MQTT QoS design: message transmission quality assurance on the Internet of Vehicles platform

foreword
In the Internet of Vehicles scenario, massive data will be generated, which can be used as the basis for vehicle diagnosis to ensure the safe and stable operation of the vehicle; it can also be linked with infrastructure such as mobile phones to provide a better driving experience. The country and the industry have also successively issued relevant policy documents, such as "Automotive Driving Automation Classification", "Guidelines for the Construction of the National IoV Industry Standard System", and "Technical Requirements for Data Security of IoV Information Services", etc. high demands. The security, stability and reliability of communication have always been the topic of the Internet of Vehicles. Therefore, a complete data transmission guarantee scheme is also a part of the Internet of Vehicles business that cannot be ignored.

QoS levels in the MQTT protocol
As the first choice of data communication protocol in the Internet of Vehicles industry today, the MQTT protocol specifies the message quality of service (Quality of Service, hereinafter referred to as QoS). QoS ensures the reliability of message delivery in different network environments, and can be used as the primary implementation technology to ensure reliable message transmission in the Internet of Vehicles scenario.
MQTT is designed with 3 QoS levels:
(1) QoS 0
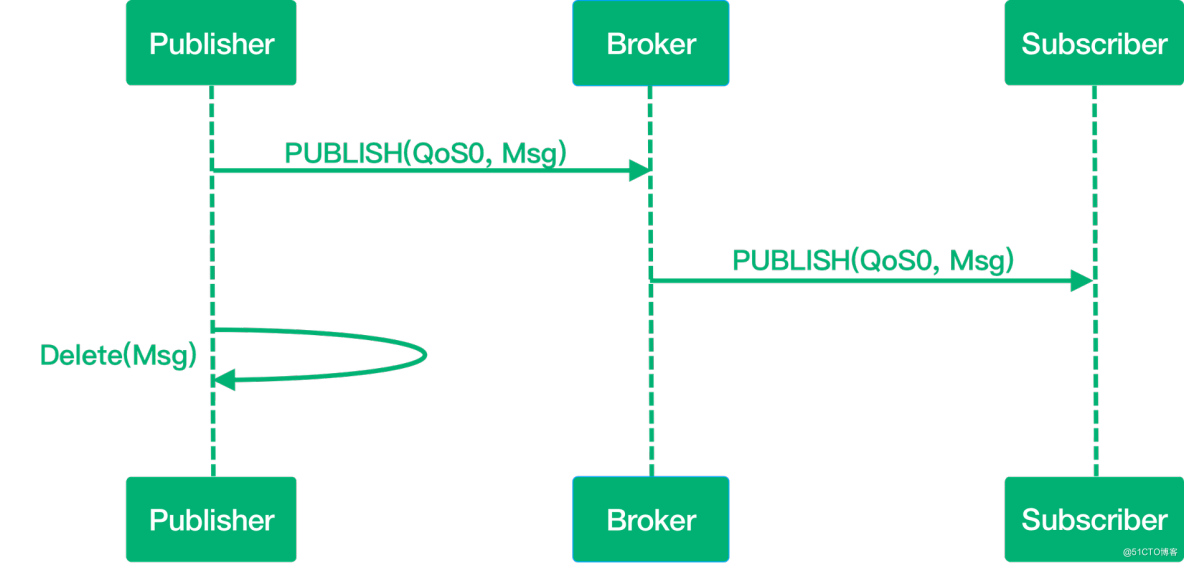
The message is delivered at most once and will be lost if the MQTT client is unavailable at that time. After the Sender (maybe Publisher or Broker) sends a message, it no longer cares whether it is sent to the other party or not, nor does it set up any retransmission mechanism.
(2) QoS 1
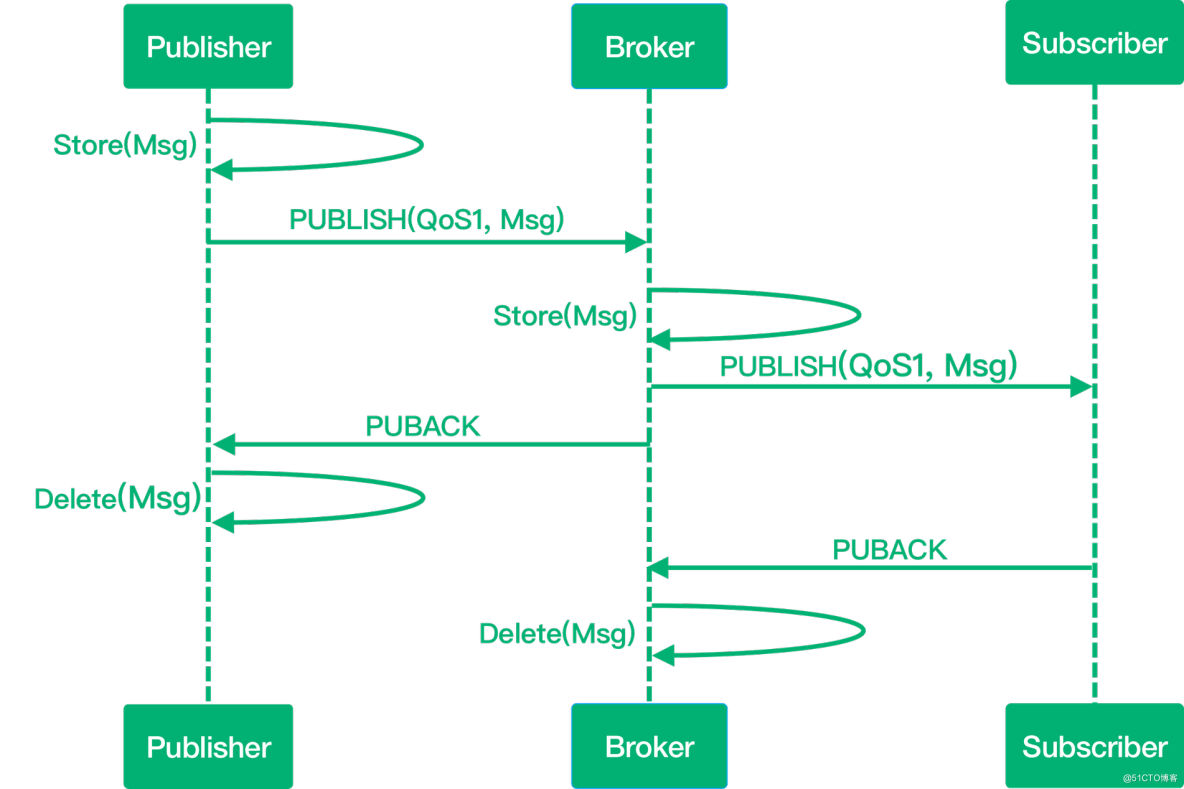
The message is delivered at least 1 time. Contains a simple retransmission mechanism. After sending the message, the sender waits for the receiver's ACK, and if it does not receive an ACK, it resends the message. This mode guarantees that the message will arrive at least once, but it cannot guarantee that the message will be repeated.
(3) QoS 2
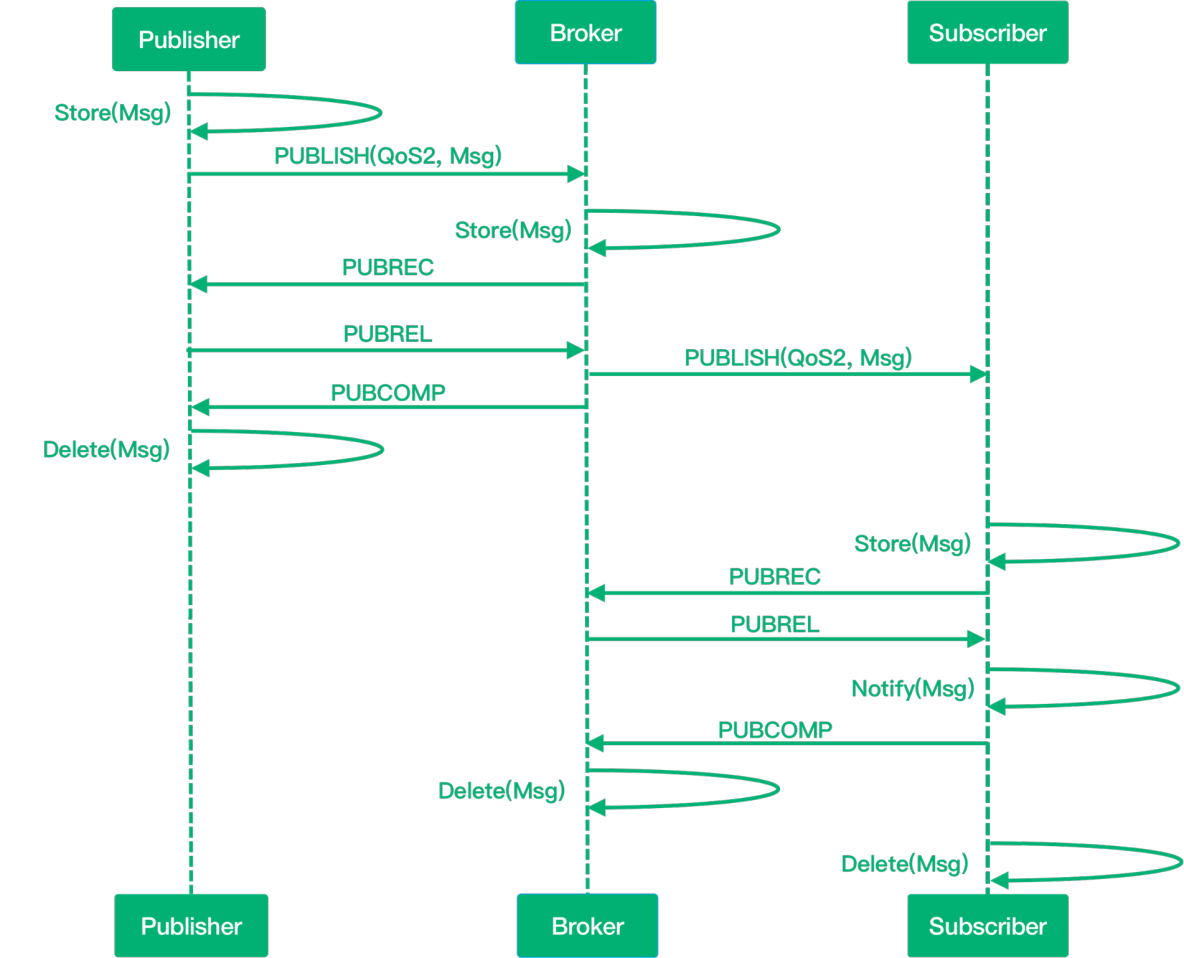
The message is delivered only once. Retransmission and duplicate message discovery mechanisms are designed to ensure that messages arrive at each other strictly only once.
Message QoS Design in the Internet of Vehicles Scenario
First of all, it needs to be clear that the higher the QoS level, the more complex the message interaction and the greater the system resource consumption. Therefore, the higher the QoS level is, the better. Applications can choose the appropriate QoS level according to their own network scenarios and business requirements.
According to the attributes and characteristics of the data related to the Internet of Vehicles information service, we can divide it into six categories: basic attribute data, vehicle industrial control data, environment perception data, vehicle control data, application service data and user personal information. So how to choose the MQTT QoS level in different car networking scenarios?
(1) QoS 0 can be selected in the following cases
QoS 0 can be selected in scenarios where occasional message loss is acceptable.
Entertainment-related multimedia services provided by the Internet of Vehicles, such as weather forecast and other data. There are also some vehicle-related service data, such as the reporting of vehicle historical driving data, historical driving operation data, etc.
(2) QoS 1 can be selected in the following cases
QoS1 is used in most scenarios of the Internet of Vehicles, which optimizes the performance of system resources and the real-time and reliability of messages.
QoS 1 is widely used in vehicle control messages, vehicle reporting data (including new energy national standards and enterprise standards), traffic safety management and control data, and early warning data related to traffic safety and road safety.
(3) QoS 2 can be selected in the following cases
For scenarios that cannot tolerate message loss, do not want to receive repeated messages, and require high data integrity and timeliness, QoS 2 can be selected.
There are not many applications of QoS 2 in the Internet of Vehicles scenario. Although it can increase message reliability, it also greatly increases resource consumption and message delay. QoS 2 is mainly used in banking, fire protection, aviation and other industries that require high data integrity and timeliness. Some OEMs choose to use QoS 2 for traffic alarms and vehicle charging pile billing messages.
special reminder:
It should be noted that QoS in MQTT publish and subscribe operations represents different meanings. QoS during publishing indicates the QoS level used by the message to be sent to the MQTT server, and QoS during subscription indicates the maximum QoS that MQTT Broker can use when forwarding messages to itself. grade. It is necessary to ensure that the QoS of sending and subscription is consistent to ensure that the final received message is of a fixed QoS level, otherwise consumption will be degraded. For example: the QoS of the message sent by A is 2, and the QoS of the message subscribed by B is 1, then the QoS of the message finally received is 1.
EMQX message transmission guarantee based on QoS level
In order to better ensure the safety and reliability of data transmission between people, vehicles, roads, networks and clouds in the process of Internet of Vehicles, while improving the efficiency of message throughput and reducing the impact of network fluctuations, the cloud-native distributed IoT message server EMQX is in On the basis of fully adapting QoS signaling interaction, functions such as flight window, message queue, message full-link tracking and offline message storage are also designed to improve message reliability.
The design of the flight window allows multiple unacknowledged QoS 1 and QoS 2 packets to exist on the network link at the same time, and the message queue can further store the message when the message exceeds the flight window in the message link, so as to prevent Meet the storage requirements of unreceived messages or unacknowledged data messages when the client is offline. The flight window also has the upgrade_qos parameter to implement functions such as forced upgrade of QoS according to subscription, which can achieve the consistency of QoS levels and ensure that there will be no consumption degradation. In addition, EMQX can also provide the ability to restrict service access to different QoS levels, data bridging QoS management, MQTT-SN protocol QoS management, etc.
Download experience: https://www.emqx.com/zh/try?product=enterprise
Epilogue
Through this article, we can see that the QoS characteristics of the MQTT protocol are of great significance for the secure transmission of message data in the Internet of Vehicles scenario. As a cloud-native distributed message server that fully supports the MQTT protocol standard, EMQX makes full use of the features and advantages of the MQTT protocol in product design to provide reliable data connection, movement, processing and integration for IoT platform and application construction.