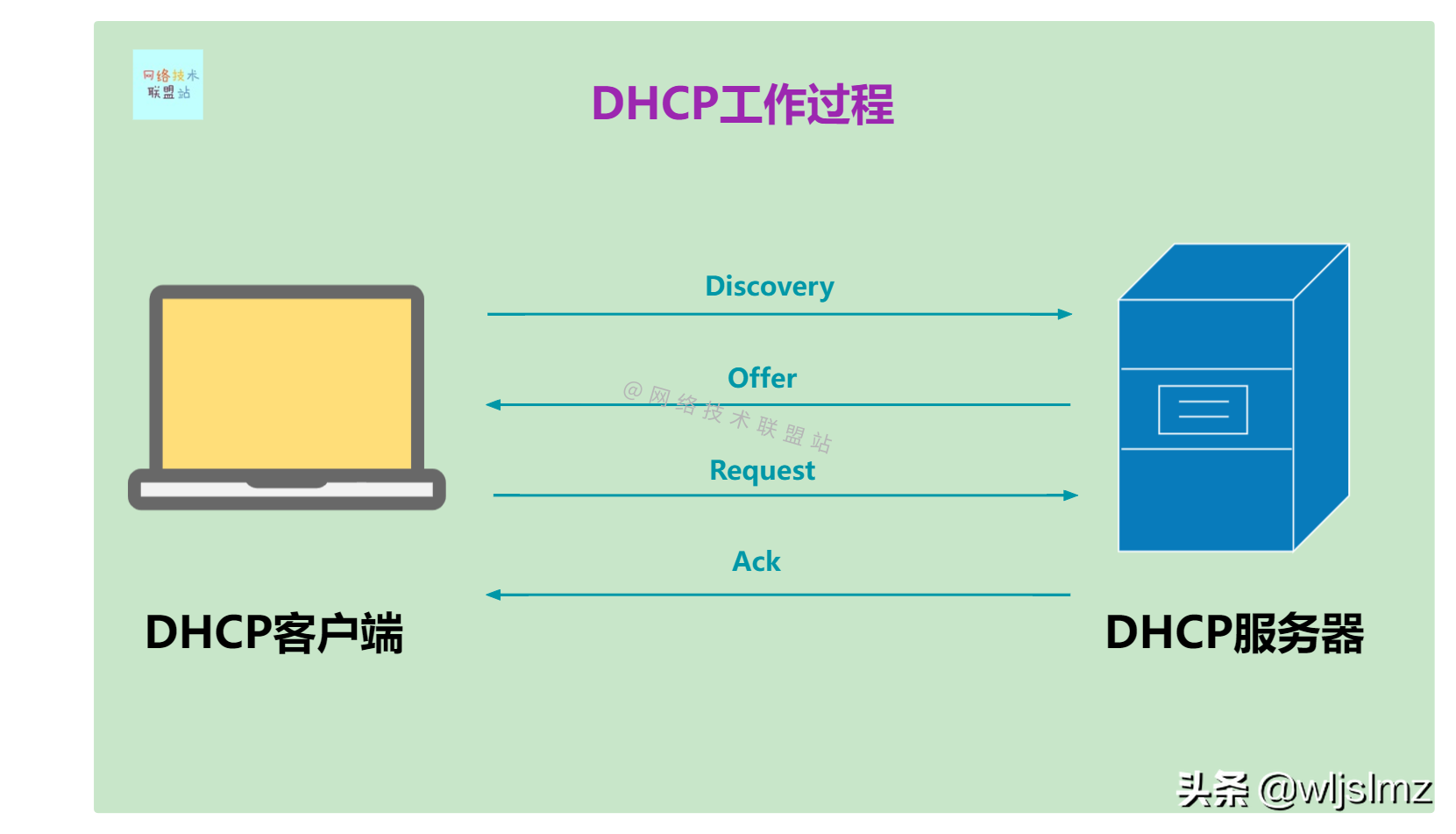
DHCP working process
Let's take a look at the packet capture of the DHCP working process:
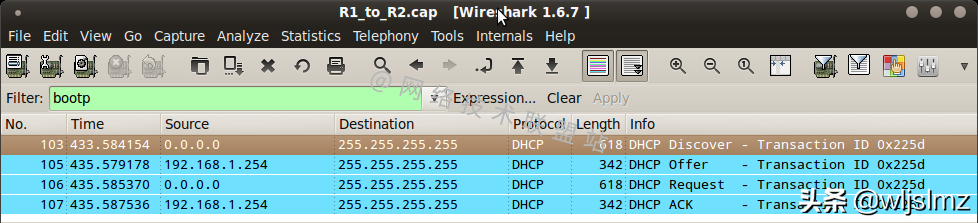
Packet Capture Analysis of DHCP Working Process
DHCP lease
Each IP address does not belong to a certain computer indefinitely, along with the IP address, the DHCP server will send an expiration date called the lease time, indicating when the host needs to renew the address, DHCP leases can be avoided to a certain extent The waste of IP addresses, because some IP addresses may be allocated, but the computer to which they belong is no longer in a local area network. If this address is not released at this time, it will cause waste over time.
The DHCP lease period is as follows:
- A client obtains an IP address lease by requesting an IP address lease assignment process from the DHCP server.
- If the client has obtained an IP address from an existing lease, it needs to refresh its IP address on reboot and contact the DHCP server to reassign the IP address.
- If the lease has not expired, the client binds the relevant lease and IP address.
- When the lease expires, the client will contact the server that originally granted the lease to renew it, gaining the right to continue using its IP address.
- If the client moves to a different network, its dynamic IP address will be terminated and it will request a new IP address from the new network's DHCP server.
Configure DHCP
Windows
Windows configuration dhcp is relatively simple, and it is almost the default configuration method:
- Open [Network and internet settings]

Network and internet settings
- Click [Properties] of the network you are connected to

network properties
- Find [IP Settings]
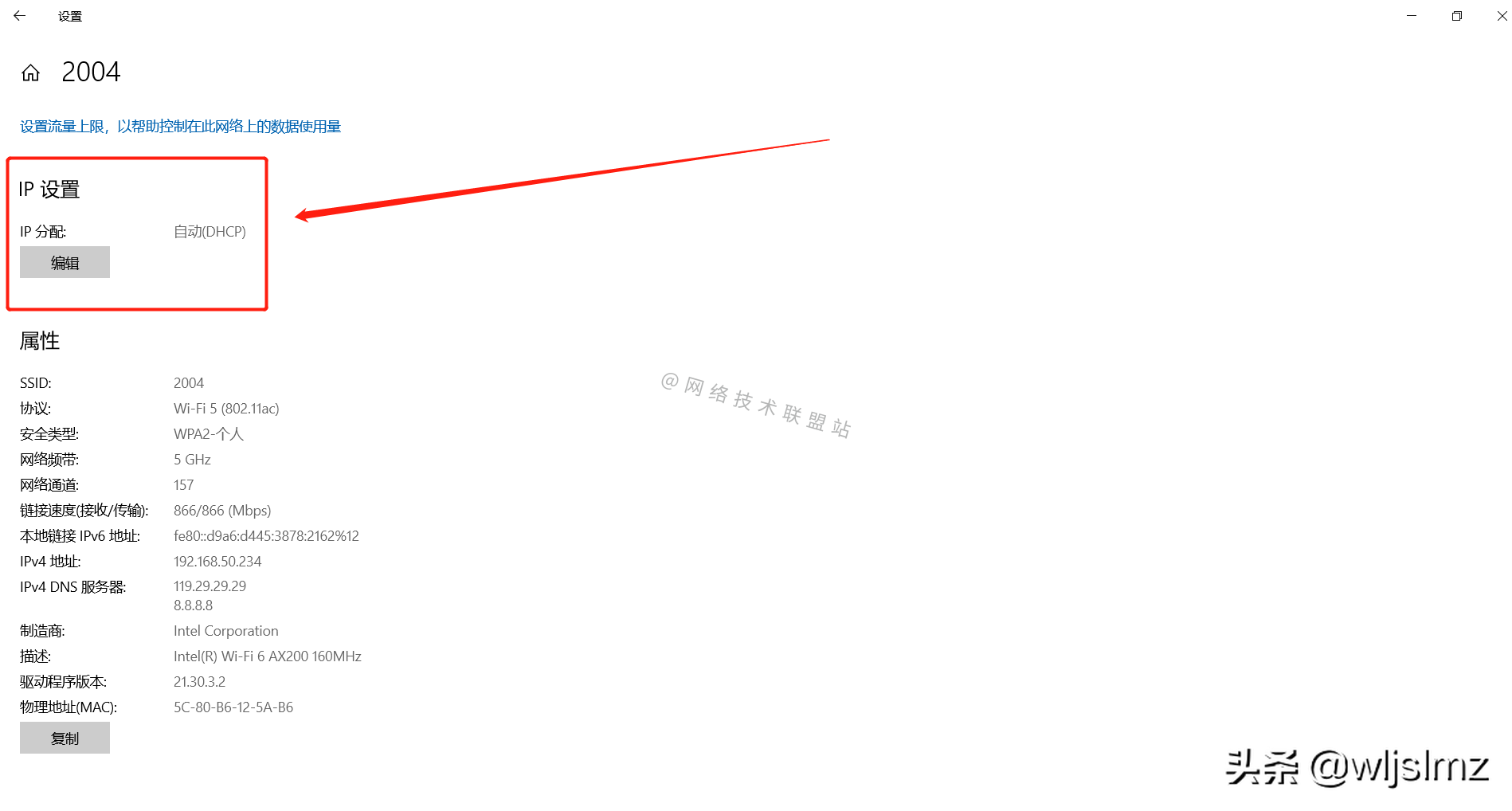

Find [IP Settings]
I can see that my computer is already set to obtain the way of DHCP.
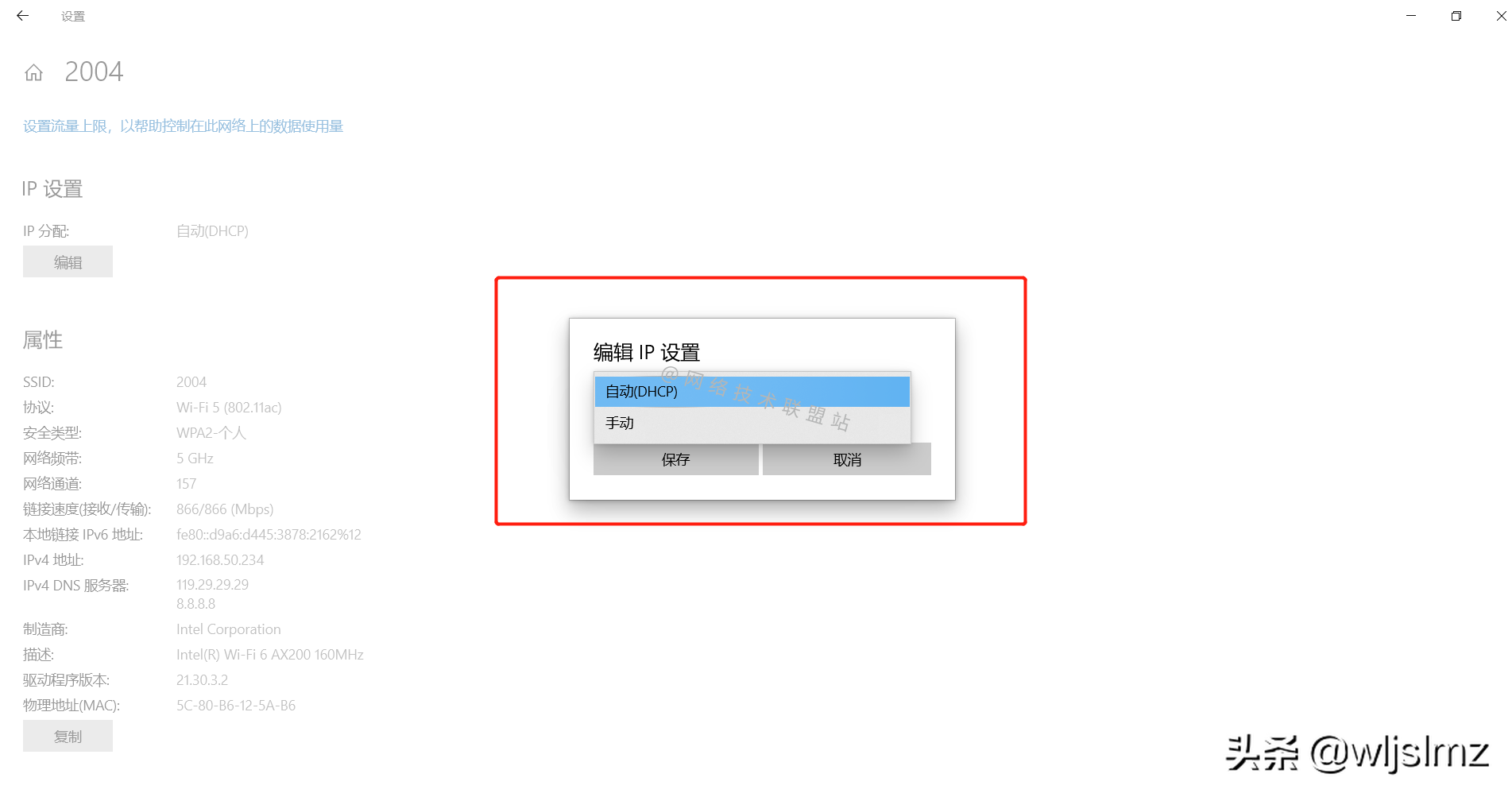
ip settings
Click on [IP Settings] and we can see that there are two setting methods: DHCP and manual.
Let's take a look at what my IP address is after setting it through DHCP:
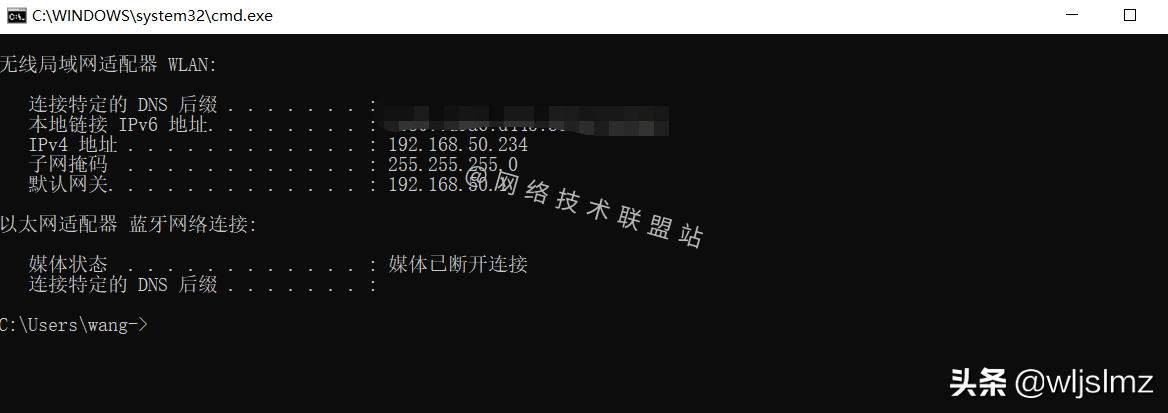
View the local IP address
It can be seen that after the automatic allocation through DHCP, the IP address of my computer is: 192.168.50.234
Linux
I will use one of my cloud servers as an example to demonstrate to you. My cloud server is based in Hong Kong and is a Centos system, so the network configuration files are all under the path /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/.
Let's take a look at the network settings of this server:
more /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0- 1.
The command line shows:
# Created by cloud-init on instance boot automatically, do not edit.
#
BOOTPROTO=dhcp
DEVICE=eth0
MTU=1450
ONBOOT=yes
TYPE=Ethernet
USERCTL=no- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
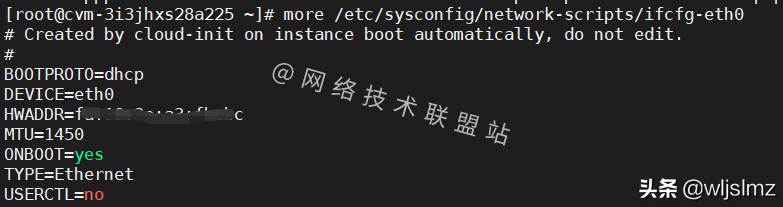
Server network settings
It can be seen that the IP address of my cloud server is also DHCP.
View DHCP-assigned address leases
How can we check the address lease assigned by DHCP?
Take my cloud server in Hong Kong as an example:
Excuting an order:
cat /var/lib/dhclient/dhclient--eth0.lease- 1.
The results show:
lease {
interface "eth0";
fixed-address 172.16.2.231;
option subnet-mask 255.255.0.0;
option routers 172.16.0.1;
option dhcp-lease-time 86400;
option dhcp-message-type 5;
option domain-name-servers 8.8.4.4;
option dhcp-server-identifier 172.16.0.2;
option interface-mtu 1450;
option dhcp-renewal-time 40305;
option classless-static-routes 32.169.254.169.254 172.16.0.2,0 172.16.0.1;
option broadcast-address 172.16.255.255;
option dhcp-rebinding-time 72705;
option host-name "host-172-16-2-231";
option domain-name "openstacklocal";
renew 6 2022/07/09 09:49:26;
rebind 6 2022/07/09 19:34:44;
expire 6 2022/07/09 23:22:59;
}
lease {
interface "eth0";
fixed-address 172.16.2.231;
option subnet-mask 255.255.0.0;
option routers 172.16.0.1;
option dhcp-lease-time 86400;
option dhcp-message-type 5;
option domain-name-servers 8.8.4.4;
option dhcp-server-identifier 172.16.0.2;
option interface-mtu 1450;
option dhcp-renewal-time 39746;
option classless-static-routes 32.169.254.169.254 172.16.0.2,0 172.16.0.1;
option broadcast-address 172.16.255.255;
option dhcp-rebinding-time 72146;
option host-name "host-172-16-2-231";
option domain-name "openstacklocal";
renew 6 2022/07/09 20:31:46;
rebind 0 2022/07/10 05:51:52;
expire 0 2022/07/10 09:49:26;
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- twenty one.
- twenty two.
- twenty three.
- twenty four.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
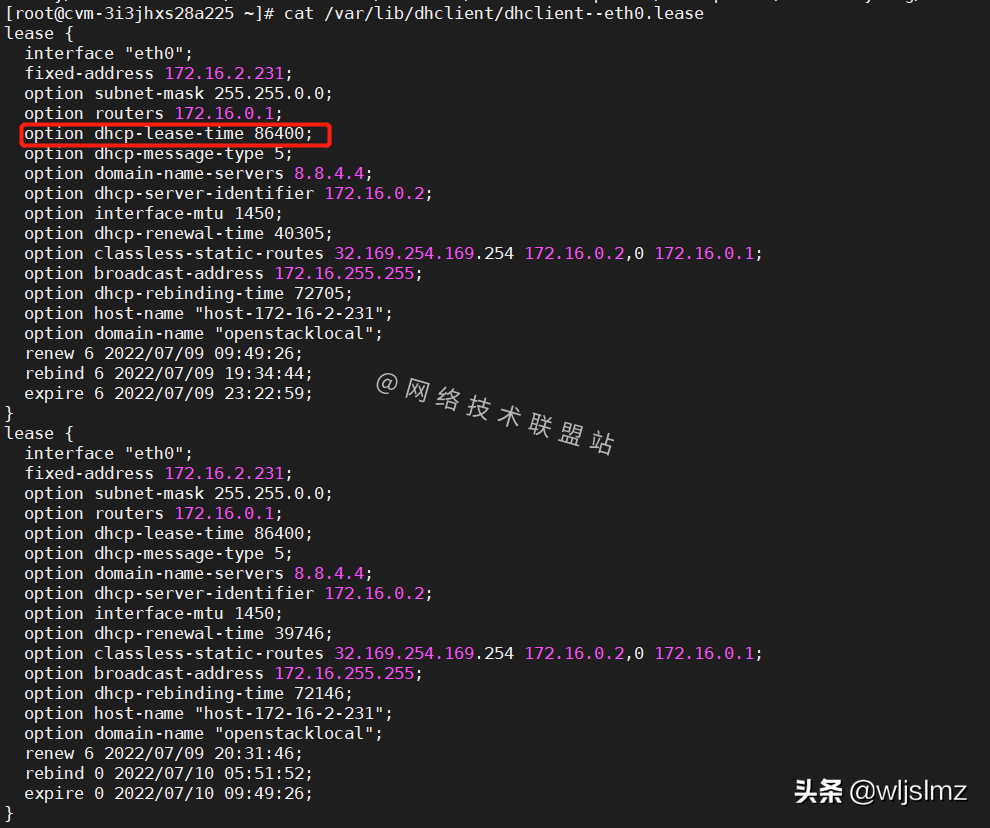
DHCP-assigned address lease
We see that there is a parameter called option dhcp-lease-time 86400, which is the lease time in seconds.
We can also see that:
- renew 6 2022/07/09 20:31:46;: reset time
- rebind 0 2022/07/10 05:51:52;: The time to rebind
- expire 0 2022/07/10 09:49:26;: Expiration time
The above is the setting part of DHCP, we finally look at the advantages and disadvantages of DHCP.
Advantages and disadvantages of DHCP
Advantages of DHCP
- Reduce IP Conflicts: Manually assigning IP addresses increases the likelihood of incorrect or duplicate addresses in the network, using DHCP ensures that addresses are assigned automatically and accurately with centralized control.
- Simplified network management: With DHCP, network administrators can easily monitor, manage and assign IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
- Reduced costs: DHCP helps save a lot of time compared to manually assigning IPs, especially for larger businesses, it also saves money and other resources as companies don’t need dedicated experts to continuously oversee intellectual property management and distribute.
Disadvantages of DHCP
DHCP itself is not secure, and if malicious actors gain access to a DHCP server, they can wreak havoc.
If the DHCP server is not backed up and the server fails, the devices it serves also fail.
If the network has only one DHCP server, the DHCP server may be a single point of failure.
Summarize
DHCP is an extension to the Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP), a 1985 network IP management protocol, used to dynamically assign IP addresses and other information to each host on a network so that they can communicate efficiently. DHCP automatically and centrally manages the assignment of IP addresses, simplifying the work of network administrators. In addition to IP addresses, DHCP also assigns configurations such as subnet masks, default gateways, and domain name server addresses to hosts, making network administrators' work easier .